Introduction to Fuzzy System
Introduction to Fuzzy System
Writer :unkonwn , Publication Date: 2004-12-12
Fuzzy Logic - a powerful new technology
Fuzzy Logic has emerged as a a profitable tool for the controlling of subway systems and complex industrial processes, as well as for household and entertainment electronics, diagnosis systems and other expert systems. Although, Fuzzy Logic was invented in the United States the rapid growth of this technology has started from Japan and has now again reached the USA and Europe also. Fuzzy Logic is still booming in Japan, the number of letters patent applied for increases exponentially. The main part deals with rather simple applications of Fuzzy Control. Fuzzy has become a key-word for marketing. Electronic articles without Fuzzy-component gradually turn out to be dead stock. As a gag, that shows the popularity of Fuzzy Logic, there even exists a toiletpaper with "Fuzzy Logic" printed on it.
In Japan Fuzzy-research is widely supported with a huge budget. In Europe and the USA efforts are being made to catch up with the tremendous japanese success. For instance, the NASA space agency is engaged in applying Fuzzy Logic for complex docking-maneuvers. Fuzzy Logic is basically a multivalued logic that allows intermediate values to be defined between conventional evaluations like yes/no, true/false, black/white, etc. Notions like rather warm or pretty cold can be formulated mathematically and processed by computers. In this way an attempt is made to apply a more human-like way of thinking in the programming of computers.
Fuzzy Logic was initiated in 1965 by Lotfi A. Zadeh, professor for computer science at the University of California in Berkeley.
What is a Fuzzy Set?
The very basic notion of fuzzy systems is a Fuzzy (sub)set. In classical mathematics we are familiar with what we call crisp sets.
Here is an example:
First we consider a set X of all real numbers between 0 and 10 which we call the universe of discourse. Now, let′s define a subset A of X of all real-numbers in the range between 5 and 8.
A = [5,8]
We now show the set A by its characteristic function, i.e. this function assigns a number 1 or 0 to each element in X, depending on whether the element is in the subset A or not. This results in the following figure: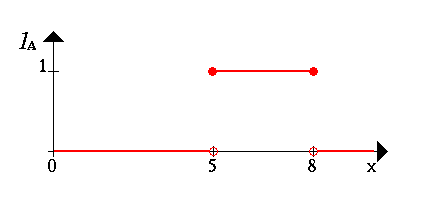
We can interpret the elements which have assigned the number 1 as The elements are in the set A and the elements which have assigned the number 0 as The elements are not in the set A. This concept is sufficient for many areas of applications. But we can easily find situations where it lacks in flexibility. In order to show this consider the following example on the next page:
In this example we want to describe the set of young people. More formally we can denote
B = {set of young people}
Since - in general - age starts at 0 the lower range of this set ought to be clear. The upper range, on the other hand, is rather hard to define. As a first attempt we set the upper range to, say, 20 years. Therefore we get B as a crisp interval, namely:
B = [0,20]
Now the question arises: why is somebody on his 20th birthday young and right on the next day not young? Obviously, this is a structural problem, for if we move the upper bound of the range from 20 to an arbitrary point we can pose the same question.
A more natural way to construct the set B would be to relax the strict separation between young and not young. We will do this by allowing not only the (crisp) decision YES he/she is in the set of young people or NO he/she is not in the set of young people but more flexible phrases like Well, he/she belongs a little bit more to the set of young people or NO, he/she belongs nearly not to the set of young people.
The next page shows how a fuzzy set allows us to define such a notion as s/he is a little young.
As stated in the introduction we want to use fuzzy sets to make computers smarter, we now have to code the above idea more formally. In our example. we coded all the elements of the Universe of Discourse with 0 or 1. A straight way to generalize this concept is to allow more values between 0 and 1. In fact, we even allow infinite many alternatives between 0 and 1, namely the unit interval I = [0, 1]. The interpretation of the numbers now assigned to all elements of the Universe of Discourse is much more difficult. Of course, again the number 1 assigned to an element means that the element is in the set B and 0 means that the element is definitely not in the set B. All other values mean a gradual membership to the set B. To be more concrete we now show the set of young people similar to our first example graphically by its characteristic function.
This way a 25 years old would still be young to a degree of 50 percent.
Now you know what a fuzzy set is. But what can you do with it?
Operations on Fuzzy Sets
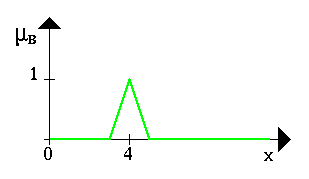
Now that we have an idea of what fuzzy sets are, we can introduce basic operations on fuzzy sets. Similar to the operations on crisp sets we also want to intersect, unify, negate fuzzy sets. In his very first paper about fuzzy sets, L. A. Zadeh suggested the minimum operator for the intersection and the maximum operator for the union of two fuzzy sets. It is easy to see that these operators coincide with the crisp unification, and intersection if we only consider the membership degrees 0 and 1. In order to clarify this, we give a few examples. Let A be a fuzzy interval between 5 and 8 and B be a fuzzy number about 4. The corresponding figures are shown below.
The following figure shows the fuzzy set between 5 and 8 AND about 4 (notice the blue line).
The Fuzzy set between 5 and 8 OR about 4 is shown in the next figure (again, it is the blue line).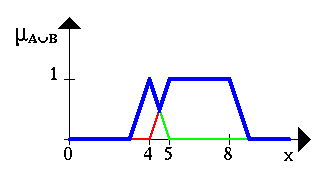
This figure gives an example for a negation. The blue line is the NEGATION of the fuzzy set A.
Applications for Fuzzy Logic
Here are some examples of how Fuzzy Logic has been applied in reality:
- Automatic control of dam gates for hydroelectric-powerplants (Tokio Electric Pow.)
- Simplified control of robots (Hirota, Fuji Electric, Toshiba, Omron)
- Camera aiming for the telecast of sporting events (Omron)
- Substitution of an expert for the assessment of stock exchange activities (Yamaichi, Hitachi)
- Preventing unwanted temperature fluctuations in air-conditioning systems (Mitsubishi, Sharp)
- Efficient and stable control of car-engines (Nissan)
- Cruise-control for automobiles (Nissan, Subaru)
- Improved efficiency and optimized function of industrial control applications (Aptronix, Omron, Meiden, Sha, Micom, Mitsubishi, Nisshin-Denki, Oku-Electronics)
- Positioning of wafer-steppers in the production of semiconductors (Canon)
- Optimized planning of bus time-tables (Toshiba, Nippon-System, Keihan-Express)
- Archiving system for documents (Mitsubishi Elec.)
- Prediction system for early recognition of earthquakes (Inst. of Seismology Bureau of Metrology, Japan)
- Medicine technology: cancer diagnosis (Kawasaki Medical School)
- Combination of Fuzzy Logic and Neural Nets (Matsushita)
- Recognition of handwritten symbols with pocket computers (Sony)
- Recognition of motives in pictures with video cameras (Canon, Minolta)
- Automatic motor-control for vacuum cleaners with recognition of surface condition and degree of soiling (Matsushita)
- Back light control for camcorders (Sanyo)
- Compensation against vibrations in camcorders (Matsushita)
- Single button control for washing-machines (Matsushita, Hitatchi)
- Recognition of handwriting, objects, voice (CSK, Hitachi, Hosai Univ., Ricoh)
- Flight aid for helicopters (Sugeno)
- Simulation for legal proceedings (Meihi Gakuin Univ, Nagoy Univ.)
- Software-design for industrial processes (Aptronix, Harima, Ishikawajima-OC Engeneering)
- Controlling of machinery speed and temperature for steel-works (Kawasaki Steel, New-Nippon Steel, NKK)
- Controlling of subway systems in order to improve driving comfort, precision of halting and power economy (Hitachi)
- Improved fuel-consumption for automobiles (NOK, Nippon Denki Tools)
- Improved sensitiveness and efficiency for elevator control (Fujitec, Hitachi, Toshiba)
- Improved savety for nuklear reactors (Hitachi, Bernard, Nuclear Fuel div.)
Reference of Fuzzy System
Books
- Kaufmann, Arnold and Gupta, Madan M., Introduction to Fuzzy Arithmetic: Theory and Applications, New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company Ltd., 1985. 350 pp.
Klir, George J. and Folger, Tina A., Fuzzy Sets, Uncertainty, and Information, Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1988. 355 pp.- Kosko, Bart A., Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems, Prentice-Hall, 1990.
- Mamdani, E.H. and Gaines, B.R., Fuzzy Reasoning and its Applications, New York: Academic Press, 1981. 380 pp.
- Negoita, Constantin Virgil, Fuzzy Systems, Cybernetics and Systems Series, Abacus Press, 1981. 120 pp.
- Sugeno, Michio, Industrial Applications of Fuzzy Control, New York: North-Holland, 1985. 270 pp.
- Togai, M., Reasoning with Uncertainty for Rule-based Expert Systems, John Wiley & Sons, in progress.
- Zimmermann, Hans J., Fuzzy Set Theory and its Applications, Boston MA: Kluwer-Nijhoff Publishing, 1985. 360 pp.
Papers
- Asai, K. and Tanaka, H., "Applications of Fuzzy Sets Theory to Decision-Making and Control," J. JAACE, 19, 235-242, 1975.
Bezdek, J.C., "Fuzzy Mathematics in Pattern Classification," Ph.D. Dissertation, Center for Applied Mathematics, Cornell University, 1973.- Blin, J.M., "Fuzzy Relations in Group Decision Theory," Journal of Cybernetics, 4, 17-22, 1974.
- Kosko, Bart A., "Foundations of Fuzzy Estimation Theory," Ph.D. Dissertation, University of California, Irvine, 1987.
- Larkin, Lawrence I., "A Fuzzy Controller for Aircraft Flight Control," Proceedings of the 23rd Conference on Decision and Control, Las Vegas, NV, December 1984.
- Togai, M., "Principles and Applications of Fuzzy Inference: A New Approach for Decision-making in an Ill-defined System," Ph.D. Dissertation, Duke University, 1982.
- Togai, M. and Watanabe, H., "An Inference Engine for Real-Time Approximate Reasoning: Toward an Expert System on a Chip," IEEE Expert, August 1986.
- Yasunobu S., Miyamoto S., and Ihara H., "Fuzzy Control for Automatic Train Operation System," IFAC-CISSS, 4th IFAC/IFIP/IFORS Conference on Control in Transportation Systems, Baden-Baden, F.R.G., April 1983.
- Zadeh, L.A., "Fuzzy Sets," Information and Control, 8, 338-353, 1965.
- Zadeh, L.A., "A Rationale for Fuzzy Control," Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement and Control, G94, 3-4, 1972.
- Zadeh, L.A., "Fuzzy Logic and Approximate Reasoning," Synthese, 30, 407-428, 1975.