浅谈spring——属性注入与事件(三)
spring配置文件,可以将String、 int 等字面值注入到Bean中,也可以将集合,Map,对象等类型数据注入到Bean中。
注:如果字面值含有 &<>" ' 特殊符时,需要在属性值外添加<![CDATA[ ]]>的特殊处理标签,以防止某些字符串对XML格式造成破坏;当然也可以使用XML转义序列表示这些特殊的字符
| 特殊符号 | 转义序列 |
| < | < |
| > | > |
| & | & |
| " | " |
| ' | ' |
对bean属性装配通常有以下几种方式:
1. bean里面定义<property name="" ref="">
2. 指定自动装配类型autowire="",byName按名字注入(使用较多),byType按类型注入(使用较少)
3. 采用注释类形式注入,@Resource @Autowired。标注@Autowired注解的Bean并不会自动进行装配,它需要一个配套的处理器(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor)
Bean的作用域通常有:singleton(默认),prototype,request,session,globalSession,常用的是前两个
默认情况下,容器在启动时会自动实例化所有的singleton的Bean并且缓存于容器中。
缺点:启动时会花费一些时间
优点:对Bean提前实例化操作及早发现一些潜在的配置问题;其次Bean以缓存的形式保存,当运行时无需再实例化了,加快了运行的效率。
如果用户不想提前实例化singleton的Bean,可以增加一个属性
<bean id="car" class="com.alibaba.china.Car" lazy-init="true"> <property name="" value=""> </bean>
容器事件:ApplicationContext允许发布事件、允许注册事件监听器,拥有一套完整的事件发布和监听机制。
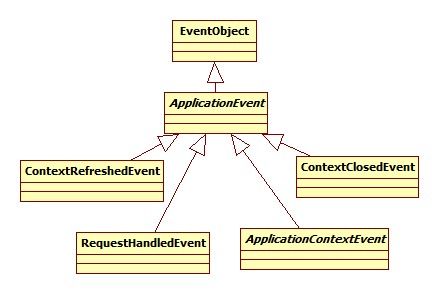
事件类图:
事件监听器类图:
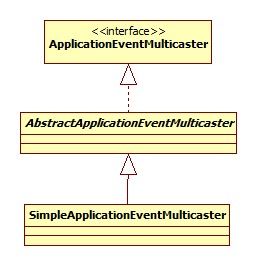
事件广播器类图:
代码实例:
事件类:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.event.ApplicationContextEvent;
public class MailSendEvent extends ApplicationContextEvent {
private String to;
public MailSendEvent(ApplicationContext source, String to) {
super(source);
this.to = to;
}
public String getTo() {
return this.to;
}
}
事件监听器类:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
public class MailSendListener implements ApplicationListener<MailSendEvent>{
public void onApplicationEvent(MailSendEvent event) {
MailSendEvent mse = (MailSendEvent) event;
System.out.println("MailSendListener:向" + mse.getTo() + "发送完一封邮件");
}
}
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
public class MailSender implements ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext ctx ;
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ctx)
throws BeansException {
this.ctx = ctx;
}
public void sendMail(String to){
System.out.println("MailSender:模拟发送邮件...");
MailSendEvent mse = new MailSendEvent(this.ctx,to);
ctx.publishEvent(mse);
}
}