A*寻路算法
A*简介
图搜索技术在游戏编程中无处不在,无论什么游戏类型,图搜索方法不可避免成为游戏AI的基础。比如下面梦幻西游自动找人的功能
A*搜寻算法就是图搜索算法的一种,俗称A星算法。这是一种在图形平面上,有多个节点的路径,求出最低通过成本的算法。常用于游戏中的NPC的移动计算,或线上游戏的BOT的移动计算上。
从Dijkstra单源最短路算法说起
Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法是典型的最短路径路由算法,用于计算一个节点到其他所有节点的最短路径。主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。Dijkstra算法能得出最短路径的最优解,但由于它遍历计算的节点很多,所以效率低。
Dijkstra算法是很有代表性的最短路算法,在很多专业课程中都作为基本内容有详细的介绍,如数据结构,图论,运筹学等等。
算法的基本步骤如下:
假设存在G=<V,E>,源顶点为V0,U={V0},dist[i]记录V0到i的最短距离,path[i]记录从V0到i路径上的i前面的一个顶点。
1.从V-U中选择使dist[i]值最小的顶点i,将i加入到U中;
2.更新与i直接相邻顶点的dist值。(dist[j]=min{dist[j],dist[i]+matrix[i][j]})
3.直到U=V,停止。
c语言实现
//djk.c 2014.10.26 Quan
#include <stdio.h>
#define INT_MAX 1000000
#define MAXN 1000
//n - node count;
//s - source node
//map[i][j] - the distance of i to j. I and j are neighboring.
//dist - record distance frome s
//pre - record the prenode
void djk(int n, int s, int map[MAXN][MAXN], int dist[MAXN], int pre[MAXN])
{
int i,j,k;
int min;
int p[MAXN];
for(i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
p[i] = 0;
if(i != s) dist[i] = map[s][i];
}
dist[s] = 0;
//array p as the mark for solution-set
p[s] = 1;
for(i = 1;i <= n-1;i++)
{
min = INT_MAX;
//k as the node which is the nearest to source and not marked
k = 0;
//find the node which is the nearest to source and not marked
for(j = 1;j <= n;j++)
{
if(!p[j]&&dist[j] < min)
{
min = dist[j];
k = j;
}
}
// no node available
if(k == 0) return;
//first node
if(i == 1) pre[k] = s;
//color the node
p[k] = 1;
//update dist[j]
for(j = 1; j <= n-1; j++)
{
if(!p[j]&&map[k][j] != INT_MAX&&dist[j] > dist[k] + map[k][j])
{
dist[j] = dist[k] + map[k][j];//renew the distance of node j to the solution-set
pre[j] = k;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j,s = 2;
int n = 6;
int dist[MAXN] = {0};
int pre[MAXN] = {0};
int map[MAXN][MAXN];
//Assign every path length to max.
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
map[i][j] = INT_MAX;
}
//Assign the length of i to i to 0.
for(i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
map[i][i] = 0;
}
map[1][2] = 50;map[1][3] = 10;
map[1][5] = 45;map[2][3] = 15;
map[2][4] = 50;map[2][5] = 10;
map[3][1] = 20;map[3][4] = 15;
map[4][2] = 20;map[4][5] = 35;
map[5][4] = 30;map[6][4] = 3;
djk(n, 2, map, dist, pre);
for(j = 1;j <= n;j++)
{
printf("%d -> %d : %d\n", s, j, dist[j]);
}
return 0;
}
编译运行
A*算法
A*算法是一种启发式搜索算法,启发式搜索就是在状态空间中的搜索对每一个搜索的位置进行评估,得到最好的位置,再从这个位置进行搜索直到目标。这样可以省略大量无谓的搜索路径,提高了效率。在启发式搜索中,对位置的估价是十分重要的。采用了不同的估价可以有不同的效果。
A*算法的公式为:f(n)=g(n)+h(n),g(n)表示从起点到任意顶点n的实际距离,h(n)表示任意顶点n到目标顶点的估算距离。 这个公式遵循以下特性:
● 如果h(n)为0,只需求出g(n),即求出起点到任意顶点n的最短路径,则转化为单源最短路径问题,即Dijkstra算法
● 如果h(n)<=“n到目标的实际距离”,则一定可以求出最优解。而且h(n)越小,需要计算的节点越多,算法效率越低。
对于函数h(n),估算距离常用的方法有:
● 曼哈顿距离:定义曼哈顿距离的正式意义为L1-距离或城市区块距离,也就是在欧几里德空间的固定直角坐标系上两点所形成的线段对轴产生的投影的距离总和。例如在平面上,坐标(x1,y1)的点P1与坐标(x2, y2)的点P2的曼哈顿距离为:|x1 - x2| + |y1 - y2|。
● 欧氏距离:是一个通常采用的距离定义,它是在m维空间中两个点之间的真实距离。在二维和三维空间中的欧氏距离的就是两点之间的距离。例如在平面上,坐标(x1,y1)的点P1与坐标(x2, y2)的点P2的欧氏距离为: sqrt((x1-x2)^2+(y1-y2)^2 )。
● 切比雪夫距离:是两个向量之间各分量差值的最大值。例如在平面上,坐标(x1, y1)的点P1与坐标(x2, y2)的点P2的切比雪夫距离为:max(|x1 - x2| , |y1 - y2|)。
A*算法最重要的就是维护两个列表,一个开启列表,一个关闭列表。算法描述如下
1,从点A开始,并且把它作为待处理点存入一个“开启列表”。开启列表就像一张购物清单。尽管现在列表里只有一个元素,但以后就会多起来。你的路径可能会通过它包含的方格,也可能不会。基本上,这是一个待检查方格的列表。
2,寻找起点周围所有可到达或者可通过的方格,跳过有墙,水,或其他无法通过地形的方格。计算出f,g,h,把他们加入开启列表。为所有这些方格保存点A作为“父方格”。当我们想描述路径的时候,父方格的资料是十分重要的。后面会解释它的具体用途。
3,从开启列表中删除点A,把它加入到一个“关闭列表”,列表中保存所有不需要再次检查的方格。
4,把它从开启列表中删除 f 值最小的节点,然后添加到关闭列表中。
5,检查所有相邻格子。跳过那些已经在关闭列表中的或者不可通过的(有墙,水的地形,或者其他无法通过的地形),计算出f,g,h,把他们添加进开启列表,如果他们还不在里面的话。把选中的方格作为新的方格的父节点。
6,如果某个相邻格已经在开启列表里了,检查现在的这条路径是否更好。换句话说,检查如果我们用新的路径到达它的话,G值是否会更低一些。如果不是,那就什么都不做。
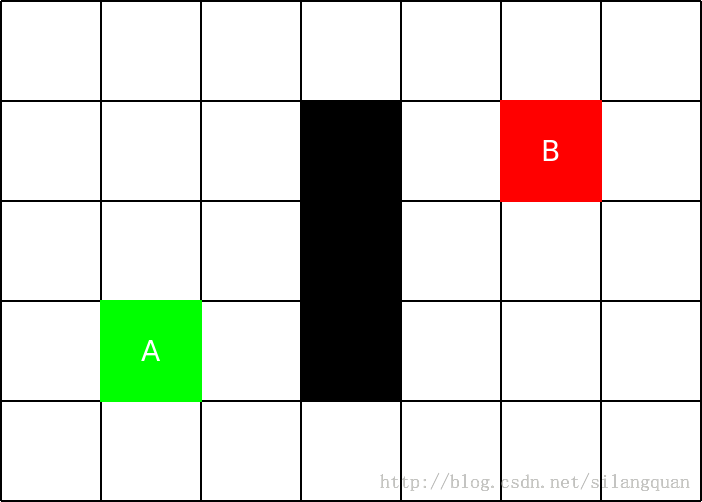
举个栗子,如下图
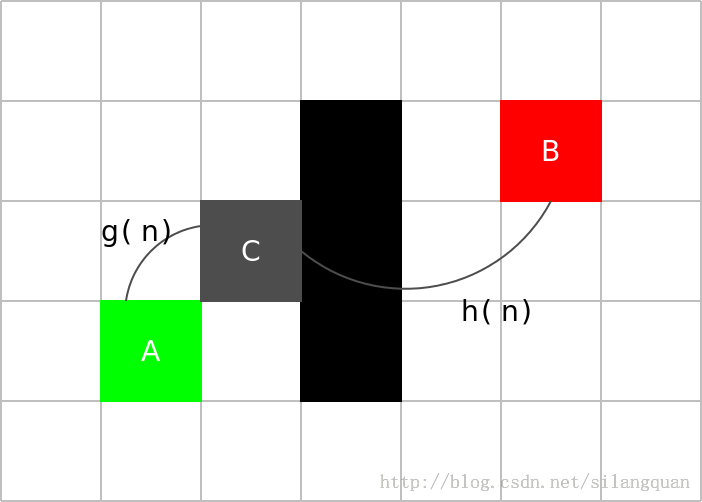
现在想要从A走到B,中间黑色是一堵墙,无法穿过。设C为n点,考虑下C点的f(n)
这里用曼哈顿距离来计算估值,方格上下左右相邻距离为10,对角线相邻为14,曼哈顿距离以10为单位,对于C,g(n) = 15, h(n) = 40.
接下来的步骤可以看下面的动画演示。
接下来是算法的c语言实现。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define STARTNODE 1
#define ENDNODE 2
#define BARRIER 3
typedef struct AStarNode
{
int s_x; // 坐标(最终输出路径需要)
int s_y;
int s_g; // 起点到此点的距离( 由g和h可以得到f,此处f省略,f=g+h )
int s_h; // 启发函数预测的此点到终点的距离
int s_style;// 结点类型:起始点,终点,障碍物
struct AStarNode * s_parent; // 父节点
int s_is_in_closetable; // 是否在close表中
int s_is_in_opentable; // 是否在open表中
}AStarNode, *pAStarNode;
AStarNode map_maze[10][10]; // 结点数组
pAStarNode open_table[100]; // open表
pAStarNode close_table[100]; // close表
int open_node_count;// open表中节点数量
int close_node_count; // close表中结点数量
pAStarNode path_stack[100]; // 保存路径的栈
int top = -1; // 栈顶
// 交换两个元素
//
void swap( int idx1, int idx2 )
{
pAStarNode tmp = open_table[idx1];
open_table[idx1] = open_table[idx2];
open_table[idx2] = tmp;
}
// 堆调整
//
void adjust_heap( int /*i*/nIndex )
{
int curr = nIndex;
int child = curr * 2 + 1; // 得到左孩子idx( 下标从0开始,所有做孩子是curr*2+1 )
int parent = ( curr - 1 ) / 2; // 得到双亲idx
if (nIndex < 0 || nIndex >= open_node_count)
{
return;
}
// 往下调整( 要比较左右孩子和cuur parent )
//
while ( child < open_node_count )
{
// 小根堆是双亲值小于孩子值
//
if ( child + 1 < open_node_count && open_table[child]->s_g + open_table[child]->s_h > open_table[child+1]->s_g + open_table[child+1]->s_h )
{
++child;// 判断左右孩子大小
}
if (open_table[curr]->s_g + open_table[curr]->s_h <= open_table[child]->s_g + open_table[child]->s_h)
{
break;
}
else
{
swap( child, curr ); // 交换节点
curr = child; // 再判断当前孩子节点
child = curr * 2 + 1; // 再判断左孩子
}
}
if (curr != nIndex)
{
return;
}
// 往上调整( 只需要比较cuur child和parent )
//
while (curr != 0)
{
if (open_table[curr]->s_g + open_table[curr]->s_h >= open_table[parent]->s_g + open_table[parent]->s_h)
{
break;
}
else
{
swap( curr, parent );
curr = parent;
parent = (curr-1)/2;
}
}
}
// 判断邻居点是否可以进入open表
//
void insert_to_opentable( int x, int y, pAStarNode curr_node, pAStarNode end_node, int w )
{
int i;
if ( map_maze[x][y].s_style != BARRIER ) // 不是障碍物
{
if ( !map_maze[x][y].s_is_in_closetable ) // 不在闭表中
{
if ( map_maze[x][y].s_is_in_opentable ) // 在open表中
{
// 需要判断是否是一条更优化的路径
//
if ( map_maze[x][y].s_g > curr_node->s_g + w ) // 如果更优化
{
map_maze[x][y].s_g = curr_node->s_g + w;
map_maze[x][y].s_parent = curr_node;
for ( i = 0; i < open_node_count; ++i )
{
if ( open_table[i]->s_x == map_maze[x][y].s_x && open_table[i]->s_y == map_maze[x][y].s_y )
{
break;
}
}
adjust_heap( i ); // 下面调整点
}
}
else // 不在open中
{
map_maze[x][y].s_g = curr_node->s_g + w;
map_maze[x][y].s_h = abs(end_node->s_x - x ) + abs(end_node->s_y - y);
map_maze[x][y].s_parent = curr_node;
map_maze[x][y].s_is_in_opentable = 1;
open_table[open_node_count++] = &(map_maze[x][y]);
}
}
}
}
// 查找邻居
// 对上下左右8个邻居进行查找
//
void get_neighbors( pAStarNode curr_node, pAStarNode end_node )
{
int x = curr_node->s_x;
int y = curr_node->s_y;
// 下面对于8个邻居进行处理!
//
if ( ( x + 1 ) >= 0 && ( x + 1 ) < 10 && y >= 0 && y < 10 )
{
insert_to_opentable( x+1, y, curr_node, end_node, 10 );
}
if ( ( x - 1 ) >= 0 && ( x - 1 ) < 10 && y >= 0 && y < 10 )
{
insert_to_opentable( x-1, y, curr_node, end_node, 10 );
}
if ( x >= 0 && x < 10 && ( y + 1 ) >= 0 && ( y + 1 ) < 10 )
{
insert_to_opentable( x, y+1, curr_node, end_node, 10 );
}
if ( x >= 0 && x < 10 && ( y - 1 ) >= 0 && ( y - 1 ) < 10 )
{
insert_to_opentable( x, y-1, curr_node, end_node, 10 );
}
if ( ( x + 1 ) >= 0 && ( x + 1 ) < 10 && ( y + 1 ) >= 0 && ( y + 1 ) < 10 )
{
insert_to_opentable( x+1, y+1, curr_node, end_node, 14 );
}
if ( ( x + 1 ) >= 0 && ( x + 1 ) < 10 && ( y - 1 ) >= 0 && ( y - 1 ) < 10 )
{
insert_to_opentable( x+1, y-1, curr_node, end_node, 14 );
}
if ( ( x - 1 ) >= 0 && ( x - 1 ) < 10 && ( y + 1 ) >= 0 && ( y + 1 ) < 10 )
{
insert_to_opentable( x-1, y+1, curr_node, end_node, 14 );
}
if ( ( x - 1 ) >= 0 && ( x - 1 ) < 10 && ( y - 1 ) >= 0 && ( y - 1 ) < 10 )
{
insert_to_opentable( x-1, y-1, curr_node, end_node, 14 );
}
}
int main()
{
// 地图数组的定义
//
AStarNode *start_node; // 起始点
AStarNode *end_node; // 结束点
AStarNode *curr_node; // 当前点
int is_found; // 是否找到路径
int maze[][10] ={ // 仅仅为了好赋值给map_maze
{ 1,0,0,3,0,3,0,0,0,0 },
{ 0,0,3,0,0,3,0,3,0,3 },
{ 3,0,0,0,0,3,3,3,0,3 },
{ 3,0,3,0,0,0,0,0,0,3 },
{ 3,0,0,0,0,3,0,0,0,3 },
{ 3,0,0,3,0,0,0,3,2,3 },
{ 3,0,0,0,0,3,3,0,0,0 },
{ 0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0 },
{ 3,3,3,0,0,3,0,3,0,3 },
{ 3,0,0,0,0,3,3,3,0,3 },
};
int i,j,x;
// 下面准备点
//
for( i = 0; i < 10; ++i )
{
for ( j = 0; j < 10; ++j )
{
map_maze[i][j].s_g = 0;
map_maze[i][j].s_h = 0;
map_maze[i][j].s_is_in_closetable = 0;
map_maze[i][j].s_is_in_opentable = 0;
map_maze[i][j].s_style = maze[i][j];
map_maze[i][j].s_x = i;
map_maze[i][j].s_y = j;
map_maze[i][j].s_parent = NULL;
if ( map_maze[i][j].s_style == STARTNODE ) // 起点
{
start_node = &(map_maze[i][j]);
}
else if( map_maze[i][j].s_style == ENDNODE ) // 终点
{
end_node = &(map_maze[i][j]);
}
printf("%d ", maze[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// 下面使用A*算法得到路径
//
open_table[open_node_count++] = start_node; // 起始点加入open表
start_node->s_is_in_opentable = 1; // 加入open表
start_node->s_g = 0;
start_node->s_h = abs(end_node->s_x - start_node->s_x) + abs(end_node->s_y - start_node->s_y);
start_node->s_parent = NULL;
if ( start_node->s_x == end_node->s_x && start_node->s_y == end_node->s_y )
{
printf("起点==终点!\n");
return 0;
}
is_found = 0;
while( 1 )
{
curr_node = open_table[0]; // open表的第一个点一定是f值最小的点(通过堆排序得到的)
open_table[0] = open_table[--open_node_count]; // 最后一个点放到第一个点,然后进行堆调整
adjust_heap( 0 ); // 调整堆
close_table[close_node_count++] = curr_node; // 当前点加入close表
curr_node->s_is_in_closetable = 1; // 已经在close表中了
if ( curr_node->s_x == end_node->s_x && curr_node->s_y == end_node->s_y )// 终点在close中,结束
{
is_found = 1;
break;
}
get_neighbors( curr_node, end_node ); // 对邻居的处理
if ( open_node_count == 0 ) // 没有路径到达
{
is_found = 0;
break;
}
}
if ( is_found )
{
printf("Road founded!\n");
printf("Start node: (%d,%d)\n", start_node->s_x, start_node->s_y);
printf("End node: (%d,%d)\n", end_node->s_x, end_node->s_y);
curr_node = end_node;
while( curr_node )
{
path_stack[++top] = curr_node;
curr_node = curr_node->s_parent;
}
while( top > 0 ) // 下面是输出路径看看~
{
if ( top > 0 )
{
printf("(%d,%d)-->", path_stack[top]->s_x, path_stack[top--]->s_y);
}
else
{
printf("(%d,%d)", path_stack[top]->s_x, path_stack[top--]->s_y);
}
}
printf("(%d,%d)", path_stack[top]->s_x, path_stack[top]->s_y);
}
else
{
printf("么有找到路径");
}
puts("");
return 0;
}
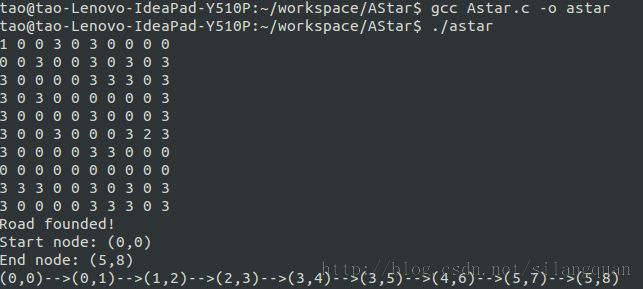
运行结果:
和其他算法的关系
A*算法,每次从OPENSET中选择 f(n) 最小的节点将其加入CLOESEDSET中,同时扩展相邻节点,可把OPENSET看成一个优先队列,key值为 f(n),优先级最高的先出。
Dijkstra算法,每次从OPENSET中选择 g(n) 最小的节点将其加入CLOSEDSET中,同时扩展相邻节点,可把OPENSET看成一个优先队列,key值为 g(n),优先级最高的先出。
DFS算法,每次从OPENSET中选择最晚被加入的节点将其加入CLOSEDSET中,同时扩展相邻节点,可把OPENSET看成一个栈,后进先出。
BFS算法,每次从OPENGSET中选择最早被加入的节点将其加入CLOSEDSET中,同时扩展相邻节点,可把OPENSET看成一个队列,先进先出。
参考
A* Pathfinding for Beginners - http://www.gamedev.net/page/resources/_/technical/artificial-intelligence/a-pathfinding-for-beginners-r2003
A*路径搜寻算法 - http://blog.csdn.net/luckyxiaoqiang/article/details/6996963
资源
A*,Dijkstra,BFS路径搜寻算法演示程序 - http://download.csdn.net/detail/walkinginthewind/3822153