JSON知识总结-Gson(一)
记录一下Gson的使用
官网地址:http://code.google.com/p/google-gson/
总结于Gson的官网文档 Gson User Guide,代码示例皆是。
1.Primitives Examples
(Serialization)
Gson gson = new Gson();
gson.toJson(1); ==> prints 1
gson.toJson("abcd"); ==> prints "abcd"
gson.toJson(new Long(10)); ==> prints 10
int[] values = { 1 };
gson.toJson(values); ==> prints [1]
(Deserialization)
int one = gson.fromJson("1", int.class);
Integer one = gson.fromJson("1", Integer.class);
Long one = gson.fromJson("1", Long.class);
Boolean false = gson.fromJson("false", Boolean.class);
String str = gson.fromJson("\"abc\"", String.class);
String anotherStr = gson.fromJson("[\"abc\"]", String.class);这里的数组好像有点问题,
@Test
public void testArray() {
String[] strArray = {"aa" , "bb" , "cc"};
String json = gson.toJson(strArray);
System.out.println("json->" + json);
Type arrayType = new TypeToken<String[]>() {}.getType();
String[] str = gson.fromJson(json , arrayType);
for(int i=0; i<str.length; i++) {
System.out.println(i + "->" + str[i]);
}
}
悲剧,这里的数组有更简单的方法:
@Test
public void testArray() {
String[] strArray = {"aa" , "bb" , "cc"};
String json = gson.toJson(strArray);
System.out.println("json->" + json);
String[] str = gson.fromJson(json , String[].class);
for(int i=0; i<str.length; i++) {
System.out.println(i + "->" + str[i]);
}
}
2.Object Examples
使用关键字 transient 修饰的 field ,不会被序列化为JSON
class BagOfPrimitives {
private int value1 = 1;
private String value2 = "abc";
private transient int value3 = 3;
BagOfPrimitives() {
// no-args constructor
}
}
(Serialization)
BagOfPrimitives obj = new BagOfPrimitives();
Gson gson = new Gson();
String json = gson.toJson(obj);
==> json is {"value1":1,"value2":"abc"}
(Deserialization)
BagOfPrimitives obj2 = gson.fromJson(json, BagOfPrimitives.class);
==> obj2 is just like obj
示例:
package org.ygy.demo;
public class BagOfPrimitives {
private int value1 = 1;
private String value2 = "abc";
private transient int value3 = 3;
public BagOfPrimitives() {}
public BagOfPrimitives(int value1, String value2, int value3) {
this.value1 = value1;
this.value2 = value2;
this.value3 = value3;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BagOfPrimitives [value1=" + value1 + ", value2=" + value2
+ ", value3=" + value3 + "]";
}
}
即使我们手动添加了 transient 修饰的 field ,反序列化出来也没有。
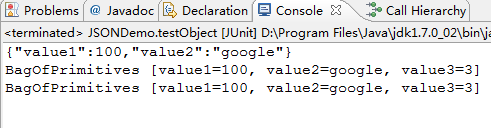
@Test
public void testObject() {
BagOfPrimitives obj = new BagOfPrimitives(100 , "google" , 200);
String json = gson.toJson(obj);
System.out.println(json);
BagOfPrimitives obj2 = gson.fromJson(json , BagOfPrimitives.class);
System.out.println(obj2);
String json2 = "{\"value1\":100,\"value2\":\"google\",\"value3\":200}";
BagOfPrimitives obj3 = gson.fromJson(json2 , BagOfPrimitives.class);
System.out.println(obj3);
}
结果:
这里不支持循环引用:
Note that you can not serialize objects with circular references since that will result in infinite recursion.
可能是这个样子:
package org.ygy.demo;
public class Child {
private String name;
private Father father;
public Child(String _name , Father _father) {
this.name = _name;
this.father = _father;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Child [name=" + name + ", father=" + father + "]";
}
}
package org.ygy.demo;
public class Father {
private String name;
private Child child;
public void setChild(Child _child) {
this.child = _child;
}
public Father(String _name) {
this.name = _name;
}
public Father(String _name , Child _child) {
this.name = _name;
this.child = _child;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Father [name=" + name + ", child=" + child + "]";
}
}
@Test
public void testReference() {
Father father = new Father("father1");
Child child = new Child("child1" , father);
father.setChild(child);
String json = gson.toJson(child);
System.out.println(json);
}
报了一个错误:java.lang.StackOverflowError