数据结构《14》----并查集 Union-Find
描述:
并查集是一种描述解决等价关系。能够方便地描述不相交的多个集合。
支持如下操作 1. 建立包含元素 x 的集合 MakeSet(x)
2. 查找给定元素所在的集合 Find(x), 返回所在集合的代表
3. 将两个不相交的集合合并 Union(s1, s2)
本文参考《数据结构与算法分析,C语言描述》这本书,利用数组,给出了并查集的一个容易实现的版本。
采用了按秩合并 和 路径压缩 的方法加速。
数据结构:
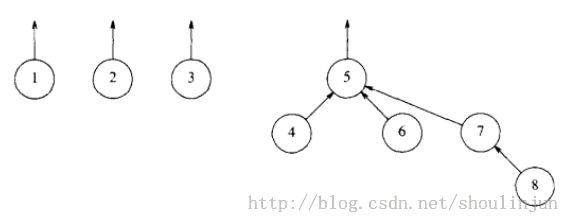
用树表示一个集合,树的跟节点就是这个集合的代表元素。
并采用一维数组来非显示地模拟这个森林:
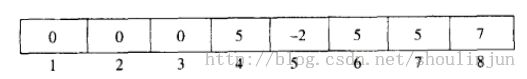
1. 数组长度是总的集合元素个数;
2. s[i] 表示元素 i 的父亲节点;
3. 如果 s[i] 是 负数,表示 i 就是代表元素; 并且负数的绝对值表示所在树的高度。(按高度压缩)
在这样的定义下,Find(x) 非常容易实现,只要从元素 x, 不断往上找,直到找到根节点返回即可。
// return the disjoint set which x belongs to
SetType Find(ElementType x, DisJointSet s)
{
if(s[x] < 0)
return x;
else
return Find(s[x], s);
}
按高度合并:
注意到,Find(x) 的复杂度是树的高度。
按高度合并就是通过将 矮的树 合并到 高的树作为其孩子,从而避免树过高。
//Assume root1 and root2 are roots
void SetUnion(DisJointSet s, SetType root1, SetType root2)
{
if(s[root1] <= s[root2])//root1 is deeper than root2
{
if(s[root1] == s[root2])
s[root1] --;
s[root2] = root1;
}
else
{
s[root1] = root2;
}
}
路径压缩:
这种方法可以与按高度合并兼容,能够得到较高的效率。
它其实是在 Find(x) 这个函数做文章。
在搜索 x 所在树的 root 节点的过程中,将中途的节点都指向 root.
看了下图,大家就能明白了。
代码非常简单:
// return the disjoint set which x belongs to
SetType Find(ElementType x, DisJointSet s)
{
if(s[x] < 0)
return x;
else
return s[x] = Find(s[x], s);
}
完整的代码如下:
/* dis-joint-set implemented by L.J. in Nov.11, 2013 */
/* union by height */
#include "disjointset.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int NumSets = 8;
typedef int DisJointSet[ NumSets + 1];
typedef int SetType;
typedef int ElementType;
void Initialize(DisJointSet s)
{
for(int i=NumSets; i>0; --i)
s[i] = 0;
}
//Assume root1 and root2 are roots
void SetUnion(DisJointSet s, SetType root1, SetType root2)
{
if(s[root1] <= s[root2])//roo1 is deeper than root2
{
if(s[root1] == s[root2])
s[root1] --;
s[root2] = root1;
}
else
{
s[root1] = root2;
}
}
// return the disjoint set which x belongs to
SetType Find(ElementType x, DisJointSet s)
{
if(s[x] < 0)
return x;
else
return Find(s[x], s);
}