短信接收--短信的接收流程应用层
短信的接收流程应用层
1、源文件
这部分代码在packages/apps/Mms下,涉及的主要类:
com.android.mms.transaction.PrivilegedSmsReceiver com.android.mms.transaction.SmsReceiver com.android.mms.transaction.SmsReceiverService com.android.mms.transaction.MessagingNotification
2、图解
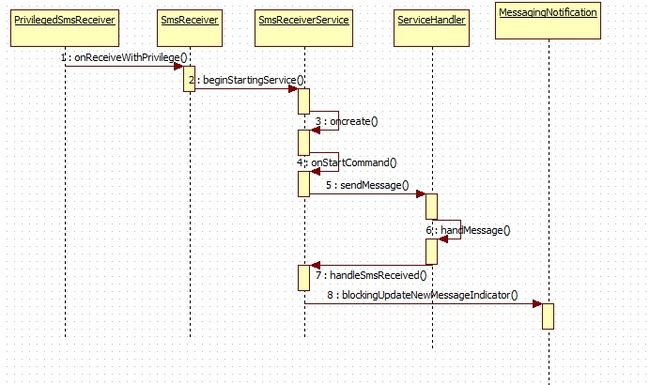
注意:SeviceHandler是SmsReceiverService的内部类,SmsReceiver是PrivlegedSmsReceiver的父类;
3、详细分析
3.1 PrivilegedSmsReceiver到SmsReceiverService
1)
PrivilegedSmsReceiver这个接收器从中间才能获取数据
PrivilegedSmsReceiver是一个广播接收器并且继承自SmsReceiver,在AndroidManifest.xml 中有如下声明:
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.provider.Telephony.SMS_RECEIVED" />
</intent-filter>android.provider.Telephony.SMS_RECEIVED该action在那被使用到了?如果大家有看过分析中间层的接收流程的童鞋就很清楚了,中间层处理接收到的短信的时侯最后会调用到SMSDispatcher的protected void dispatchPdus(byte[][] pdus) 方法,让我们回眸一下:
protected void dispatchPdus(byte[][] pdus) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intents.SMS_RECEIVED_ACTION);
intent.putExtra("pdus", pdus);
intent.putExtra("encoding", getEncoding());
intent.putExtra("sub_id", mPhone.getSubscription()); //Subscription information to be passed in an intent
dispatch(intent, "android.permission.RECEIVE_SMS");
}大家肯定会问dispatch又干了些什么了?
请看下面:
void dispatch(Intent intent, String permission) {
mWakeLock.acquire(WAKE_LOCK_TIMEOUT);
mContext.sendOrderedBroadcast(intent, permission, mResultReceiver,
this, Activity.RESULT_OK, null, null);
}看到这就不用我多说了吧,很显然是发送了一个叫做Intents.SMS_RECEIVED_ACTION的广播,那又有人刨根问底儿了,上面两个值一样吗?请看intent中对该变量的定义:
@SdkConstant(SdkConstantType.BROADCAST_INTENT_ACTION)
public static final String SMS_RECEIVED_ACTION =
"android.provider.Telephony.SMS_RECEIVED";
到这大家应该明白PrivilegedSmsReceiver会接收到中间层的广播,并且该广播很不一般它承载了短信的内容,它从中间层接过接力棒继续向上传递。
2)
PrivilegedSmsReceiver传递数据
PrivilegedSmsReceiver从中间层获取到短信的数据后会调用onReceiveWithPrivilege()方法,该方法定义在它的父类SmsReceiver中。该方法没有做太多的操作,仅仅是传递消息,一下是其核心代码:
protected void onReceiveWithPrivilege(Context context, Intent intent, boolean privileged) {
if (!privileged && (intent.getAction().equals(Intents.SMS_RECEIVED_ACTION)
|| intent.getAction().equals(Intents.SMS_CB_RECEIVED_ACTION))) {
return;
}
intent.setClass(context, SmsReceiverService.class);
intent.putExtra("result", getResultCode());
beginStartingService(context, intent);
}它将处理短信的任务交到SmsReceiverService的手中,SmsReceiverService才是真正干活的家伙。
3)SmsReceiverService处理
SmsReceiverService它是一个服务,当它开启的时候:首先是在onCreate中初始化,其中初始化最重要的工作就是实例化ServiceHandler对象,ServiceHandler该类是SmsReceiverService的一个内部类,继承自Handler,以下是它的定义代码:
private final class ServiceHandler extends Handler {
public ServiceHandler(Looper looper) {
super(looper);
}
/**
* Handle incoming transaction requests.
* The incoming requests are initiated by the MMSC Server or by the MMS Client itself.
*/
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
int serviceId = msg.arg1;
Intent intent = (Intent)msg.obj;
if (intent != null) {
String action = intent.getAction();
int error = intent.getIntExtra("errorCode", 0);
if (MESSAGE_SENT_ACTION.equals(intent.getAction())) {
handleSmsSent(intent, error);
} else if (SMS_RECEIVED_ACTION.equals(action)) {
handleSmsReceived(intent, error);
} else if (SMS_CB_RECEIVED_ACTION.equals(action)) {
handleCbSmsReceived(intent, error);
} else if (ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED.equals(action)) {
handleBootCompleted();
} else if (TelephonyIntents.ACTION_SERVICE_STATE_CHANGED.equals(action)) {
handleServiceStateChanged(intent);
} else if (ACTION_SEND_MESSAGE.endsWith(action)) {
handleSendMessage(intent);
}
}
// NOTE: We MUST not call stopSelf() directly, since we need to
// make sure the wake lock acquired by AlertReceiver is released.
SmsReceiver.finishStartingService(SmsReceiverService.this, serviceId);
}
}
走到这我们可以看出该对象的重要性,即是处理短信真正的苦力,我们继续看是怎么调用到这的。
onCreate走完请看 onStartCommand方法:
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
mResultCode = intent != null ? intent.getIntExtra("result", 0) : 0;
Message msg = mServiceHandler.obtainMessage();
msg.arg1 = startId;
msg.obj = intent;
mServiceHandler.sendMessage(msg);
return Service.START_NOT_STICKY;
}看到吗,到这它已经顺利脱手交给
ServiceHandler对象去异步处理。
4)ServiceHandler处理接收到的短信
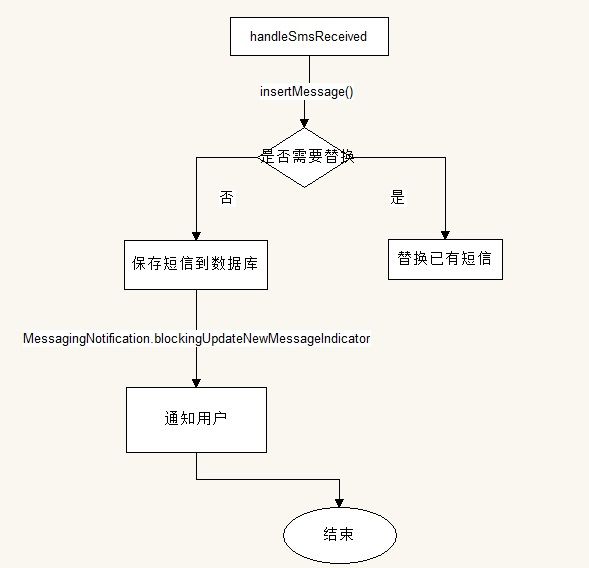
根据不同的action处理,由于这里是短信的接收SMS_RECEIVED_ACTION,所以调用 handleSmsReceived(intent, error)方法,该方法的处理逻辑如下所示:
说明在insertMessage方法时会判断当前是替换还是插入,对于替换短信,笔者不是很清楚在什么情况下会走这条路。blockingUpdateNewMessageIndicator方法会用notification提醒用户,并且在方法内会判断当前用户是否需要显示发送报告。
3.2 刷新会话列表
走到上面的代码,短信已经入库,但界面的刷新是如何实现的了?
1)会话列表的初始化
ConversationList继承自ListActivity,用于显示短信的会话列表,在该类的onStart方法里有调用了一个重要的方法startAsyncQuery()方法:
private void startAsyncQuery() {
try {
setTitle(getString(R.string.refreshing));
setProgressBarIndeterminateVisibility(true);
Conversation.startQueryForAll(mQueryHandler, THREAD_LIST_QUERY_TOKEN);
} catch (SQLiteException e) {
SqliteWrapper.checkSQLiteException(this, e);
}
}解析:
startQueryForAll方法定义:
public static void startQueryForAll(AsyncQueryHandler handler, int token) {
handler.cancelOperation(token);
handler.startQuery(token, null, sAllThreadsUri,
ALL_THREADS_PROJECTION, null, null, Conversations.DEFAULT_SORT_ORDER);
}
这里会使用mQueryHandler去查询数据库,查询完后会回调该对象的onQueryComplete方法,在该方法里填充了mListAdapter,使得会话列表得以显示到界面上。以下代码是其定义:
private final class ThreadListQueryHandler extends AsyncQueryHandler {
public ThreadListQueryHandler(ContentResolver contentResolver) {
super(contentResolver);
}
@Override
protected void onQueryComplete(int token, Object cookie, Cursor cursor) {
switch (token) {
case THREAD_LIST_QUERY_TOKEN:
mListAdapter.changeCursor(cursor);
setTitle(mTitle);
setProgressBarIndeterminateVisibility(false);
if (mNeedToMarkAsSeen) {
mNeedToMarkAsSeen = false;
Conversation.markAllConversationsAsSeen(getApplicationContext());
// Database will be update at this time in some conditions.
// Wait 1s and ensure update complete.
mQueryHandler.postDelayed(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
// Delete any obsolete threads. Obsolete threads are threads that aren't
// referenced by at least one message in the pdu or sms tables.
Conversation.asyncDeleteObsoleteThreads(mQueryHandler,
DELETE_OBSOLETE_THREADS_TOKEN);
}
}, 1000);
}
break;
default:
Log.e(TAG, "onQueryComplete called with unknown token " + token);
}
}
}这里为什么要特别提到该对象了,后面更新的操作与它有着密不可分的关系。
mListAdapter该对象是ConversationListAdapter的对象,该对象在ConversationList的oncreate方法里调用 initListAdapter()进行的初始化。 initListAdapter()对adapter进行初始化:
private void initListAdapter() {
mListAdapter = new ConversationListAdapter(this, null);
mListAdapter.setOnContentChangedListener(mContentChangedListener);
setListAdapter(mListAdapter);
getListView().setRecyclerListener(mListAdapter);
}mListAdapter.setOnContentChangedListener(mContentChangedListener);是当adapter的内容发生变化,会去执行监听器的onContentChanged的方法。那为了弄清楚
mContentChangedListener的定义,查看以下代码:
private final ConversationListAdapter.OnContentChangedListener mContentChangedListener =
new ConversationListAdapter.OnContentChangedListener() {
public void onContentChanged(ConversationListAdapter adapter) {
startAsyncQuery();
}
};
重新调用startAsyncQuery() 该方法刷新。
2)会话列表的更新
看到上面监听器所做的工作大家应该明白啦,会话列表的更新靠的就是这个监听器,当内容发生改变就会重新查询,界面进行刷新,到此为止 短信的界面刷新完成。
看到上面监听器所做的工作大家应该明白啦,会话列表的更新靠的就是这个监听器,当内容发生改变就会重新查询,界面进行刷新,到此为止 短信的界面刷新完成。
特别注意:该情况是用户在短信会话列表这个界面,如果不在这个界面大概还有其他两种情况: 1、在某个会话中;2、没有进入mms程序。对于前一种情况会在下面继续分析,对于后一种情况我想也不用多说在这种情况下会走activity的声明周期函数,在onstart方法里进行查询显示前面已经提到。那还有一种特殊的情况就是在从某个会话中返回到会话列表时的处理。下面请看ConversationList的声明:
<activity android:name=".ui.ConversationList"
android:label="@string/app_label"
android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden"
android:launchMode="singleTop">属性是singleTop,大家都知道这种情况会去调用onNewIntent方法:
@Override
protected void onNewIntent(Intent intent) {
// Handle intents that occur after the activity has already been created.
startAsyncQuery();
}
该方法又会去重新查询刷新界面。
3.23刷新会话内容
刷新ui除了刷新会话列表之外,还有一种情况就是当用户在某个会话时,这时该会话接收到新的消息,这时需要刷新会话的内容,这是怎么实现的?
用于会话显示的activity:ComposeMessageActivity;用于显示会话的短信内容组件: MessageListView;填充listview的adapter是:MessageListAdapter
1)初始化
ComposeMessageActivity的onCreate方法调用initialize方法,initialize方法再调用initMessageList()完成初始化
private void initMessageList() {
if (mMsgListAdapter != null) {
return;
}
String highlightString = getIntent().getStringExtra("highlight");
Pattern highlight = highlightString == null
? null
: Pattern.compile("\\b" + Pattern.quote(highlightString), Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE);
// Initialize the list adapter with a null cursor.
mMsgListAdapter = new MessageListAdapter(this, null, mMsgListView, true, highlight);
mMsgListAdapter.setOnDataSetChangedListener(mDataSetChangedListener);
mMsgListAdapter.setMsgListItemHandler(mMessageListItemHandler);
mMsgListView.setAdapter(mMsgListAdapter);
mMsgListView.setItemsCanFocus(false);
mMsgListView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mMsgListView.setOnCreateContextMenuListener(mMsgListMenuCreateListener);
mMsgListView.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
if (view != null) {
((MessageListItem) view).onMessageListItemClick();
}
}
});
}
说明:MessageListAdapter定义了一个监听器当数据发生变化的时候回调监听器的onContentChanged的方法,该方法会重新查询该会话相关的内容并刷新显示,以下是其定义:
private final MessageListAdapter.OnDataSetChangedListener
mDataSetChangedListener = new MessageListAdapter.OnDataSetChangedListener() {
public void onDataSetChanged(MessageListAdapter adapter) {
mPossiblePendingNotification = true;
}
public void onContentChanged(MessageListAdapter adapter) {
startMsgListQuery();
}
};
ComposeMessageActivity的onStart函数里面调用一个重要的方法loadMessageContent();该方法会继续调用startMsgListQuery(),在上面的adapter的监听器里当内容有变动时回调函数也会调用该方法,以下代码是该方法做的具体工作:
private void startMsgListQuery() {
Uri conversationUri = mConversation.getUri();
if (conversationUri == null) {
return;
}
if (Log.isLoggable(LogTag.APP, Log.VERBOSE)) {
log("for " + conversationUri);
}
// Cancel any pending queries
mBackgroundQueryHandler.cancelOperation(MESSAGE_LIST_QUERY_TOKEN);
try {
// Kick off the new query
mBackgroundQueryHandler.startQuery(
MESSAGE_LIST_QUERY_TOKEN, null, conversationUri,
PROJECTION, null, null, null);
} catch (SQLiteException e) {
SqliteWrapper.checkSQLiteException(this, e);
}
}分析:该方法所做的工作就是使用mBackgroundQueryHandler查询数据库(
mBackgroundQueryHandler是一个AsyncQueryHandler的对象),查询完成后会回调
mBackgroundQueryHandler该对象的onQueryComplete方法,以下是其核心代码:
@Override
protected void onQueryComplete(int token, Object cookie, Cursor cursor) {
switch(token) {
case MESSAGE_LIST_QUERY_TOKEN:
// Set last sub used in this conversation thread.
if (cursor.getCount() > 0) {
cursor.moveToLast();
mLastSubInConv = cursor.getInt(COLUMN_SUB_ID); //TODO: ADD SUBSCRIPION HERE
cursor.moveToPosition(-1);
} else {
mLastSubInConv = SUBSCRIPTION_ID_INVALID;
}
int newSelectionPos = -1;
long targetMsgId = getIntent().getLongExtra("select_id", -1);
if (targetMsgId != -1) {
cursor.moveToPosition(-1);
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
long msgId = cursor.getLong(COLUMN_ID);
if (msgId == targetMsgId) {
newSelectionPos = cursor.getPosition();
break;
}
}
}
mMsgListAdapter.changeCursor(cursor);
if (newSelectionPos != -1) {
mMsgListView.setSelection(newSelectionPos);
}
if (cursor.getCount() == 0 && !isRecipientsEditorVisible() && !mSentMessage) {
initRecipientsEditor();
}
mTextEditor.requestFocus();
mConversation.blockMarkAsRead(false);
mConversation.setMessageCount(cursor.getCount());
return;
}
}代码虽多,但其核心就是对mMsgListAdapter的内容重新赋值刷新界面完毕。
3)刷新
刷新就很简单啦,当数据有变化的时候会触发OnDataSetChangedListener这个监听器,这个监听器会调用onContentChanged函数重新查询达到刷新的效果。
4、总结
短信的接收大致过程就是这样,对于上面提到的替换短信,该情况暂时不清楚,有些细节描述的很粗糙,希望大家多提意见,一起研究研究