POJ 1365 / Central Europe 1997 Prime Land (数论)
Prime Land
http://poj.org/problem?id=1365
Time Limit:
1000MS
Memory Limit: 10000K
Description
Everybody in the Prime Land is using a prime base number system. In this system, each positive integer x is represented as follows: Let {pi}i=0,1,2,... denote the increasing sequence of all prime numbers. We know that x > 1 can be represented in only one way in the form of product of powers of prime factors. This implies that there is an integer kx and uniquely determined integers e
kx, e
kx-1, ..., e
1, e
0, (e
kx > 0), that
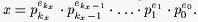 The sequence (e
kx, e
kx-1, ... ,e
1, e
0) is considered to be the representation of x in prime base number system.
The sequence (e
kx, e
kx-1, ... ,e
1, e
0) is considered to be the representation of x in prime base number system.
It is really true that all numerical calculations in prime base number system can seem to us a little bit unusual, or even hard. In fact, the children in Prime Land learn to add to subtract numbers several years. On the other hand, multiplication and division is very simple.
Recently, somebody has returned from a holiday in the Computer Land where small smart things called computers have been used. It has turned out that they could be used to make addition and subtraction in prime base number system much easier. It has been decided to make an experiment and let a computer to do the operation ``minus one''.
Help people in the Prime Land and write a corresponding program.
For practical reasons we will write here the prime base representation as a sequence of such pi and ei from the prime base representation above for which ei > 0. We will keep decreasing order with regard to pi.
It is really true that all numerical calculations in prime base number system can seem to us a little bit unusual, or even hard. In fact, the children in Prime Land learn to add to subtract numbers several years. On the other hand, multiplication and division is very simple.
Recently, somebody has returned from a holiday in the Computer Land where small smart things called computers have been used. It has turned out that they could be used to make addition and subtraction in prime base number system much easier. It has been decided to make an experiment and let a computer to do the operation ``minus one''.
Help people in the Prime Land and write a corresponding program.
For practical reasons we will write here the prime base representation as a sequence of such pi and ei from the prime base representation above for which ei > 0. We will keep decreasing order with regard to pi.
Input
The input consists of lines (at least one) each of which except the last contains prime base representation of just one positive integer greater than 2 and less or equal 32767. All numbers in the line are separated by one space. The last line contains number 0.
Output
The output contains one line for each but the last line of the input. If x is a positive integer contained in a line of the input, the line in the output will contain x - 1 in prime base representation. All numbers in the line are separated by one space. There is no line in the output corresponding to the last ``null'' line of the input.
Sample Input
17 1 5 1 2 1 509 1 59 1 0
Sample Output
2 4 3 2 13 1 11 1 7 1 5 1 3 1 2 1
学英语:
The input consists of lines (at least one) each of which except the last contains prime base representation of just one positive integer greater than 2 and less or equal 32767.
输入有至少一行,除了最后一行,每行都包含了一个数的素因子分解表示,该数大于2且小于或等于32767.
完整代码:
/*0ms,116KB*/
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
char s[24];///刚好
int base[6], index[6];///刚好
int main(void)
{
while (gets(s), s[0] != '0')
{
memset(base, 0, sizeof(base));
memset(index, 0, sizeof(index));
int temp = 0, count = 0;
bool which = true;
for (int i = 0; s[i]; ++i)
{
if (s[i] != ' ')
temp = temp * 10 + s[i] - '0';
else
{
if (which)
base[count] = temp;
else
index[count++] = temp;
which = (which ? false : true);
temp = 0;
}
}
///最后s[i] == '\0'退出
index[count++] = temp;
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < index[i]; ++j)
ans *= base[i];///整数的幂运算最好用for代替!
--ans;
count = 0;
int sqrtans = (int)sqrt((double)ans);
for (int i = 2; i <= sqrtans; ++i)
{
if (ans % i == 0)
{
index[count] = 0;
base[count] = i;
while (ans % i == 0)
{
++index[count];
ans /= i;
}
count++;
}
}
if (ans > 1) ///无法分解
{
base[count] = ans;
index[count++] = 1;
}
///逆序输出
for (int i = count - 1; i > 0; --i)
printf("%d %d ", base[i], index[i]);
printf("%d %d\n", base[0], index[0]);
}
return 0;
}
先打表的方法:
/*16ms,128KB*/
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
char s[24];///刚好
int base[6], index[6], prime[43], c = 0;
bool vis[192];
inline void create_prime()
{
for (int i = 2; i <= 191; ++i)
if (!vis[i])
{
prime[c++] = i;
for (int j = i * i; j <= 191; j += i)
vis[j] = true;
}
}
int main(void)
{
create_prime();
while (gets(s), s[0] != '0')
{
memset(base, 0, sizeof(base));
memset(index, 0, sizeof(index));
int temp = 0, count = 0;
bool which = true;
for (int i = 0; s[i]; ++i)
{
if (s[i] != ' ')
temp = temp * 10 + s[i] - '0';
else
{
if (which)
base[count] = temp;
else
index[count++] = temp;
which = (which ? false : true);
temp = 0;
}
}
///最后s[i] == '\0'退出
index[count++] = temp;
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < index[i]; ++j)
ans *= base[i];///整数的幂运算最好用for代替!
--ans;
count = 0;
int sqrtans = (int)sqrt((double)ans);
for (int i = 0; prime[i] <= sqrtans; ++i)
{
if (ans % prime[i] == 0)
{
index[count] = 0;
base[count] = prime[i];
while (ans % prime[i] == 0)
{
++index[count];
ans /= prime[i];
}
count++;
}
}
if (ans > 1) ///无法分解
{
base[count] = ans;
index[count++] = 1;
}
///逆序输出
for (int i = count - 1; i > 0; --i)
printf("%d %d ", base[i], index[i]);
printf("%d %d\n", base[0], index[0]);
}
return 0;
}