Controller是MVC中比较重要的一部分。几乎所有的业务逻辑都是在这里进行处理的,并且从Model中取出数据。在ASP.NET MVC Preview5中,将原来的Controller类一分为二,分为了Controller类和ControllerBase类。Controller类继承自ControllerBase类,而ControllerBase实现是了IController接口。
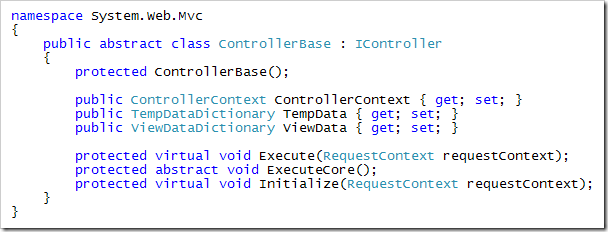
ControllerBase实现了IController接口的Execute方法,在Route匹配到Controller之后,就会调用Execute方法来进入Controller的处理。这里还定义了一个抽象的方法ExecuteCore方法,该方法会在Execute方法的最后被调用。ControllerBase还定义了三个核心的属性。我们在后面会详细讨论TempData和ViewData。
Controller类除了继承自ControllerBase类以外,还实现了好几个Filter接口,Filter我们在后面再详细讨论。
public
abstract
class
Controller : ControllerBase, IActionFilter, IAuthorizationFilter, IDisposable, IExceptionFilter, IResultFilter{ }
Controller类还定义很多有用的方法,我们新建的Controller都必须继承自这个Controller类。例如我们新建一个AdminController:
public
class
AdminController : Controller
{
}
Action方法
下面谈一下在Controller中比较重要的Action方法。在ASP.NET MVC中URL都是映射到Controller中的某个Action中,然后由匹配的Action来处理我们的业务逻辑并返回view的。
Controller中的public的方法都被当作是Action方法。Action方法通常返回一个ActionResult的结果。例如我们为前面的AdminController定义一个Setting的Action方法,用于设置Blog的一些基本参数:
public
class
AdminController : Controller
{
public
ActionResult Setting()
{
throw
new
NotImplementedException();
}
}
默认情况下,Action方法的方法名就是这个Action的Action名(Action名指的是Route中匹配Action方法的URL的那部分。例如url:Home/Index,其中Index就是Action名)。这里为什么要提到这个Action名呢?应为Action名是可以定义的,使用ActionNameAttribute来定义。请看下面的示例:
public
ActionResult Setting()
{
throw
new
NotImplementedException();
}
[ActionName(
"
Setting
"
)]
public
ActionResult SaveSetting()
{
throw
new
NotImplementedException();
}
这两个Action方法的Action名都为"Setting",即对于url:Admin/Setting ,能同时匹配到这两个Action方法。如果一个URL同时匹配到两个Action方法的话,程序会抛出一个错误:

如果我们希望这两个Action的Action名都为Setting,Setting()就用于显示一个表单页面给用户,而SaveSetting()就用于保存用户提交过来的表单数据,我们该怎么做呢?我们可以利用AcceptVerbsAttribute来设置,这个Attribute用来定义Action方法会匹配指定的HttpMethod。例如下面的代码:
[AcceptVerbs(
"
GET
"
)]
public
ActionResult Setting()
{
throw
new
NotImplementedException();
}
[ActionName(
"
Setting
"
), AcceptVerbs(
"
POST
"
)]
public
ActionResult SaveSetting()
{
throw
new
NotImplementedException();
}
这样,对于HttpMethod为"GET"的客户端请求,就会匹配到Setting()来显示一个表单给用户,如果用户POST回来的表单数据,则会匹配到SaveSetting()上面去,我们就可以处理用户POST过来的数据并保存到数据库。
在这里AcceptVerbsAttribute是继承自ActionSelectionAttribute的,我们也可以继承自ActionSelectionAttribute来自定义自己想要实现的功能。这个我们后面会详细讲解。如果你比较心急,可以看下Asp.net Mvc Preview 5 体验--实现ActionSelectionAttribute来判断是否为AJAX请求而选择不同的Action这篇文章。
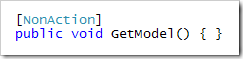
如果你想将一个public的方法设置为不是Action方法,那么你就要为该public的方法添加NonAction的Attribute:
Action方法的参数
例如我们要在AdminController中定义一个编辑日志的Action方法:
public
ActionResult EditPost(
int
?
id)
{
throw
new
NotImplementedException();
}
对于URL:Admin/EditPost/2 ,上面的参数会自动被赋值为2。ASP.NET MVC在匹配Route的时候会根据Route的设置自动为Action方法的参数赋值。所以前面的id参数会被自动赋值为2的前提是,在Route配置的时候,必须指定了id参数,例如:
routes.MapRoute(
"
Default
"
,
//
Route 的名称
"
{controller}/{action}/{id}
"
,
//
带有参数的URL
new
{ controller
=
"
Home
"
, action
=
"
Index
"
, id
=
""
}
//
设置默认的参数
);
如果我们将Route修改为:
routes.MapRoute(
"
Default
"
,
//
Route 的名称
"
{controller}/{action}/{para}
"
,
//
带有参数的URL
new
{ controller
=
"
Home
"
, action
=
"
Index
"
,para
=
""
}
//
设置默认的参数
);
则前面的Action方法的参数必须修改为public ActionResult EditPost(int? para){ },使Action方法的参数和Route中定义的参数名相同,ASP.NET MVC才能自动为Action方法的参数赋值。
ActionResult
Action方法返回ActionResult类型的结果。ASP.NET MVC为我们提供了几种ActionResult的实现,如下:
-
ViewResult. 呈现视图页给客户端。由View 方法返回.
-
RedirectToRouteResult. 重定向到另外一个Route。由RedirectToAction 和RedirectToRoute 方法返回.
-
RedirectResult. 重定向到另外一个URL。由Redirect 方法返回.
-
ContentResult. 返回普通的内容。例如一段字符串。由Content 方法返回.
-
JsonResult. 返回JSON结果。由Json 方法返回.
-
EmptyResult. 如果Action必须返回空值,可以返回这个结果。Controller中没有实现的方法,可以return new EmptyResult();.
当然我们也可以自定一个我们的ActionResult返回给客户端,例如一个RssResult。可以参考Asp.Net MVC实践 - 自定义ActionResult实现Rss输出 (基于ASP.NET MVC Preview 3)这篇文章。
通常情况下,我们的Controller可能有一些相同的情况,例如我们在各个Controller中都有可能会在出错或者什么时候想要显示一条提示信息给用户,或者有一些共同的数据要呈现的。这时候,我们最好就定义一个我们自己的Controller的基类:
public
class
BaseController : Controller
{
public
BaseController()
{
}
protected
ActionResult ShowMsg(List
<
string
>
msgs)
{
throw
new
NotImplementedException();
}
public
ActionResult Message()
{
throw
new
NotImplementedException();
}
}
然后,其他的Controller都继承自这个BaseController :
public
class
AdminController : BaseController
{
[AcceptVerbs(
"
GET
"
)]
public
ActionResult Setting()
{
throw
new
NotImplementedException();
}
[ActionName(
"
Setting
"
), AcceptVerbs(
"
POST
"
)]
public
ActionResult SaveSetting()
{
throw
new
NotImplementedException();
}
public
ActionResult EditPost(
int
?
id)
{
throw
new
NotImplementedException();
}
}


