DBCP和JDBC学习总结(应用篇)
DBCP和JDBC学习总结(应用篇)
DBCP是一个常用的数据库连接池,JDBC是数据库连接的一套API。从应用层面学习一下两个的使用。
JDBC 连接示例
public class DataBaseTest {
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException,ClassNotFoundException {
/**
* 在加载这个类的时候,会执行静态代码块中的代码,将自己注册到DriverManager类中
*/
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://server/yourdatabase";
String username="xxxx";
String password = "xxxx";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
return conn;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Connection conn = getConnection();
Statement sqlStatement = conn.createStatement();
String query = "select * from sequence";
ResultSet result = sqlStatement.executeQuery(query);
while(result.next()) {
Date gmtModified = result.getDate("gmt_modified");
String name = result.getString("name");
Integer value = result.getInt("value");
System.out.println("gmt_modified="+gmtModified+" name="+name+" value="+value);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
以上是一个jdbc连接数据库的一个demo。要是用jdbc连接mysql,首先要将mysql的驱动程序注册到 DriverManager中,注册这个操作通过Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");来完成的, 这行代码是怎么完成mysql驱动程序的注册的呢?其实这个注册的功能主要是驱动程序自己完成的,在通过Class.forName()显示加载com.mysql.jdbc.Driver的时候,会执行Driver的静态代码块,这个静态代码块就调用了DriverManager添加驱动的方法,将自己注册到了驱动管理器中。 com.mysql.jdbc.Driver将自己注册到驱动管理器的源代码如下:
static {
try {
java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException E) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
以上这段代码位于驱动程序的静态代码块中,在类被Class.forName显示加载的时候会被执行,从代码中看以看到把自己注册到了DriverManager中。注册了mysql驱动之后,就可以通过DB连接信息获取到数据库的一个Connection了。获取Connection的这个逻辑主要是这个样子的: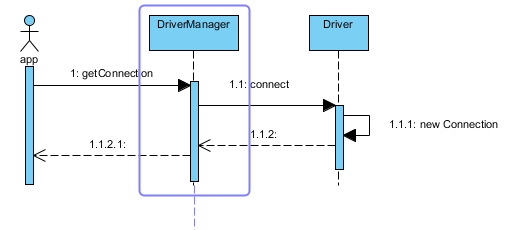
应用通过DriverManager获取Connection,DriverManager找到合适的驱动程序后,调用驱动程序来获取一个Connection,这个Connection一般情况下都是重新new一个,主要和连接池技术是相对的。 DriverManager部分源码:
for (int i = 0; i < drivers.size(); i++) {
DriverInfo di = (DriverInfo)drivers.elementAt(i);
// If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then
// skip it.
if ( getCallerClass(callerCL, di.driverClassName ) != di.driverClass ) {
println(" skipping: " + di);
continue;
}
try {
println(" trying " + di);
Connection result = di.driver.connect(url, info);
if (result != null) {
// Success!
println("getConnection returning " + di);
return (result);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
if (reason == null) {
reason = ex;
}
}
}
以上这个逻辑就是循环的遍历资源管理器列表,找到合适的驱动程序获取连接。 driver.connect()这个主要的源码如下:
public java.sql.Connection connect(String url, Properties info)
throws SQLException {
if (url != null) {
if (StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(url, LOADBALANCE_URL_PREFIX)) {
return connectLoadBalanced(url, info);
} else if (StringUtils.startsWithIgnoreCase(url,
REPLICATION_URL_PREFIX)) {
return connectReplicationConnection(url, info);
}
}
Properties props = null;
if ((props = parseURL(url, info)) == null) {
return null;
}
try {
Connection newConn = new com.mysql.jdbc.Connection(host(props),
port(props), props, database(props), url);
return newConn;
} catch (SQLException sqlEx) {
// Don't wrap SQLExceptions, throw
// them un-changed.
throw sqlEx;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw SQLError.createSQLException(Messages
.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.17") //$NON-NLS-1$
+ ex.toString()
+ Messages.getString("NonRegisteringDriver.18"), //$NON-NLS-1$
SQLError.SQL_STATE_UNABLE_TO_CONNECT_TO_DATASOURCE);
}
}
DBCP使用DEMO:
public class DbcpConnection {
private static DataSource dataSource;
private static Connection con;
public DbcpConnection() {
}
public static Connection getConnection() {
if (dataSource == null) {
initDataSource();
}
try {
con = dataSource.getConnection();
print();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
public static void initDataSource() {
FileInputStream is = null;
Properties p = new Properties();
String driverClassName = null;
String url = null;
String username = null;
String password = null;
int initialSize = 0;
int minIdle = 0;
int maxIdle = 0;
int maxWait = 0;
int maxActive = 0;
try {
String path = DbcpConnection.class.getClass().getResource("/")
.getPath();
is = new FileInputStream(path + "dbcp.properties");
p.load(is);
driverClassName = p.getProperty("dbcp.driverClassName");
url = p.getProperty("dbcp.url");
username = p.getProperty("dbcp.username");
password = p.getProperty("dbcp.password");
initialSize = Integer.parseInt(p.getProperty("dbcp.initialSize"));
minIdle = Integer.parseInt(p.getProperty("dbcp.minIdle"));
maxIdle = Integer.parseInt(p.getProperty("dbcp.maxIdle"));
maxWait = Integer.parseInt(p.getProperty("dbcp.maxWait"));
maxActive = Integer.parseInt(p.getProperty("dbcp.maxActive"));
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
BasicDataSource ds = new BasicDataSource();
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
ds.setUsername(username);
ds.setPassword(password);
ds.setInitialSize(initialSize); // 初始的连接数;
ds.setMaxActive(maxActive);
ds.setMinIdle(minIdle);
ds.setMaxIdle(maxIdle);
ds.setMaxWait(maxWait);
ds.setRemoveAbandoned(true);
ds.setRemoveAbandonedTimeout(2000);
dataSource = ds;
}
/* 用于测试连接状态的方法 */
public static void print() {
BasicDataSource ds = (BasicDataSource) dataSource;
System.out.println(ds.getInitialSize());
System.out.println(ds.getNumActive());
System.out.println(ds.getNumIdle());
System.out.println(ds.getDefaultAutoCommit());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con;
try {
con = DbcpConnection.getConnection();
print();
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
ResultSet result = stmt.executeQuery("select * from sequence");
while (result.next()) {
Date gmtModified = result.getDate("gmt_modified");
String name = result.getString("name");
Integer value = result.getInt("value");
System.out.println("gmt_modified="+gmtModified+" name="+name+" value="+value);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
} }
这段代码主要使用了DBCP连接池连接数据库的一个DEMO,前面一堆就是设置了数据库连接池的一些参数,这些参数是从一个props文件中读取的。通过javax.sql.DataSource可以获取数据的连接。 javax.sql.DataSource定义了DataSource的一套接口。javax中DataSource的概念可以这么解释: DataSource作为DriverManager的替代项,从其定义的接口中可以获取物理数据源的连接,是获取数据源连接的一个首选方法。DataSource接口的对象通常在基于JNDI API的命名服务中注册。 DataSource接口的驱动实现由各供应商提供,共有三种类型的实现: (1)基本实现:生成标准的Connection对象(就是每次new个Connection出来) (2)连接池实现:生成自动参与连接池的Connection对象。此实现与中间层连接池管理器一起使用 (3)分布式事务实现:生成一个Connection对象,该对象可用于分布式事务,大多数情况下总是参与连接池。此实现与中间层事务管理器一起使用,大多数情况下总是与连接池管理器一起使用。 common-dbcp是common-pool在数据库访问方面的一个具体应用,即dbcp是依赖common-tool的。
tomcat数据源配置DEMO
在tomcat中配置数据源也是非常方便的,tomcat中内置了dbcp连接池。可以在context.xml中配置datasource的基础信息,然后再代码中通过jndi方式获取连接。具体的实例如下: 在 %CATALINA_HOME%/conf/context.xml中 添加如下这段代码:
<Resource
name="jdbc/testdbcp"
auth="Container"
type="javax.sql.DataSource"
maxActive="20"
maxIdel="10"
maxWait="1000"
username="xxxx"
password="xxxx"
driverClassName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
url="jdbc:mysql://dbserver/yourdatabase">
</Resource>
主要填写一下数据库连接的基础信息。然后在java代码中调用示例如下:
public void exeSql(String sql) {
try {
Context context = new InitialContext();
/**
* java:/comp/env/ 是固定写法,后面接的是context.xml中的Resource中name属性的值
*/
DataSource ds = (DataSource)context.lookup("java:/comp/env/jdbc/testdbcp");
Connection conn = ds.getConnection();
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet result = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(result.next()) {
Date gmtModified = result.getDate("gmt_modified");
String name = result.getString("name");
Integer value = result.getInt("value");
System.out.println("gmt_modified="+gmtModified+" name="+name+" value="+value);
}
} catch (NamingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
通过JNDI的方式获取到DataSource,然后就可以轻松的获取DB连接执行sql了,整个过程没有看到涉及到DBCP的东西,因为DBCP的东西完全内置在tomcat中了,在初始化JNDI上下文的时候,会根据Context.xml文件中配置的datasource信息来装配具体的Datasource信息来完成对外服务。
对于tomcat对context.xml中数据源的解析可以参考这篇博客: http://blog.csdn.net/lantian0802/article/details/9099977 这里就不在多说了! 这篇文章主要从应用层面简单的总结下DataSource,下篇将从源码角度分析下DBCP连接池,以及tomcat的加载流程。 我的博客:http://blog.csdn.net/lantian0802