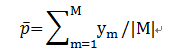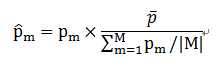机器学习评价方法之NRIG
by wangben 2015.11
在工业界,逻辑回归是很常用的模型,一般大家在用逻辑回归做机器学习排序或者广告预估时常用AUC来判断排序的效果,逻辑回归是概率模型,除了排序的指标之外,有时会出现AUC比较好,但是概率拟合较差(很有可能是收敛的不好),在广告GSP(Generalized second-price auction)竞价模式中尤为重要,所以我们还希望验证模型对真实概率的拟合程度,这时就需要其他指标来衡量。
最常见的方式是MSE(Mean Square Error):
这个方式需要先收集一部分充分统计量的item,给出其统计CTR并且与模型给出的pCTR(predict ctr)进行比较,判断拟合程度:
另一种选择是使用NRIG(Normalized RelativeInformation Gain),NRIG是RIG的归一化版本。
给定一个测试集M,整个数据集的统计CTR可以定义为:
其中ym是真实label,取值为0或者1
那么数据整体熵的定义就是:
对于模型预测结果,我们可以给出其交叉熵cross entropy(Loss Function):
其中pm指的是模型对第m个样本所预测的概率。
从而模型能够得到的相对信息增益定义如下:
从公式可以看出,如果增益越大,说明收敛的越好,模型质量应该越高
如果我们对每一个样本的预测概率相对于整体CTR做归一化,就可以得到相应的NRIG,归一化的预测概率如下:
python测试代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/python #by [email protected] 20151020 NRIG SCORE,big is better,infomation gain is bigger import sys import math # def entropy(p): return -( p * math.log(p,2) + (1 - p) * math.log(1 - p,2) ) def crossEntropy( label, p ): return -( label * math.log(p,2) + (1 - label) * math.log(1 - p,2) ) if __name__ == "__main__": listScore = [] sum = 0.0 test_size = 0.0 ce_sum = 0.0 avg_pre = 0.0 #input format: #label\tpredictScore for line in open(sys.argv[1]): line = line.rstrip() listLine = line.split() if len(listLine) != 2: continue label = float(listLine[0]) value = float(listLine[1]) test_size += 1.0 if label > 0: sum += label ce_sum += crossEntropy( label , value) #print "debug :",ce_sum avg_pre += value listScore.append([label,value]) print "empirical CTR(avg CTR): ",sum,test_size,sum/test_size avg_p = sum/test_size Hp = entropy(avg_p) print "entropy: ",Hp ce = ce_sum/test_size print "cross entropy: ",ce_sum,test_size,ce print "RIG: ",(Hp-ce)/Hp #NRIG n_ce = 0.0 avg_pre /= test_size print "average prediction: ",avg_pre diff_rate = avg_p/avg_pre for item in listScore: n_ce += crossEntropy( item[0] , item[1]*diff_rate ) n_ce /= test_size print "normalized ce: ",n_ce print "NRIG: ",(Hp-n_ce)/Hp
reference:
Click-through Prediction for Advertising in Twitter Timeline. kdd2015