基于s3c6410 otg controller的gadget driver及usb枚举分 析
一.简介
二. usb枚举过程分析
图2 以s3c6410为设备控制器的usb枚举过程设备侧程序流程1
图3 以s3c6410为设备控制器的usb枚举过程设备侧程序流程2
如图2,由于usb设备处理被动地位,不能主动去发送数据,所有的请求都是由主机发起,而usb设备在接收到来自主机的请求后,产生接收数据中断,在中断处理程序中,通过不同的请求类型响应不同操作。
三.程序分析
struct usb_gadget_driver:用来存放gadget驱动;struct usb_request:用来存放usb device侧usb请求数据;struct usb_gadget:用来表示一个usb设备侧设备;struct usb_gadget_ops:gadget API函数接口,和设备控制器相关;struct usb_ep_ops:用于操作usb设备endpoint函数接口,和设备控制器相关。struct usb_composite_driver:复合型设备驱动;struct usb_composite_dev:复合型设备;
1. usb device controller注册
s3c6410 otg controller driver通过平台注册方式注册,当平台驱动和平台设备通过platform_match时,就会调用s3c_hsotg_probe.
static int __devinit s3c_hsotg_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct s3c_hsotg_plat *plat = pdev->dev.platform_data;
struct device *dev = &pdev->dev;
struct s3c_hsotg *hsotg;
struct resource *res;
int epnum;
int ret;
if (!plat)
plat = &s3c_hsotg_default_pdata;
hsotg = kzalloc(sizeof(struct s3c_hsotg) +
sizeof(struct s3c_hsotg_ep) * S3C_HSOTG_EPS,
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!hsotg) {
dev_err(dev, "cannot get memory\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
hsotg->dev = dev;
hsotg->plat = plat;
hsotg->clk = clk_get(&pdev->dev, "otg");
if (IS_ERR(hsotg->clk)) {
dev_err(dev, "cannot get otg clock\n");
ret = PTR_ERR(hsotg->clk);
goto err_mem;
}
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, hsotg);
res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);
if (!res) {
dev_err(dev, "cannot find register resource 0\n");
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err_clk;
}
hsotg->regs_res = request_mem_region(res->start, resource_size(res),
dev_name(dev));
if (!hsotg->regs_res) {
dev_err(dev, "cannot reserve registers\n");
ret = -ENOENT;
goto err_clk;
}
hsotg->regs = ioremap(res->start, resource_size(res));
if (!hsotg->regs) {
dev_err(dev, "cannot map registers\n");
ret = -ENXIO;
goto err_regs_res;
}
ret = platform_get_irq(pdev, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(dev, "cannot find IRQ\n");
goto err_regs;
}
hsotg->irq = ret;
ret = request_irq(ret, s3c_hsotg_irq, 0, dev_name(dev), hsotg);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(dev, "cannot claim IRQ\n");
goto err_regs;
}
dev_info(dev, "regs %p, irq %d\n", hsotg->regs, hsotg->irq);
device_initialize(&hsotg->gadget.dev);
dev_set_name(&hsotg->gadget.dev, "gadget");
hsotg->gadget.is_dualspeed = 1;
hsotg->gadget.ops = &s3c_hsotg_gadget_ops;
hsotg->gadget.name = dev_name(dev);
hsotg->gadget.dev.parent = dev;
hsotg->gadget.dev.dma_mask = dev->dma_mask;
/* setup endpoint information */
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&hsotg->gadget.ep_list);
hsotg->gadget.ep0 = &hsotg->eps[0].ep;
/* allocate EP0 request */
hsotg->ctrl_req = s3c_hsotg_ep_alloc_request(&hsotg->eps[0].ep,
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!hsotg->ctrl_req) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to allocate ctrl req\n");
goto err_regs;
}
/* reset the system */
clk_enable(hsotg->clk);
s3c_hsotg_gate(pdev, true);
s3c_hsotg_otgreset(hsotg);
s3c_hsotg_corereset(hsotg);
s3c_hsotg_init(hsotg);
/* initialise the endpoints now the core has been initialised */
for (epnum = 0; epnum < S3C_HSOTG_EPS; epnum++)
s3c_hsotg_initep(hsotg, &hsotg->eps[epnum], epnum);
ret = usb_add_gadget_udc(&pdev->dev, &hsotg->gadget);
if (ret)
goto err_add_udc;
s3c_hsotg_create_debug(hsotg);
s3c_hsotg_dump(hsotg);
our_hsotg = hsotg;
return 0;
err_add_udc:
s3c_hsotg_gate(pdev, false);
clk_disable(hsotg->clk);
clk_put(hsotg->clk);
err_regs:
iounmap(hsotg->regs);
err_regs_res:
release_resource(hsotg->regs_res);
kfree(hsotg->regs_res);
err_clk:
clk_put(hsotg->clk);
err_mem:
kfree(hsotg);
return ret;
}
2.usb composite driver和gadget driver注册
static struct usb_composite_driver zero_driver = {
.name = "zero",
.dev = &device_desc,
.strings = dev_strings,
.max_speed = USB_SPEED_SUPER,
.unbind = zero_unbind,
.suspend = zero_suspend,
.resume = zero_resume,
};
zero_driver中dev定义了初始的usb设备描述符,之后会在zero_bind中补全其它参量,在usb枚举的过程中会将这个完整的设备描述符发送回给host。
static int __init init(void)
{
return usb_composite_probe(&zero_driver, zero_bind);
}
module_init(init);
static void __exit cleanup(void)
{
usb_composite_unregister(&zero_driver);
}
module_exit(cleanup);
int usb_composite_probe(struct usb_composite_driver *driver,
int (*bind)(struct usb_composite_dev *cdev))
{
if (!driver || !driver->dev || !bind || composite)
return -EINVAL;
if (!driver->name)
driver->name = "composite";
if (!driver->iProduct)
driver->iProduct = driver->name;
composite_driver.function = (char *) driver->name;
composite_driver.driver.name = driver->name;
composite_driver.speed = min((u8)composite_driver.speed,
(u8)driver->max_speed);
composite = driver;
composite_gadget_bind = bind;
return usb_gadget_probe_driver(&composite_driver, composite_bind);
}
usb_composite_probe用来将usb_composite_driver注册到composite driver框架中,这里通过一个composite变量用来保存composite driver,composite_gadget_bind保存bind,并通过composite driver中的些变量来补全一个usb_gadget_driver composite_driver.之前简介里有提到过,gadget设备侧程序主要由gadget driver和device controller driver组成 ,这里这个composite_driver就是device controller driver上面的那与硬件无关的那一层,composite_driver定义如下:
static struct usb_gadget_driver composite_driver = {
#ifdef CONFIG_USB_GADGET_SUPERSPEED
.speed = USB_SPEED_SUPER,
#else
.speed = USB_SPEED_HIGH,
#endif
.unbind = composite_unbind,
.setup = composite_setup,
.disconnect = composite_disconnect,
.suspend = composite_suspend,
.resume = composite_resume,
.driver = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
};
composite_driver中的setup函数最为重要,简介中曾经说过,device controller driver用来完成和硬件相关的设备或回应,如设置usb设备地址,ACK应答之类机制。但像获取设备描述符,设置配置,设置接口等机制并没有实现,这些请求的处理机制就是在这个setup里完成的。
int usb_gadget_probe_driver(struct usb_gadget_driver *driver,
int (*bind)(struct usb_gadget *))
{
struct usb_udc *udc = NULL;
int ret;
if (!driver || !bind || !driver->setup)
return -EINVAL;
mutex_lock(&udc_lock);
list_for_each_entry(udc, &udc_list, list) {
/* For now we take the first one */
if (!udc->driver)
goto found;
}
pr_debug("couldn't find an available UDC\n");
mutex_unlock(&udc_lock);
return -ENODEV;
found:
dev_dbg(&udc->dev, "registering UDC driver [%s]\n",
driver->function);
udc->driver = driver;
udc->dev.driver = &driver->driver;
if (udc_is_newstyle(udc)) {
ret = bind(udc->gadget);
if (ret)
goto err1;
ret = usb_gadget_udc_start(udc->gadget, driver);
if (ret) {
driver->unbind(udc->gadget);
goto err1;
}
usb_gadget_connect(udc->gadget);
} else {
ret = usb_gadget_start(udc->gadget, driver, bind);
if (ret)
goto err1;
}
kobject_uevent(&udc->dev.kobj, KOBJ_CHANGE);
mutex_unlock(&udc_lock);
return 0;
err1:
dev_err(&udc->dev, "failed to start %s: %d\n",
udc->driver->function, ret);
udc->driver = NULL;
udc->dev.driver = NULL;
mutex_unlock(&udc_lock);
return ret;
} 这前在讲device controller 注册时讲过,通过usb_add_gadget_udc注册device controller时,linux系统是通过一个struct usb_udc结构的udc_list列表中进行管理设备控制器的,struct usb_udc结构如下:
struct usb_udc {
struct usb_gadget_driver *driver;
struct usb_gadget *gadget;
struct device dev;
struct list_head list;
}; driver用于表示一个udc驱动,而 list就是用来加入到udc_list列表的入口变量。
int (*udc_start)(struct usb_gadget *, struct usb_gadget_driver *); int (*udc_stop)(struct usb_gadget *, struct usb_gadget_driver *); /* Those two are deprecated */ int (*start)(struct usb_gadget_driver *, int (*bind)(struct usb_gadget *)); int (*stop)(struct usb_gadget_driver *);其中,udc_start 和udc_stop为新版本操作接口 ,而start 和stop老版本操作接口。
static int composite_bind(struct usb_gadget *gadget)
{
struct usb_composite_dev *cdev;
int status = -ENOMEM;
cdev = kzalloc(sizeof *cdev, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cdev)
return status;
spin_lock_init(&cdev->lock);
cdev->gadget = gadget;
set_gadget_data(gadget, cdev);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cdev->configs);
/* preallocate control response and buffer */
cdev->req = usb_ep_alloc_request(gadget->ep0, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cdev->req)
goto fail;
cdev->req->buf = kmalloc(USB_BUFSIZ, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cdev->req->buf)
goto fail;
cdev->req->complete = composite_setup_complete;
gadget->ep0->driver_data = cdev;
cdev->bufsiz = USB_BUFSIZ;
cdev->driver = composite;
/*
* As per USB compliance update, a device that is actively drawing
* more than 100mA from USB must report itself as bus-powered in
* the GetStatus(DEVICE) call.
*/
if (CONFIG_USB_GADGET_VBUS_DRAW <= USB_SELF_POWER_VBUS_MAX_DRAW)
usb_gadget_set_selfpowered(gadget);
/* interface and string IDs start at zero via kzalloc.
* we force endpoints to start unassigned; few controller
* drivers will zero ep->driver_data.
*/
usb_ep_autoconfig_reset(cdev->gadget);
/* composite gadget needs to assign strings for whole device (like
* serial number), register function drivers, potentially update
* power state and consumption, etc
*/
status = composite_gadget_bind(cdev);
if (status < 0)
goto fail;
cdev->desc = *composite->dev;
/* standardized runtime overrides for device ID data */
if (idVendor)
cdev->desc.idVendor = cpu_to_le16(idVendor);
if (idProduct)
cdev->desc.idProduct = cpu_to_le16(idProduct);
if (bcdDevice)
cdev->desc.bcdDevice = cpu_to_le16(bcdDevice);
/* string overrides */
if (iManufacturer || !cdev->desc.iManufacturer) {
if (!iManufacturer && !composite->iManufacturer &&
!*composite_manufacturer)
snprintf(composite_manufacturer,
sizeof composite_manufacturer,
"%s %s with %s",
init_utsname()->sysname,
init_utsname()->release,
gadget->name);
cdev->manufacturer_override =
override_id(cdev, &cdev->desc.iManufacturer);
}
if (iProduct || (!cdev->desc.iProduct && composite->iProduct))
cdev->product_override =
override_id(cdev, &cdev->desc.iProduct);
if (iSerialNumber)
cdev->serial_override =
override_id(cdev, &cdev->desc.iSerialNumber);
/* has userspace failed to provide a serial number? */
if (composite->needs_serial && !cdev->desc.iSerialNumber)
WARNING(cdev, "userspace failed to provide iSerialNumber\n");
/* finish up */
status = device_create_file(&gadget->dev, &dev_attr_suspended);
if (status)
goto fail;
INFO(cdev, "%s ready\n", composite->name);
return 0;
fail:
composite_unbind(gadget);
return status;
} 在将gadget driver和usb device controller联系在一起后,composite_bind将会生成一个composite dev数据结构,并对其进行初始化,然后申请用于回复endpoint0的控制端口的usb request资源,最后调用composite回调函数zero_bind用来为composite usb device 添加配置。
static int __init zero_bind(struct usb_composite_dev *cdev)
{
int gcnum;
struct usb_gadget *gadget = cdev->gadget;
int id;
/* Allocate string descriptor numbers ... note that string
* contents can be overridden by the composite_dev glue.
*/
id = usb_string_id(cdev);
if (id < 0)
return id;
strings_dev[STRING_MANUFACTURER_IDX].id = id;
device_desc.iManufacturer = id;
id = usb_string_id(cdev);
if (id < 0)
return id;
strings_dev[STRING_PRODUCT_IDX].id = id;
device_desc.iProduct = id;
id = usb_string_id(cdev);
if (id < 0)
return id;
strings_dev[STRING_SERIAL_IDX].id = id;
device_desc.iSerialNumber = id;
setup_timer(&autoresume_timer, zero_autoresume, (unsigned long) cdev);
/* Register primary, then secondary configuration. Note that
* SH3 only allows one config...
*/
if (loopdefault) {
loopback_add(cdev, autoresume != 0);
sourcesink_add(cdev, autoresume != 0);
} else {
sourcesink_add(cdev, autoresume != 0);
loopback_add(cdev, autoresume != 0);
}
gcnum = usb_gadget_controller_number(gadget);
if (gcnum >= 0)
device_desc.bcdDevice = cpu_to_le16(0x0200 + gcnum);
else {
/* gadget zero is so simple (for now, no altsettings) that
* it SHOULD NOT have problems with bulk-capable hardware.
* so just warn about unrcognized controllers -- don't panic.
*
* things like configuration and altsetting numbering
* can need hardware-specific attention though.
*/
pr_warning("%s: controller '%s' not recognized\n",
longname, gadget->name);
device_desc.bcdDevice = cpu_to_le16(0x9999);
}
INFO(cdev, "%s, version: " DRIVER_VERSION "\n", longname);
snprintf(manufacturer, sizeof manufacturer, "%s %s with %s",
init_utsname()->sysname, init_utsname()->release,
gadget->name);
return 0;
} zero_bind主要用于设置设备描述符中bcdDevice,iManufacturer,iProduct及iSerialNumber,然后通过loopback_add和sourcesink_add添加usb配置。
int __init loopback_add(struct usb_composite_dev *cdev, bool autoresume)
{
int id;
/* allocate string ID(s) */
id = usb_string_id(cdev);
if (id < 0)
return id;
strings_loopback[0].id = id;
loopback_intf.iInterface = id;
loopback_driver.iConfiguration = id;
/* support autoresume for remote wakeup testing */
if (autoresume)
sourcesink_driver.bmAttributes |= USB_CONFIG_ATT_WAKEUP;
/* support OTG systems */
if (gadget_is_otg(cdev->gadget)) {
loopback_driver.descriptors = otg_desc;
loopback_driver.bmAttributes |= USB_CONFIG_ATT_WAKEUP;
}
return usb_add_config(cdev, &loopback_driver, loopback_bind_config);
}
loopback_add主要是完成loopback这个配置描述符里的配置ID设置,并通过usb_add_config向usb设备添加loopback_driver这个配置。
static struct usb_configuration loopback_driver = {
.label = "loopback",
.strings = loopback_strings,
.bConfigurationValue = 2,
.bmAttributes = USB_CONFIG_ATT_SELFPOWER,
/* .iConfiguration = DYNAMIC */
}; label为配置名字,strings里用于申明配置功能的string,bConfigurationValue用来表示当前配置值,在USB枚举时就能通过选择合适的配置值来设备usb设备的配置,bmAttributes用来表明配置的特性,如自供电,远程唤醒等。
int usb_add_config(struct usb_composite_dev *cdev,
struct usb_configuration *config,
int (*bind)(struct usb_configuration *))
{
int status = -EINVAL;
struct usb_configuration *c;
DBG(cdev, "adding config #%u '%s'/%p\n",
config->bConfigurationValue,
config->label, config);
if (!config->bConfigurationValue || !bind)
goto done;
/* Prevent duplicate configuration identifiers */
list_for_each_entry(c, &cdev->configs, list) {
if (c->bConfigurationValue == config->bConfigurationValue) {
status = -EBUSY;
goto done;
}
}
config->cdev = cdev;
list_add_tail(&config->list, &cdev->configs);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&config->functions);
config->next_interface_id = 0;
status = bind(config);
if (status < 0) {
list_del(&config->list);
config->cdev = NULL;
} else {
unsigned i;
DBG(cdev, "cfg %d/%p speeds:%s%s%s\n",
config->bConfigurationValue, config,
config->superspeed ? " super" : "",
config->highspeed ? " high" : "",
config->fullspeed
? (gadget_is_dualspeed(cdev->gadget)
? " full"
: " full/low")
: "");
for (i = 0; i < MAX_CONFIG_INTERFACES; i++) {
struct usb_function *f = config->interface[i];
if (!f)
continue;
DBG(cdev, " interface %d = %s/%p\n",
i, f->name, f);
}
}
/* set_alt(), or next bind(), sets up
* ep->driver_data as needed.
*/
usb_ep_autoconfig_reset(cdev->gadget);
done:
if (status)
DBG(cdev, "added config '%s'/%u --> %d\n", config->label,
config->bConfigurationValue, status);
return status;
}usb_add_config用来向复合型usb设备添加一个usb配置,并对配置进行初始化,最后调用配置的回调函数loopback_bind_config向当前配置添加usb接口。
static int __init loopback_bind_config(struct usb_configuration *c)
{
struct f_loopback *loop;
int status;
loop = kzalloc(sizeof *loop, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!loop)
return -ENOMEM;
loop->function.name = "loopback";
loop->function.descriptors = fs_loopback_descs;
loop->function.bind = loopback_bind;
loop->function.unbind = loopback_unbind;
loop->function.set_alt = loopback_set_alt;
loop->function.disable = loopback_disable;
status = usb_add_function(c, &loop->function);
if (status)
kfree(loop);
return status;
}
loopback_bind_config用来向当前配置添加接口功能,它先申请了一个f_loopback数据结构,里面包含了usb的接口和端口,然后对接口一些函数接口进行初始化,最后调用usb_add_function把接口添加到配置中。在接口的操作函数接口中,bind和set_alt相对比较重要,在usb_add_function中会调用bind来完成某个接口中各端口(endpoint)的初始化,而在枚举过程中设置接口USB请求就是通过这个接口实现。
int usb_add_function(struct usb_configuration *config,
struct usb_function *function)
{
int value = -EINVAL;
DBG(config->cdev, "adding '%s'/%p to config '%s'/%p\n",
function->name, function,
config->label, config);
if (!function->set_alt || !function->disable)
goto done;
function->config = config;
list_add_tail(&function->list, &config->functions);
/* REVISIT *require* function->bind? */
if (function->bind) {
value = function->bind(config, function);
if (value < 0) {
list_del(&function->list);
function->config = NULL;
}
} else
value = 0;
/* We allow configurations that don't work at both speeds.
* If we run into a lowspeed Linux system, treat it the same
* as full speed ... it's the function drivers that will need
* to avoid bulk and ISO transfers.
*/
if (!config->fullspeed && function->descriptors)
config->fullspeed = true;
if (!config->highspeed && function->hs_descriptors)
config->highspeed = true;
if (!config->superspeed && function->ss_descriptors)
config->superspeed = true;
done:
if (value)
DBG(config->cdev, "adding '%s'/%p --> %d\n",
function->name, function, value);
return value;
}
static int __init
loopback_bind(struct usb_configuration *c, struct usb_function *f)
{
struct usb_composite_dev *cdev = c->cdev;
struct f_loopback *loop = func_to_loop(f);
int id;
/* allocate interface ID(s) */
id = usb_interface_id(c, f);
if (id < 0)
return id;
loopback_intf.bInterfaceNumber = id;
/* allocate endpoints */
loop->in_ep = usb_ep_autoconfig(cdev->gadget, &fs_loop_source_desc);
if (!loop->in_ep) {
autoconf_fail:
ERROR(cdev, "%s: can't autoconfigure on %s\n",
f->name, cdev->gadget->name);
return -ENODEV;
}
loop->in_ep->driver_data = cdev; /* claim */
loop->out_ep = usb_ep_autoconfig(cdev->gadget, &fs_loop_sink_desc);
if (!loop->out_ep)
goto autoconf_fail;
loop->out_ep->driver_data = cdev; /* claim */
/* support high speed hardware */
if (gadget_is_dualspeed(c->cdev->gadget)) {
hs_loop_source_desc.bEndpointAddress =
fs_loop_source_desc.bEndpointAddress;
hs_loop_sink_desc.bEndpointAddress =
fs_loop_sink_desc.bEndpointAddress;
f->hs_descriptors = hs_loopback_descs;
}
/* support super speed hardware */
if (gadget_is_superspeed(c->cdev->gadget)) {
ss_loop_source_desc.bEndpointAddress =
fs_loop_source_desc.bEndpointAddress;
ss_loop_sink_desc.bEndpointAddress =
fs_loop_sink_desc.bEndpointAddress;
f->ss_descriptors = ss_loopback_descs;
}
DBG(cdev, "%s speed %s: IN/%s, OUT/%s\n",
(gadget_is_superspeed(c->cdev->gadget) ? "super" :
(gadget_is_dualspeed(c->cdev->gadget) ? "dual" : "full")),
f->name, loop->in_ep->name, loop->out_ep->name);
return 0;
}loopback_bind主要用于配置接口中的端口。
第16-23和25-28行,分别 调用usb_ep_autoconfig函数,从gadget的ep_list找到in和out端口;
struct usb_ep *usb_ep_autoconfig(
struct usb_gadget *gadget,
struct usb_endpoint_descriptor *desc
)
{
return usb_ep_autoconfig_ss(gadget, desc, NULL);
}
usb_ep_autoconfig函数是从gadget里的ep_list找到与所给端口描述符相匹配的端口,函数里面实际上是调用usb_ep_autoconfig_ss来实现端口匹配的。
struct usb_ep *usb_ep_autoconfig_ss(
struct usb_gadget *gadget,
struct usb_endpoint_descriptor *desc,
struct usb_ss_ep_comp_descriptor *ep_comp
)
{
struct usb_ep *ep;
u8 type;
type = desc->bmAttributes & USB_ENDPOINT_XFERTYPE_MASK;
/* First, apply chip-specific "best usage" knowledge.
* This might make a good usb_gadget_ops hook ...
*/
if (gadget_is_net2280 (gadget) && type == USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_INT) {
/* ep-e, ep-f are PIO with only 64 byte fifos */
ep = find_ep (gadget, "ep-e");
if (ep && ep_matches(gadget, ep, desc, ep_comp))
return ep;
ep = find_ep (gadget, "ep-f");
if (ep && ep_matches(gadget, ep, desc, ep_comp))
return ep;
} else if (gadget_is_goku (gadget)) {
if (USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_INT == type) {
/* single buffering is enough */
ep = find_ep(gadget, "ep3-bulk");
if (ep && ep_matches(gadget, ep, desc, ep_comp))
return ep;
} else if (USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_BULK == type
&& (USB_DIR_IN & desc->bEndpointAddress)) {
/* DMA may be available */
ep = find_ep(gadget, "ep2-bulk");
if (ep && ep_matches(gadget, ep, desc,
ep_comp))
return ep;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_BLACKFIN
} else if (gadget_is_musbhdrc(gadget)) {
if ((USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_BULK == type) ||
(USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_ISOC == type)) {
if (USB_DIR_IN & desc->bEndpointAddress)
ep = find_ep (gadget, "ep5in");
else
ep = find_ep (gadget, "ep6out");
} else if (USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_INT == type) {
if (USB_DIR_IN & desc->bEndpointAddress)
ep = find_ep(gadget, "ep1in");
else
ep = find_ep(gadget, "ep2out");
} else
ep = NULL;
if (ep && ep_matches(gadget, ep, desc, ep_comp))
return ep;
#endif
}
/* Second, look at endpoints until an unclaimed one looks usable */
list_for_each_entry (ep, &gadget->ep_list, ep_list) {
if (ep_matches(gadget, ep, desc, ep_comp))
return ep;
}
/* Fail */
return NULL;
}usb_ep_autoconfig_ss函数有三个形参,分别是表示usb设备侧设备gadget,端口描述符desc和专门用于描述超高速端口特性(usb 3.0里才有)的ep_comp,它首先通过匹配设备控制器芯片和端口传输类型来选择端口,如没有找到则在gadget的ep_list列表中寻找ep,并通过ep_matches匹配,如果找到相匹配的endpoint就返回该端口,否则返回null。
static int
ep_matches (
struct usb_gadget *gadget,
struct usb_ep *ep,
struct usb_endpoint_descriptor *desc,
struct usb_ss_ep_comp_descriptor *ep_comp
)
{
u8 type;
const char *tmp;
u16 max;
int num_req_streams = 0;
/* endpoint already claimed? */
if (NULL != ep->driver_data)
return 0;
/* only support ep0 for portable CONTROL traffic */
type = desc->bmAttributes & USB_ENDPOINT_XFERTYPE_MASK;
if (USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_CONTROL == type)
return 0;
/* some other naming convention */
if ('e' != ep->name[0])
return 0;
/* type-restriction: "-iso", "-bulk", or "-int".
* direction-restriction: "in", "out".
*/
if ('-' != ep->name[2]) {
tmp = strrchr (ep->name, '-');
if (tmp) {
switch (type) {
case USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_INT:
/* bulk endpoints handle interrupt transfers,
* except the toggle-quirky iso-synch kind
*/
if ('s' == tmp[2]) // == "-iso"
return 0;
/* for now, avoid PXA "interrupt-in";
* it's documented as never using DATA1.
*/
if (gadget_is_pxa (gadget)
&& 'i' == tmp [1])
return 0;
break;
case USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_BULK:
if ('b' != tmp[1]) // != "-bulk"
return 0;
break;
case USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_ISOC:
if ('s' != tmp[2]) // != "-iso"
return 0;
}
} else {
tmp = ep->name + strlen (ep->name);
}
/* direction-restriction: "..in-..", "out-.." */
tmp--;
if (!isdigit (*tmp)) {
if (desc->bEndpointAddress & USB_DIR_IN) {
if ('n' != *tmp)
return 0;
} else {
if ('t' != *tmp)
return 0;
}
}
}
/*
* Get the number of required streams from the EP companion
* descriptor and see if the EP matches it
*/
if (usb_endpoint_xfer_bulk(desc)) {
if (ep_comp) {
num_req_streams = ep_comp->bmAttributes & 0x1f;
if (num_req_streams > ep->max_streams)
return 0;
/* Update the ep_comp descriptor if needed */
if (num_req_streams != ep->max_streams)
ep_comp->bmAttributes = ep->max_streams;
}
}
/*
* If the protocol driver hasn't yet decided on wMaxPacketSize
* and wants to know the maximum possible, provide the info.
*/
if (desc->wMaxPacketSize == 0)
desc->wMaxPacketSize = cpu_to_le16(ep->maxpacket);
/* endpoint maxpacket size is an input parameter, except for bulk
* where it's an output parameter representing the full speed limit.
* the usb spec fixes high speed bulk maxpacket at 512 bytes.
*/
max = 0x7ff & le16_to_cpu(desc->wMaxPacketSize);
switch (type) {
case USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_INT:
/* INT: limit 64 bytes full speed, 1024 high/super speed */
if (!gadget->is_dualspeed && max > 64)
return 0;
/* FALLTHROUGH */
case USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_ISOC:
/* ISO: limit 1023 bytes full speed, 1024 high/super speed */
if (ep->maxpacket < max)
return 0;
if (!gadget->is_dualspeed && max > 1023)
return 0;
/* BOTH: "high bandwidth" works only at high speed */
if ((desc->wMaxPacketSize & cpu_to_le16(3<<11))) {
if (!gadget->is_dualspeed)
return 0;
/* configure your hardware with enough buffering!! */
}
break;
}
/* MATCH!! */
/* report address */
desc->bEndpointAddress &= USB_DIR_IN;
if (isdigit (ep->name [2])) {
u8 num = simple_strtoul (&ep->name [2], NULL, 10);
desc->bEndpointAddress |= num;
#ifdef MANY_ENDPOINTS
} else if (desc->bEndpointAddress & USB_DIR_IN) {
if (++in_epnum > 15)
return 0;
desc->bEndpointAddress = USB_DIR_IN | in_epnum;
#endif
} else {
if (++epnum > 15)
return 0;
desc->bEndpointAddress |= epnum;
}
/* report (variable) full speed bulk maxpacket */
if ((USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_BULK == type) && !ep_comp) {
int size = ep->maxpacket;
/* min() doesn't work on bitfields with gcc-3.5 */
if (size > 64)
size = 64;
desc->wMaxPacketSize = cpu_to_le16(size);
}
ep->address = desc->bEndpointAddress;
return 1;
}ep_matches通过端口描述符的一些特性来和gadget ep_list进行比较,device controller在初始化endpoint时,会将endpoint的名字设置成好几种类型:
1.ep1, ep2, ... 地址确定,方向和类型不确定;
2. ep1in, ep2out, ...地址和方向确定,类型不确定;
3. ep1-bulk, ep2-bulk, ... 地址和类型确定,方向不确定;
4. ep1in-bulk, ep2out-iso, ... 地址,方向和类型都确定;
5. ep-* ... 没有任何限制;
ep_matches首先通过比较端口传输地址,方向和类型,然后再比较速度等信息来匹配,如果不匹配则返回0,否则如果条件都满足则返回1。
31-58行,首先根据endpoint的name和端口描述符所指定的传输类型进行比较,对于中断传输如'-'后面第二个字符是s,即表示iso,那肯定不匹配,直接返回,对于批量传输如果‘-’后面第一个字符不是b,则不匹配,对于等时传输,‘-’后第二个字符应该是s.
62-69根据端口描述符中的bEndpointAddress和endpoint中的name进行比较,如果端口传输方向为in,但发现name却不是以n字符结尾,则不匹配,如果端口传输方面是out,而name不以t结尾,则不匹配;
77-87行是对超高速设备进行判断;
93-94行,如果端口描述符里没有指定最大传输长度,但将当前endpoint的最大传输长度赋值给端口描述符。
端口描述符中的wMaxPacketSize用来表示,wMaxPacketSize中低11位用来表示最大传输长度,对于高速的中断和等时传输类型,wMaxPacketSize中的第12,13位用来表示每帧数据里额外传输事务的数量。
100-105行,通过端点传输类型,传输最大长度和端口速度来进行匹配,对于全速的中断传输,最大数据长度为64个字节,如大于64个字节,则不匹配;
108-120行,对于等时传输,如端口描述符里指定的最大传输长度大于endpoint里的最大传输长度,那肯定不匹配,在全速时最大数据长度不能超过1023个字节,而额外事务传输只有是在高速的情况下才能满足。
如果当前端口通过上面这些匹配条件,表明当前的endpoint就是所需的端口,接下来进行一些如端口传输方向,地址等设置。
运行到目前为止,device controller ,composite driver, gadget driver都已经成功注册到系统中,并完成了对复合设备配置,接口和端口添加和配置,表示usb设备准备完成 ,可以开始响应host 端的枚举请求。
3. 响应host枚举
a. 当hub检测到hub状态寄存器发生变化时,去唤醒hub的守护进程,去查看具体是那 一个port引起的;
b. 如果发现有设备插入,等待100ms使设备稳定后,root hub会向插入设备的port发送reset请求,reset成功后usb设备处于default状态;c. 向新插入的设备发送设置地址请求,用来设置设备地址;d. 获取usb设备的设备描述符;e.根据usb设备的配置个数,获取对应usb设备配置描述符;
f. 选择e获取的配置描述符,选择合适 的usb配置,对usb设备进行配置;
对于usb device 而言,它不会主动的去和host进行数据传输,它都是处于被动的位置,它只是对host请求做出响应,请求都是由host发起。
由图2可以看到usb设备侧对host的请求都是通过中断进行触发的, device controller中断是在控制器初始化过程中申请的,中断处理函数为s3c_hsotg_irq,对于host的请求都是从这个函数开始。
static irqreturn_t s3c_hsotg_irq(int irq, void *pw)
{
struct s3c_hsotg *hsotg = pw;
int retry_count = 8;
u32 gintsts;
u32 gintmsk;
irq_retry:
gintsts = readl(hsotg->regs + S3C_GINTSTS);
gintmsk = readl(hsotg->regs + S3C_GINTMSK);
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: %08x %08x (%08x) retry %d\n",
__func__, gintsts, gintsts & gintmsk, gintmsk, retry_count);
gintsts &= gintmsk;
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_OTGInt) {
u32 otgint = readl(hsotg->regs + S3C_GOTGINT);
dev_info(hsotg->dev, "OTGInt: %08x\n", otgint);
writel(otgint, hsotg->regs + S3C_GOTGINT);
}
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_DisconnInt) {
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: DisconnInt\n", __func__);
writel(S3C_GINTSTS_DisconnInt, hsotg->regs + S3C_GINTSTS);
s3c_hsotg_disconnect_irq(hsotg);
}
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_SessReqInt) {
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: SessReqInt\n", __func__);
writel(S3C_GINTSTS_SessReqInt, hsotg->regs + S3C_GINTSTS);
}
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_EnumDone) {
writel(S3C_GINTSTS_EnumDone, hsotg->regs + S3C_GINTSTS);
s3c_hsotg_irq_enumdone(hsotg);
}
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_ConIDStsChng) {
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "ConIDStsChg (DSTS=0x%08x, GOTCTL=%08x)\n",
readl(hsotg->regs + S3C_DSTS),
readl(hsotg->regs + S3C_GOTGCTL));
writel(S3C_GINTSTS_ConIDStsChng, hsotg->regs + S3C_GINTSTS);
}
if (gintsts & (S3C_GINTSTS_OEPInt | S3C_GINTSTS_IEPInt)) {
u32 daint = readl(hsotg->regs + S3C_DAINT);
u32 daint_out = daint >> S3C_DAINT_OutEP_SHIFT;
u32 daint_in = daint & ~(daint_out << S3C_DAINT_OutEP_SHIFT);
int ep;
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: daint=%08x\n", __func__, daint);
for (ep = 0; ep < 15 && daint_out; ep++, daint_out >>= 1) {
if (daint_out & 1)
s3c_hsotg_epint(hsotg, ep, 0);
}
for (ep = 0; ep < 15 && daint_in; ep++, daint_in >>= 1) {
if (daint_in & 1)
s3c_hsotg_epint(hsotg, ep, 1);
}
}
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_USBRst) {
dev_info(hsotg->dev, "%s: USBRst\n", __func__);
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "GNPTXSTS=%08x\n",
readl(hsotg->regs + S3C_GNPTXSTS));
writel(S3C_GINTSTS_USBRst, hsotg->regs + S3C_GINTSTS);
kill_all_requests(hsotg, &hsotg->eps[0], -ECONNRESET, true);
/* it seems after a reset we can end up with a situation
* where the TXFIFO still has data in it... the docs
* suggest resetting all the fifos, so use the init_fifo
* code to relayout and flush the fifos.
*/
s3c_hsotg_init_fifo(hsotg);
s3c_hsotg_enqueue_setup(hsotg);
}
/* check both FIFOs */
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_NPTxFEmp) {
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "NPTxFEmp\n");
/* Disable the interrupt to stop it happening again
* unless one of these endpoint routines decides that
* it needs re-enabling */
s3c_hsotg_disable_gsint(hsotg, S3C_GINTSTS_NPTxFEmp);
s3c_hsotg_irq_fifoempty(hsotg, false);
}
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_PTxFEmp) {
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "PTxFEmp\n");
/* See note in S3C_GINTSTS_NPTxFEmp */
s3c_hsotg_disable_gsint(hsotg, S3C_GINTSTS_PTxFEmp);
s3c_hsotg_irq_fifoempty(hsotg, true);
}
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_RxFLvl) {
/* note, since GINTSTS_RxFLvl doubles as FIFO-not-empty,
* we need to retry s3c_hsotg_handle_rx if this is still
* set. */
s3c_hsotg_handle_rx(hsotg);
}
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_ModeMis) {
dev_warn(hsotg->dev, "warning, mode mismatch triggered\n");
writel(S3C_GINTSTS_ModeMis, hsotg->regs + S3C_GINTSTS);
}
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_USBSusp) {
dev_info(hsotg->dev, "S3C_GINTSTS_USBSusp\n");
writel(S3C_GINTSTS_USBSusp, hsotg->regs + S3C_GINTSTS);
call_gadget(hsotg, suspend);
}
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_WkUpInt) {
dev_info(hsotg->dev, "S3C_GINTSTS_WkUpIn\n");
writel(S3C_GINTSTS_WkUpInt, hsotg->regs + S3C_GINTSTS);
call_gadget(hsotg, resume);
}
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_ErlySusp) {
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "S3C_GINTSTS_ErlySusp\n");
writel(S3C_GINTSTS_ErlySusp, hsotg->regs + S3C_GINTSTS);
}
/* these next two seem to crop-up occasionally causing the core
* to shutdown the USB transfer, so try clearing them and logging
* the occurrence. */
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_GOUTNakEff) {
dev_info(hsotg->dev, "GOUTNakEff triggered\n");
writel(S3C_DCTL_CGOUTNak, hsotg->regs + S3C_DCTL);
s3c_hsotg_dump(hsotg);
}
if (gintsts & S3C_GINTSTS_GINNakEff) {
dev_info(hsotg->dev, "GINNakEff triggered\n");
writel(S3C_DCTL_CGNPInNAK, hsotg->regs + S3C_DCTL);
s3c_hsotg_dump(hsotg);
}
/* if we've had fifo events, we should try and go around the
* loop again to see if there's any point in returning yet. */
if (gintsts & IRQ_RETRY_MASK && --retry_count > 0)
goto irq_retry;
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
s3c_hsotg_irq通过读取中断状态寄存器来确定发生什么中断,再通过中断使能寄存器来确定那些中断那是中断是合法的,然后清除中断的状态位,重新使能中断,最后根据不同中断源进行不同处理。
在这里有两个类型中断最为重要,端口中断和接收中断,如果发生了端口中断,则需要进一步去读取端口中断状态寄存器,来确定产生中断的端口及产生中断原因;如果产生了接收中断,则去FIFO里读取数据,如果当前帧接收完成,则会调用注册request时确定的回调函数通知request请求者;
51-68行,产生了端口中断,先去设备端口中断寄存器里读取产生中断端口,设备端口中断寄存器是一个32位寄存器,高16位对应out的16个端口,bit16对应out endpoint0 ,bit31对应out endpoint 15,而低16位对应in的16个端口,bit0对应in endpoint 0,bit15对应in endpoint15. 在确定产生中断的端口后,调用s3c_hsotg_epint()分别对out和in中产生中断的各端口进行处理。
static void s3c_hsotg_epint(struct s3c_hsotg *hsotg, unsigned int idx,
int dir_in)
{
struct s3c_hsotg_ep *hs_ep = &hsotg->eps[idx];
u32 epint_reg = dir_in ? DIEPINT(idx) : DOEPINT(idx);
u32 epctl_reg = dir_in ? DIEPCTL(idx) : DOEPCTL(idx);
u32 epsiz_reg = dir_in ? DIEPTSIZ(idx) : DOEPTSIZ(idx);
u32 ints;
ints = readl(hsotg->regs + epint_reg);
/* Clear endpoint interrupts */
writel(ints, hsotg->regs + epint_reg);
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: ep%d(%s) DxEPINT=0x%08x\n",
__func__, idx, dir_in ? "in" : "out", ints);
if (ints & DxEPINT_XferCompl) {
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev,
"%s: XferCompl: DxEPCTL=0x%08x, DxEPTSIZ=%08x\n",
__func__, readl(hsotg->regs + epctl_reg),
readl(hsotg->regs + epsiz_reg));
/*
* we get OutDone from the FIFO, so we only need to look
* at completing IN requests here
*/
if (dir_in) {
s3c_hsotg_complete_in(hsotg, hs_ep);
if (idx == 0 && !hs_ep->req)
s3c_hsotg_enqueue_setup(hsotg);
} else if (using_dma(hsotg)) {
/*
* We're using DMA, we need to fire an OutDone here
* as we ignore the RXFIFO.
*/
s3c_hsotg_handle_outdone(hsotg, idx, false);
}
}
if (ints & DxEPINT_EPDisbld) {
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: EPDisbld\n", __func__);
if (dir_in) {
int epctl = readl(hsotg->regs + epctl_reg);
s3c_hsotg_txfifo_flush(hsotg, idx);
if ((epctl & DxEPCTL_Stall) &&
(epctl & DxEPCTL_EPType_Bulk)) {
int dctl = readl(hsotg->regs + DCTL);
dctl |= DCTL_CGNPInNAK;
writel(dctl, hsotg->regs + DCTL);
}
}
}
if (ints & DxEPINT_AHBErr)
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: AHBErr\n", __func__);
if (ints & DxEPINT_Setup) { /* Setup or Timeout */
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: Setup/Timeout\n", __func__);
if (using_dma(hsotg) && idx == 0) {
/*
* this is the notification we've received a
* setup packet. In non-DMA mode we'd get this
* from the RXFIFO, instead we need to process
* the setup here.
*/
if (dir_in)
WARN_ON_ONCE(1);
else
s3c_hsotg_handle_outdone(hsotg, 0, true);
}
}
if (ints & DxEPINT_Back2BackSetup)
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: B2BSetup/INEPNakEff\n", __func__);
if (dir_in) {
/* not sure if this is important, but we'll clear it anyway */
if (ints & DIEPMSK_INTknTXFEmpMsk) {
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: ep%d: INTknTXFEmpMsk\n",
__func__, idx);
}
/* this probably means something bad is happening */
if (ints & DIEPMSK_INTknEPMisMsk) {
dev_warn(hsotg->dev, "%s: ep%d: INTknEP\n",
__func__, idx);
}
/* FIFO has space or is empty (see GAHBCFG) */
if (hsotg->dedicated_fifos &&
ints & DIEPMSK_TxFIFOEmpty) {
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: ep%d: TxFIFOEmpty\n",
__func__, idx);
if (!using_dma(hsotg))
s3c_hsotg_trytx(hsotg, hs_ep);
}
}
}s3c_hsotg_epint会根据产生中断的不同方向和中断类型做出不同处理。
18-41行,表示端口产生了传输完成中断,它即可对应输入in类型,也可以对应输出out类型。如里是输入类型传输完成中断,即完成device->host传输,则会调用s3c_hsotg_complete_in对发送长度等信息进行统计,如需要发送0长数据做为发送结束,则向host传输0长度数据帧,如已发送数据长度,少于期望长度则继续开始发送请求,否则调用request的回调函数通知上层;对于out类型传输,即对应接收中断,usb设备会专门产生接收中断,它不在这里处理。
64-80表示,表示端口产生setup传输完成或超时中断。
回到s3c_hsotg_irq 的112-118行,这里表示RXFIFO非空,有数据需要读取,通过s3c_hsotg_handle_rx去处理。
static void s3c_hsotg_handle_rx(struct s3c_hsotg *hsotg)
{
u32 grxstsr = readl(hsotg->regs + S3C_GRXSTSP);
u32 epnum, status, size;
WARN_ON(using_dma(hsotg));
epnum = grxstsr & S3C_GRXSTS_EPNum_MASK;
status = grxstsr & S3C_GRXSTS_PktSts_MASK;
size = grxstsr & S3C_GRXSTS_ByteCnt_MASK;
size >>= S3C_GRXSTS_ByteCnt_SHIFT;
if (1)
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: GRXSTSP=0x%08x (%d@%d)\n",
__func__, grxstsr, size, epnum);
#define __status(x) ((x) >> S3C_GRXSTS_PktSts_SHIFT)
switch (status >> S3C_GRXSTS_PktSts_SHIFT) {
case __status(S3C_GRXSTS_PktSts_GlobalOutNAK):
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "GlobalOutNAK\n");
break;
case __status(S3C_GRXSTS_PktSts_OutDone):
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "OutDone (Frame=0x%08x)\n",
s3c_hsotg_read_frameno(hsotg));
if (!using_dma(hsotg))
s3c_hsotg_handle_outdone(hsotg, epnum, false);
break;
case __status(S3C_GRXSTS_PktSts_SetupDone):
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev,
"SetupDone (Frame=0x%08x, DOPEPCTL=0x%08x)\n",
s3c_hsotg_read_frameno(hsotg),
readl(hsotg->regs + S3C_DOEPCTL(0)));
s3c_hsotg_handle_outdone(hsotg, epnum, true);
break;
case __status(S3C_GRXSTS_PktSts_OutRX):
s3c_hsotg_rx_data(hsotg, epnum, size);
break;
case __status(S3C_GRXSTS_PktSts_SetupRX):
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev,
"SetupRX (Frame=0x%08x, DOPEPCTL=0x%08x)\n",
s3c_hsotg_read_frameno(hsotg),
readl(hsotg->regs + S3C_DOEPCTL(0)));
s3c_hsotg_rx_data(hsotg, epnum, size);
break;
default:
dev_warn(hsotg->dev, "%s: unknown status %08x\n",
__func__, grxstsr);
s3c_hsotg_dump(hsotg);
break;
}
}当RXFIFO中数据不为空时,表示有接收到数据,需要进行处理,s3c_hsotg_handle_rx,它会先确定产生中断的endpoint及数据包状态,然后再根据不同的状态做处不同处理。
08-18行,用来确定产生中断的endpoint端口号和接收到数据长度及数据包状态,共有5种数据包状态:OUT NAK, 收到OUT数据包,OUT数据包传输完成(设备侧接收完成),SETUP包传输完成,收到SETUP数据包;
21-23行,out nak中断,表示接收者不能接收数据;
不管是正常数据包还是SETUP包,收到数据都是通过s3c_hsotg_rx_data从FIFO读取数据,而如果当前的数据帧接收完成,则会通过s3c_hsotg_handle_outdone函数调用s3c_hsotg_complete_request来通知上层;
static void s3c_hsotg_complete_request(struct s3c_hsotg *hsotg,
struct s3c_hsotg_ep *hs_ep,
struct s3c_hsotg_req *hs_req,
int result)
{
bool restart;
if (!hs_req) {
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: nothing to complete?\n", __func__);
return;
}
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "complete: ep %p %s, req %p, %d => %p\n",
hs_ep, hs_ep->ep.name, hs_req, result, hs_req->req.complete);
/*
* only replace the status if we've not already set an error
* from a previous transaction
*/
if (hs_req->req.status == -EINPROGRESS)
hs_req->req.status = result;
hs_ep->req = NULL;
list_del_init(&hs_req->queue);
if (using_dma(hsotg))
s3c_hsotg_unmap_dma(hsotg, hs_ep, hs_req);
/*
* call the complete request with the locks off, just in case the
* request tries to queue more work for this endpoint.
*/
if (hs_req->req.complete) {
spin_unlock(&hsotg->lock);
hs_req->req.complete(&hs_ep->ep, &hs_req->req);
spin_lock(&hsotg->lock);
}
/*
* Look to see if there is anything else to do. Note, the completion
* of the previous request may have caused a new request to be started
* so be careful when doing this.
*/
if (!hs_ep->req && result >= 0) {
restart = !list_empty(&hs_ep->queue);
if (restart) {
hs_req = get_ep_head(hs_ep);
s3c_hsotg_start_req(hsotg, hs_ep, hs_req, false);
}
}
}
s3c_hsotg_complete_request首先会把req本身从endpoint的request队列里删除,然后再调用request的回调函数req->complete通知request请求者,在这里对应的回调函数为s3c_hsotg_complete_setup,最后会根据result的值来确定是否继续开始当前endpoint的其它request;
static void s3c_hsotg_complete_setup(struct usb_ep *ep,
struct usb_request *req)
{
struct s3c_hsotg_ep *hs_ep = our_ep(ep);
struct s3c_hsotg *hsotg = hs_ep->parent;
if (req->status < 0) {
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "%s: failed %d\n", __func__, req->status);
return;
}
if (req->actual == 0)
s3c_hsotg_enqueue_setup(hsotg);
else
s3c_hsotg_process_control(hsotg, req->buf);
}s3c_hsotg_complete_setup它会调用s3c_hsotg_process_control对来自host的请求做出相应的处理;
static void s3c_hsotg_process_control(struct s3c_hsotg *hsotg,
struct usb_ctrlrequest *ctrl)
{
struct s3c_hsotg_ep *ep0 = &hsotg->eps[0];
int ret = 0;
u32 dcfg;
ep0->sent_zlp = 0;
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "ctrl Req=%02x, Type=%02x, V=%04x, L=%04x\n",
ctrl->bRequest, ctrl->bRequestType,
ctrl->wValue, ctrl->wLength);
/*
* record the direction of the request, for later use when enquing
* packets onto EP0.
*/
ep0->dir_in = (ctrl->bRequestType & USB_DIR_IN) ? 1 : 0;
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "ctrl: dir_in=%d\n", ep0->dir_in);
/*
* if we've no data with this request, then the last part of the
* transaction is going to implicitly be IN.
*/
if (ctrl->wLength == 0)
ep0->dir_in = 1;
if ((ctrl->bRequestType & USB_TYPE_MASK) == USB_TYPE_STANDARD) {
switch (ctrl->bRequest) {
case USB_REQ_SET_ADDRESS:
dcfg = readl(hsotg->regs + DCFG);
dcfg &= ~DCFG_DevAddr_MASK;
dcfg |= ctrl->wValue << DCFG_DevAddr_SHIFT;
writel(dcfg, hsotg->regs + DCFG);
dev_info(hsotg->dev, "new address %d\n", ctrl->wValue);
ret = s3c_hsotg_send_reply(hsotg, ep0, NULL, 0);
return;
case USB_REQ_GET_STATUS:
ret = s3c_hsotg_process_req_status(hsotg, ctrl);
break;
case USB_REQ_CLEAR_FEATURE:
case USB_REQ_SET_FEATURE:
ret = s3c_hsotg_process_req_feature(hsotg, ctrl);
break;
}
}
/* as a fallback, try delivering it to the driver to deal with */
if (ret == 0 && hsotg->driver) {
ret = hsotg->driver->setup(&hsotg->gadget, ctrl);
if (ret < 0)
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "driver->setup() ret %d\n", ret);
}
/*
* the request is either unhandlable, or is not formatted correctly
* so respond with a STALL for the status stage to indicate failure.
*/
if (ret < 0) {
u32 reg;
u32 ctrl;
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev, "ep0 stall (dir=%d)\n", ep0->dir_in);
reg = (ep0->dir_in) ? DIEPCTL0 : DOEPCTL0;
/*
* DxEPCTL_Stall will be cleared by EP once it has
* taken effect, so no need to clear later.
*/
ctrl = readl(hsotg->regs + reg);
ctrl |= DxEPCTL_Stall;
ctrl |= DxEPCTL_CNAK;
writel(ctrl, hsotg->regs + reg);
dev_dbg(hsotg->dev,
"written DxEPCTL=0x%08x to %08x (DxEPCTL=0x%08x)\n",
ctrl, reg, readl(hsotg->regs + reg));
/*
* don't believe we need to anything more to get the EP
* to reply with a STALL packet
*/
}
}s3c_hsotg_process_control实现了一些和低层usb device controller相关的操作,如枚举时的设置地址请求,就是从这里开始的。
31-41行,对应USB枚举过程中的设备地址请求,在收到HOST的设备地址请求后,根据地址值会配置相应的地址寄存器,并通过s3c_hsotg_send_reply向HOST回复一个0长度的数据帧表示控制传输中的status传输。
42-44行,表示host请求获取设备,接口和端口状态,在收到请求后通过s3c_hsotg_send_reply回复host请求的状态;
47-49行,表示设置或清除设备的DEVICE_REMOTE_WAKEUP,端口的ENDPOINT_HALT等特征,这里实现了端口endpoint_halt设置和清除功能,在设置或清除后,向HOST回复0长度的数据帧。
55-59行,如果host发送了获取设备描述符,设置配置等和usb功能相关的请求,这些请求是和设备的功能相关,但和具体硬件无关,它一般在gadget driver里实现,这里会调用gadget driver 中的composite_setup函数,它实现了除和硬件相关之外的其它usb请求。
static int
composite_setup(struct usb_gadget *gadget, const struct usb_ctrlrequest *ctrl)
{
struct usb_composite_dev *cdev = get_gadget_data(gadget);
struct usb_request *req = cdev->req;
int value = -EOPNOTSUPP;
int status = 0;
u16 w_index = le16_to_cpu(ctrl->wIndex);
u8 intf = w_index & 0xFF;
u16 w_value = le16_to_cpu(ctrl->wValue);
u16 w_length = le16_to_cpu(ctrl->wLength);
struct usb_function *f = NULL;
u8 endp;
/* partial re-init of the response message; the function or the
* gadget might need to intercept e.g. a control-OUT completion
* when we delegate to it.
*/
req->zero = 0;
req->complete = composite_setup_complete;
req->length = 0;
gadget->ep0->driver_data = cdev;
switch (ctrl->bRequest) {
/* we handle all standard USB descriptors */
case USB_REQ_GET_DESCRIPTOR:
if (ctrl->bRequestType != USB_DIR_IN)
goto unknown;
switch (w_value >> 8) {
case USB_DT_DEVICE:
cdev->desc.bNumConfigurations =
count_configs(cdev, USB_DT_DEVICE);
cdev->desc.bMaxPacketSize0 =
cdev->gadget->ep0->maxpacket;
if (gadget_is_superspeed(gadget)) {
if (gadget->speed >= USB_SPEED_SUPER) {
cdev->desc.bcdUSB = cpu_to_le16(0x0300);
cdev->desc.bMaxPacketSize0 = 9;
} else {
cdev->desc.bcdUSB = cpu_to_le16(0x0210);
}
}
value = min(w_length, (u16) sizeof cdev->desc);
memcpy(req->buf, &cdev->desc, value);
break;
case USB_DT_DEVICE_QUALIFIER:
if (!gadget_is_dualspeed(gadget) ||
gadget->speed >= USB_SPEED_SUPER)
break;
device_qual(cdev);
value = min_t(int, w_length,
sizeof(struct usb_qualifier_descriptor));
break;
case USB_DT_OTHER_SPEED_CONFIG:
if (!gadget_is_dualspeed(gadget) ||
gadget->speed >= USB_SPEED_SUPER)
break;
/* FALLTHROUGH */
case USB_DT_CONFIG:
value = config_desc(cdev, w_value);
if (value >= 0)
value = min(w_length, (u16) value);
break;
case USB_DT_STRING:
value = get_string(cdev, req->buf,
w_index, w_value & 0xff);
if (value >= 0)
value = min(w_length, (u16) value);
break;
case USB_DT_BOS:
if (gadget_is_superspeed(gadget)) {
value = bos_desc(cdev);
value = min(w_length, (u16) value);
}
break;
}
break;
/* any number of configs can work */
case USB_REQ_SET_CONFIGURATION:
if (ctrl->bRequestType != 0)
goto unknown;
if (gadget_is_otg(gadget)) {
if (gadget->a_hnp_support)
DBG(cdev, "HNP available\n");
else if (gadget->a_alt_hnp_support)
DBG(cdev, "HNP on another port\n");
else
VDBG(cdev, "HNP inactive\n");
}
spin_lock(&cdev->lock);
value = set_config(cdev, ctrl, w_value);
spin_unlock(&cdev->lock);
break;
case USB_REQ_GET_CONFIGURATION:
if (ctrl->bRequestType != USB_DIR_IN)
goto unknown;
if (cdev->config)
*(u8 *)req->buf = cdev->config->bConfigurationValue;
else
*(u8 *)req->buf = 0;
value = min(w_length, (u16) 1);
break;
/* function drivers must handle get/set altsetting; if there's
* no get() method, we know only altsetting zero works.
*/
case USB_REQ_SET_INTERFACE:
if (ctrl->bRequestType != USB_RECIP_INTERFACE)
goto unknown;
if (!cdev->config || intf >= MAX_CONFIG_INTERFACES)
break;
f = cdev->config->interface[intf];
if (!f)
break;
if (w_value && !f->set_alt)
break;
value = f->set_alt(f, w_index, w_value);
if (value == USB_GADGET_DELAYED_STATUS) {
DBG(cdev,
"%s: interface %d (%s) requested delayed status\n",
__func__, intf, f->name);
cdev->delayed_status++;
DBG(cdev, "delayed_status count %d\n",
cdev->delayed_status);
}
break;
case USB_REQ_GET_INTERFACE:
if (ctrl->bRequestType != (USB_DIR_IN|USB_RECIP_INTERFACE))
goto unknown;
if (!cdev->config || intf >= MAX_CONFIG_INTERFACES)
break;
f = cdev->config->interface[intf];
if (!f)
break;
/* lots of interfaces only need altsetting zero... */
value = f->get_alt ? f->get_alt(f, w_index) : 0;
if (value < 0)
break;
*((u8 *)req->buf) = value;
value = min(w_length, (u16) 1);
break;
/*
* USB 3.0 additions:
* Function driver should handle get_status request. If such cb
* wasn't supplied we respond with default value = 0
* Note: function driver should supply such cb only for the first
* interface of the function
*/
case USB_REQ_GET_STATUS:
if (!gadget_is_superspeed(gadget))
goto unknown;
if (ctrl->bRequestType != (USB_DIR_IN | USB_RECIP_INTERFACE))
goto unknown;
value = 2; /* This is the length of the get_status reply */
put_unaligned_le16(0, req->buf);
if (!cdev->config || intf >= MAX_CONFIG_INTERFACES)
break;
f = cdev->config->interface[intf];
if (!f)
break;
status = f->get_status ? f->get_status(f) : 0;
if (status < 0)
break;
put_unaligned_le16(status & 0x0000ffff, req->buf);
break;
/*
* Function drivers should handle SetFeature/ClearFeature
* (FUNCTION_SUSPEND) request. function_suspend cb should be supplied
* only for the first interface of the function
*/
case USB_REQ_CLEAR_FEATURE:
case USB_REQ_SET_FEATURE:
if (!gadget_is_superspeed(gadget))
goto unknown;
if (ctrl->bRequestType != (USB_DIR_OUT | USB_RECIP_INTERFACE))
goto unknown;
switch (w_value) {
case USB_INTRF_FUNC_SUSPEND:
if (!cdev->config || intf >= MAX_CONFIG_INTERFACES)
break;
f = cdev->config->interface[intf];
if (!f)
break;
value = 0;
if (f->func_suspend)
value = f->func_suspend(f, w_index >> 8);
if (value < 0) {
ERROR(cdev,
"func_suspend() returned error %d\n",
value);
value = 0;
}
break;
}
break;
default:
unknown:
VDBG(cdev,
"non-core control req%02x.%02x v%04x i%04x l%d\n",
ctrl->bRequestType, ctrl->bRequest,
w_value, w_index, w_length);
/* functions always handle their interfaces and endpoints...
* punt other recipients (other, WUSB, ...) to the current
* configuration code.
*
* REVISIT it could make sense to let the composite device
* take such requests too, if that's ever needed: to work
* in config 0, etc.
*/
switch (ctrl->bRequestType & USB_RECIP_MASK) {
case USB_RECIP_INTERFACE:
if (!cdev->config || intf >= MAX_CONFIG_INTERFACES)
break;
f = cdev->config->interface[intf];
break;
case USB_RECIP_ENDPOINT:
endp = ((w_index & 0x80) >> 3) | (w_index & 0x0f);
list_for_each_entry(f, &cdev->config->functions, list) {
if (test_bit(endp, f->endpoints))
break;
}
if (&f->list == &cdev->config->functions)
f = NULL;
break;
}
if (f && f->setup)
value = f->setup(f, ctrl);
else {
struct usb_configuration *c;
c = cdev->config;
if (c && c->setup)
value = c->setup(c, ctrl);
}
goto done;
}
/* respond with data transfer before status phase? */
if (value >= 0 && value != USB_GADGET_DELAYED_STATUS) {
req->length = value;
req->zero = value < w_length;
value = usb_ep_queue(gadget->ep0, req, GFP_ATOMIC);
if (value < 0) {
DBG(cdev, "ep_queue --> %d\n", value);
req->status = 0;
composite_setup_complete(gadget->ep0, req);
}
} else if (value == USB_GADGET_DELAYED_STATUS && w_length != 0) {
WARN(cdev,
"%s: Delayed status not supported for w_length != 0",
__func__);
}
done:
/* device either stalls (value < 0) or reports success */
return value;
}
composite_setup会根据host的不同请求做出不同处理,这里主要包含获取设备,配置及字符串描述符请求、设置和获取usb配置请求、设备和获取usb接口请求、获取usb状态请求、设置和清除usb feature请求。
32-48表示获取设备描述符请求,将保存于composite_dev里的device desc拷贝到用来存放request发送数据的buf里。
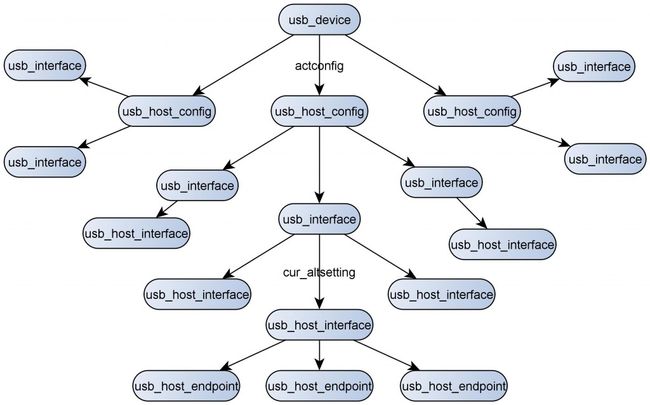
57-61表示用来获取配置描述符请求,一个USB设备它有可能有多个配置,在枚举的时候,HOST端会遍历每个配置,获取相应的配置描述符。对于获取配置描述符这个请求,device端不仅仅会将配置描述符拷贝到用于存放request数据的buf里, 还会把这个配置里的接口,再对应接口里的端口描述符一起拷贝到有buf里,所以在host发送获取配置描述符后,它就得到了这个配置下面的接口和端口信息,如果它是OTG设备,它还会包含OTG的信息。
67-72,它用来获取USB设备的字符串描述符。
83-97表示收到设置配置请求,它会调用set_config函数去设置USB配置。
static int set_config(struct usb_composite_dev *cdev,
const struct usb_ctrlrequest *ctrl, unsigned number)
{
struct usb_gadget *gadget = cdev->gadget;
struct usb_configuration *c = NULL;
int result = -EINVAL;
unsigned power = gadget_is_otg(gadget) ? 8 : 100;
int tmp;
if (number) {
list_for_each_entry(c, &cdev->configs, list) {
if (c->bConfigurationValue == number) {
/*
* We disable the FDs of the previous
* configuration only if the new configuration
* is a valid one
*/
if (cdev->config)
reset_config(cdev);
result = 0;
break;
}
}
if (result < 0)
goto done;
} else { /* Zero configuration value - need to reset the config */
if (cdev->config)
reset_config(cdev);
result = 0;
}
INFO(cdev, "%s speed config #%d: %s\n",
({ char *speed;
switch (gadget->speed) {
case USB_SPEED_LOW:
speed = "low";
break;
case USB_SPEED_FULL:
speed = "full";
break;
case USB_SPEED_HIGH:
speed = "high";
break;
case USB_SPEED_SUPER:
speed = "super";
break;
default:
speed = "?";
break;
} ; speed; }), number, c ? c->label : "unconfigured");
if (!c)
goto done;
cdev->config = c;
/* Initialize all interfaces by setting them to altsetting zero. */
for (tmp = 0; tmp < MAX_CONFIG_INTERFACES; tmp++) {
struct usb_function *f = c->interface[tmp];
struct usb_descriptor_header **descriptors;
if (!f)
break;
/*
* Record which endpoints are used by the function. This is used
* to dispatch control requests targeted at that endpoint to the
* function's setup callback instead of the current
* configuration's setup callback.
*/
switch (gadget->speed) {
case USB_SPEED_SUPER:
descriptors = f->ss_descriptors;
break;
case USB_SPEED_HIGH:
descriptors = f->hs_descriptors;
break;
default:
descriptors = f->descriptors;
}
for (; *descriptors; ++descriptors) {
struct usb_endpoint_descriptor *ep;
int addr;
if ((*descriptors)->bDescriptorType != USB_DT_ENDPOINT)
continue;
ep = (struct usb_endpoint_descriptor *)*descriptors;
addr = ((ep->bEndpointAddress & 0x80) >> 3)
| (ep->bEndpointAddress & 0x0f);
set_bit(addr, f->endpoints);
}
result = f->set_alt(f, tmp, 0);
if (result < 0) {
DBG(cdev, "interface %d (%s/%p) alt 0 --> %d\n",
tmp, f->name, f, result);
reset_config(cdev);
goto done;
}
if (result == USB_GADGET_DELAYED_STATUS) {
DBG(cdev,
"%s: interface %d (%s) requested delayed status\n",
__func__, tmp, f->name);
cdev->delayed_status++;
DBG(cdev, "delayed_status count %d\n",
cdev->delayed_status);
}
}
/* when we return, be sure our power usage is valid */
power = c->bMaxPower ? (2 * c->bMaxPower) : CONFIG_USB_GADGET_VBUS_DRAW;
done:
usb_gadget_vbus_draw(gadget, power);
if (result >= 0 && cdev->delayed_status)
result = USB_GADGET_DELAYED_STATUS;
return result;
}
对于一个复合型USB设备, 它的当前配置保存在cdev->config里,在设置设备的配置时,它会根据配置的值先将与配置值相对应的配置初始化,然后将所需的配置保存到cdev->config里,一个配置里包含多个接口,一个接口下包含多个接口设置,一个接口设置里包含多个端口,在把指定配置保存到cdev->config后,调用usb配置中的set_alt函数将接口下的接口设置设置成0,这里通过sourcesink_set_alt来说明,set_alt的具体工作。
static int sourcesink_set_alt(struct usb_function *f,
unsigned intf, unsigned alt)
{
struct f_sourcesink *ss = func_to_ss(f);
struct usb_composite_dev *cdev = f->config->cdev;
if (ss->in_ep->driver_data)
disable_source_sink(ss);
return enable_source_sink(cdev, ss, alt);
}
sourcesink_set_alt中有三个参数,一个是接口功能usb_function,
通过配置得到f_sourcesink和cdev ,然后判断端口中driver_data是不是已经赋值,如果已经赋值则把相应的端口disable,最后调用enable_source_sink函数;
static int
enable_source_sink(struct usb_composite_dev *cdev, struct f_sourcesink *ss)
{
int result = 0;
struct usb_ep *ep;
/* one endpoint writes (sources) zeroes IN (to the host) */
ep = ss->in_ep;
result = config_ep_by_speed(cdev->gadget, &(ss->function), ep);
if (result)
return result;
result = usb_ep_enable(ep);
if (result < 0)
return result;
ep->driver_data = ss;
result = source_sink_start_ep(ss, true);
if (result < 0) {
fail:
ep = ss->in_ep;
usb_ep_disable(ep);
ep->driver_data = NULL;
return result;
}
/* one endpoint reads (sinks) anything OUT (from the host) */
ep = ss->out_ep;
result = config_ep_by_speed(cdev->gadget, &(ss->function), ep);
if (result)
goto fail;
result = usb_ep_enable(ep);
if (result < 0)
goto fail;
ep->driver_data = ss;
result = source_sink_start_ep(ss, false);
if (result < 0) {
usb_ep_disable(ep);
ep->driver_data = NULL;
goto fail;
}
DBG(cdev, "%s enabled\n", ss->function.name);
return result;
}
usb接口功能usb_function数据结构中有专门用来保存不同速度情况下接口和端口描述符头指针数组,descriptors用来存放全速描述符头指针,hs_descriptors用来存放高速描述符头指针,ss_descriptors用来存放超速描述符头指针,虽然usb端口可以在不同速度下工作,但是对于一个gadget device它的速度是固定的, 所以对一个USB端口进行配置时要根据gadget的速度来确定端口,在10-13行中,enable_source_sink会根据gadget所支持的速度来完成usb_ep配置。
int config_ep_by_speed(struct usb_gadget *g,
struct usb_function *f,
struct usb_ep *_ep)
{
struct usb_endpoint_descriptor *chosen_desc = NULL;
struct usb_descriptor_header **speed_desc = NULL;
struct usb_ss_ep_comp_descriptor *comp_desc = NULL;
int want_comp_desc = 0;
struct usb_descriptor_header **d_spd; /* cursor for speed desc */
if (!g || !f || !_ep)
return -EIO;
/* select desired speed */
switch (g->speed) {
case USB_SPEED_SUPER:
if (gadget_is_superspeed(g)) {
speed_desc = f->ss_descriptors;
want_comp_desc = 1;
break;
}
/* else: Fall trough */
case USB_SPEED_HIGH:
if (gadget_is_dualspeed(g)) {
speed_desc = f->hs_descriptors;
break;
}
/* else: fall through */
default:
speed_desc = f->descriptors;
}
/* find descriptors */
for_each_ep_desc(speed_desc, d_spd) {
chosen_desc = (struct usb_endpoint_descriptor *)*d_spd;
if (chosen_desc->bEndpointAddress == _ep->address)
goto ep_found;
}
return -EIO;
ep_found:
/* commit results */
_ep->maxpacket = le16_to_cpu(chosen_desc->wMaxPacketSize);
_ep->desc = chosen_desc;
_ep->comp_desc = NULL;
_ep->maxburst = 0;
_ep->mult = 0;
if (!want_comp_desc)
return 0;
/*
* Companion descriptor should follow EP descriptor
* USB 3.0 spec, #9.6.7
*/
comp_desc = (struct usb_ss_ep_comp_descriptor *)*(++d_spd);
if (!comp_desc ||
(comp_desc->bDescriptorType != USB_DT_SS_ENDPOINT_COMP))
return -EIO;
_ep->comp_desc = comp_desc;
if (g->speed == USB_SPEED_SUPER) {
switch (usb_endpoint_type(_ep->desc)) {
case USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_BULK:
case USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_INT:
_ep->maxburst = comp_desc->bMaxBurst;
break;
case USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_ISOC:
/* mult: bits 1:0 of bmAttributes */
_ep->mult = comp_desc->bmAttributes & 0x3;
break;
default:
/* Do nothing for control endpoints */
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
17-33行,根据gadget的速度来获取端口描述符头指针,并保存在chose_desc里;
35-39行,从端口描述符头指针里获取端口描述符,并于给定的ep的地址比较,如果相同,表示找到相应端口,找到端口后补全usb_ep结构中的最大传输长度和端口描述符,如果是超速USB设备,则还需要补全用于描述高速端口的描述符。
由config_ep_by_speed找到相匹配的端口后,通过usb_ep_enable使能端口,usb_ep_enable里调用了和硬件相关的usb_ep_ops中的enable函数,这里是s3c_hsotg_ep_enable,接着赋值ep的driver_data.
在使能端口后,就要为这个端口申请用于request的资源,回调函数,并将request加入到端口的请求队列里,这个工作由38行的source_sink_start_ep完成。
static int source_sink_start_ep(struct f_sourcesink *ss, bool is_in)
{
struct usb_ep *ep;
struct usb_request *req;
int status;
ep = is_in ? ss->in_ep : ss->out_ep;
req = alloc_ep_req(ep);
if (!req)
return -ENOMEM;
req->complete = source_sink_complete;
if (is_in)
reinit_write_data(ep, req);
else
memset(req->buf, 0x55, req->length);
status = usb_ep_queue(ep, req, GFP_ATOMIC);
if (status) {
struct usb_composite_dev *cdev;
cdev = ss->function.config->cdev;
ERROR(cdev, "start %s %s --> %d\n",
is_in ? "IN" : "OUT",
ep->name, status);
free_ep_req(ep, req);
}
return status;
}08行,调用alloc_ep_req为endpoint申请request请求数据结构,并为request分配用于存放传输数据的buf。
12行,将request的回调函数赋值给req->complete,当这个端口传输完成后通过这个回调函数来通知上层,实现source_sink功能;
13行,如果是in类型传输,即从device->host则根据pattern来初始化传输的数据。
18行,将当前端口的request加入到端口的request队列中,这个功能通过调用与硬件相关的queue函数实现,这里是调用s3c_hsotg_ep_queue。
对于source_sink配置,它有两个端口,即in和out,一个用于接收来自HOST的数据,一个用于向host发送数据,所以配置完in端口后,还需要配置out端口,到这里为止就算设置完成 配置了。
由此可见,对于来自host的设置配置请求,对于复合型的设备,它将配置值对应的配置保存在复合型结构cdev的config中,用来表示当前配置,再将这个配置下的接口和端口使能,并为各个端口申请请求资源,将其加入到端口的请求队列中,等待事件处发。
讲完了usb设备的设置配置请求后,回到composite_bind。
98-106行,获取usb当前配置值,把它保存在用于存放request传输数据的buf里。
111-129行,配置当前配置接口设置请求,通过调用sourcesink_set_alt函数来为当前usb配置下由usb请求中中的index指定的接口配置由w_value指定的接口设置。
131-146,获取当前配置下某个接口的接口设置。
对于接下来的获取某个状态和设置、清除feature这里就不深入研究了。
其实到这里为止,USB的枚举已经算是完成了,与枚举有关的USB请求主要有设置USB地址,获取设备,配置描述符,然后是设置配置。