struts2 分析
转自:http://www.javaeye.com/topic/450979
1. Struts2架构图 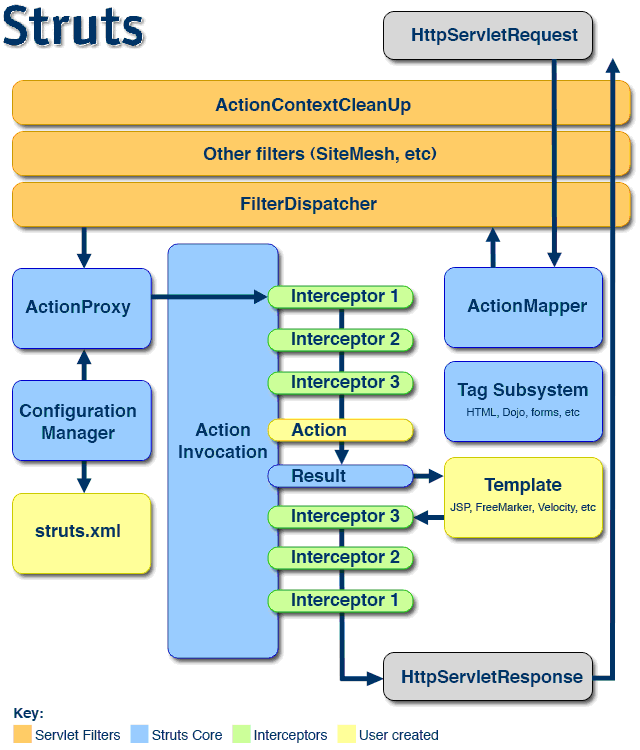
请求首先通过Filter chain,Filter主要包括ActionContextCleanUp,它主要清理当前线程的ActionContext和Dispatcher;FilterDispatcher主要通过AcionMapper来决定需要调用哪个Action。
ActionMapper取得了ActionMapping后,在Dispatcher的serviceAction方法里创建ActionProxy,ActionProxy创建ActionInvocation,然后ActionInvocation调用Interceptors,执行Action本身,创建Result并返回,当然,如果要在返回之前做些什么,可以实现PreResultListener。
2. Struts2部分类介绍
这部分从Struts2参考文档中翻译就可以了。
ActionMapper
ActionMapper其实是HttpServletRequest和Action调用请求的一个映射,它屏蔽了Action对于Request等java Servlet类的依赖。Struts2中它的默认实现类是DefaultActionMapper,ActionMapper很大的用处可以根据自己的需要来设计url格式,它自己也有Restful的实现,具体可以参考文档的docs/actionmapper.html。
ActionProxy&ActionInvocation
Action的一个代理,由ActionProxyFactory创建,它本身不包括Action实例,默认实现DefaultActionProxy是由ActionInvocation持有Action实例。ActionProxy作用是如何取得Action,无论是本地还是远程。而ActionInvocation的作用是如何执行Action,拦截器的功能就是在ActionInvocation中实现的。
ConfigurationProvider&Configuration
ConfigurationProvider就是Struts2中配置文件的解析器,Struts2中的配置文件主要是尤其实现类XmlConfigurationProvider及其子类StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider来解析。
3. Struts2请求流程
1、客户端发送请求
2、请求先通过ActionContextCleanUp-->FilterDispatcher
3、FilterDispatcher通过ActionMapper来决定这个Request需要调用哪个Action
4、如果ActionMapper决定调用某个Action,FilterDispatcher把请求的处理交给ActionProxy,这儿已经转到它的Delegate--Dispatcher来执行
5、ActionProxy根据ActionMapping和ConfigurationManager找到需要调用的Action类
6、ActionProxy创建一个ActionInvocation的实例
7、ActionInvocation调用真正的Action,当然这涉及到相关拦截器的调用
8、Action执行完毕,ActionInvocation创建Result并返回,当然,如果要在返回之前做些什么,可以实现PreResultListener。添加PreResultListener可以在Interceptor中实现,不知道其它还有什么方式?
4. Struts2(2.1.2)部分源码阅读
从org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.FilterDispatcher开始
- //创建Dispatcher,此类是一个Delegate,它是真正完成根据url解析,读取对应Action的地方
- public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
- try {
- this.filterConfig = filterConfig;
- initLogging();
- dispatcher = createDispatcher(filterConfig);
- dispatcher.init();
- dispatcher.getContainer().inject(this);
- //读取初始参数pakages,调用parse(),解析成类似/org/apache/struts2/static,/template的数组
- String param = filterConfig.getInitParameter("packages");
- String packages = "org.apache.struts2.static template org.apache.struts2.interceptor.debugging";
- if (param != null) {
- packages = param + " " + packages;
- }
- this.pathPrefixes = parse(packages);
- } finally {
- ActionContext.setContext(null);
- }
- }
顺着流程我们看Disptcher的init方法。init方法里就是初始读取一些配置文件等,先看init_DefaultProperties,主要是读取properties配置文件。
- private void init_DefaultProperties() {
- configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider(new DefaultPropertiesProvider());
- }
打开DefaultPropertiesProvider
- public void register(ContainerBuilder builder, LocatableProperties props)
- throws ConfigurationException {
- Settings defaultSettings = null;
- try {
- defaultSettings = new PropertiesSettings("org/apache/struts2/default");
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new ConfigurationException("Could not find or error in org/apache/struts2/default.properties", e);
- }
- loadSettings(props, defaultSettings);
- }
- //PropertiesSettings
- //读取org/apache/struts2/default.properties的配置信息,如果项目中需要覆盖,可以在classpath里的struts.properties里覆写
- public PropertiesSettings(String name) {
- URL settingsUrl = ClassLoaderUtils.getResource(name + ".properties", getClass());
- if (settingsUrl == null) {
- LOG.debug(name + ".properties missing");
- settings = new LocatableProperties();
- return;
- }
- settings = new LocatableProperties(new LocationImpl(null, settingsUrl.toString()));
- // Load settings
- InputStream in = null;
- try {
- in = settingsUrl.openStream();
- settings.load(in);
- } catch (IOException e) {
- throw new StrutsException("Could not load " + name + ".properties:" + e, e);
- } finally {
- if(in != null) {
- try {
- in.close();
- } catch(IOException io) {
- LOG.warn("Unable to close input stream", io);
- }
- }
- }
- }
再来看init_TraditionalXmlConfigurations方法,这个是读取struts-default.xml和Struts.xml的方法。
- private void init_TraditionalXmlConfigurations() {
- //首先读取web.xml中的config初始参数值
- //如果没有配置就使用默认的"struts-default.xml,struts-plugin.xml,struts.xml",
- //这儿就可以看出为什么默认的配置文件必须取名为这三个名称了
- //如果不想使用默认的名称,直接在web.xml中配置config初始参数即可
- String configPaths = initParams.get("config");
- if (configPaths == null) {
- configPaths = DEFAULT_CONFIGURATION_PATHS;
- }
- String[] files = configPaths.split("//s*[,]//s*");
- //依次解析配置文件,xwork.xml单独解析
- for (String file : files) {
- if (file.endsWith(".xml")) {
- if ("xwork.xml".equals(file)) {
- configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider(new XmlConfigurationProvider(file, false));
- } else {
- configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider(new StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider(file, false, servletContext));
- }
- } else {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid configuration file name");
- }
- }
- }
对于其它配置文件只用StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider,此类继承XmlConfigurationProvider,而XmlConfigurationProvider又实现ConfigurationProvider接口。类XmlConfigurationProvider负责配置文件的读取和解析,addAction()方法负责读取<action>标签,并将数据保存在ActionConfig中;addResultTypes()方法负责将<result-type>标签转化为ResultTy