自己写的哈希表以及解决哈希冲突
哈希表就是键值key-value对,使用hash函数让key产生哈希值,当不同的key产生相同的哈希值时就是哈希冲突了,产生哈希冲突可以使用拉链法。
hash.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "hash.h"
static unsigned int table_size[] = {
7, 13, 31, 61, 127, 251, 509, 1021, 2039, 4093, 8191,
16381, 32749, 65521, 131071,
262143, 524287, 1048575, 2097151, 4194303, 8388607,
16777211, 33554431, 67108863, 134217727, 268435455,
536870911, 1073741823, 2147483647, 0};
/* hash function: return unsignde int */
static unsigned int hash(const char *key)
{
unsigned int seed = 131;
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*key) {
hash = hash * seed + (*key++);
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % SIZE;
}
void hash_insert(struct hash_table *ht, char *key, char *value)
{
unsigned int h;
struct hash_node *node,*pnode,*fnode;
node=pnode=(struct hash_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct hash_node));
fnode=(struct hash_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct hash_node));
memset(node,0,sizeof(struct hash_node));
node->next=NULL;
memset(fnode,0,sizeof(struct hash_node));
fnode->next=NULL;
h = hash(key);
if(ht[h].ht==0)
{
ht[h].ht=fnode;
}
pnode=ht[h].ht;
while(pnode->next!=NULL)
{
pnode=pnode->next;
}
pnode->key=key;
pnode->value=value;
pnode->next=node;
}
char* search(struct hash_table *ht, char *key)
{
unsigned int h;
struct hash_node *pnode;
char *ret=(char*)malloc(sizeof(char));
pnode=(struct hash_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct hash_node));
h = hash(key);
if(ht[h].ht==0)
{
return ret=NULL;
}
else{
pnode=ht[h].ht;
while(pnode->next!=NULL&&pnode->key!=key)
{
pnode=pnode->next;
}
if(pnode->key==key)
{
return ret=pnode->value;
}
else
{
return ret=NULL;
}
}
}
int main() {
int i;char *a1;char *a2;
char *search_key;char *search_ret;
struct hash_table *h;
struct hash_node *node;
h=(struct hash_table *)malloc(sizeof(struct hash_table)*SIZE);
memset(h,0,sizeof(struct hash_table)*SIZE);
/*for(i=0;i<SIZE;i++)
{
node=(struct hash_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct hash_node));
memset(node,0,sizeof(struct hash_node));
node->next=NULL;
h[i].ht=node;
}*/
a1="aaa";
a2="abc";
hash_insert(h,a1,a2);
a1="bbb";
a2="jkjhk";
hash_insert(h,a1,a2);
a1="ccc";
a2="reew";
hash_insert(h,a1,a2);
a1="ddd";
a2="hyte";
hash_insert(h,a1,a2);
a1="eee";
a2="wwq";
hash_insert(h,a1,a2);
a1="fff";
a2="fd4";
hash_insert(h,a1,a2);
search_key="dddd";
search_ret=search(h,search_key);
return 0;
}
另一种方法一开始就for循环初始化node
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "hash.h"
static unsigned int table_size[] = {
7, 13, 31, 61, 127, 251, 509, 1021, 2039, 4093, 8191,
16381, 32749, 65521, 131071,
262143, 524287, 1048575, 2097151, 4194303, 8388607,
16777211, 33554431, 67108863, 134217727, 268435455,
536870911, 1073741823, 2147483647, 0};
/* hash function: return unsignde int */
static unsigned int hash(const char *key)
{
unsigned int seed = 131;
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*key) {
hash = hash * seed + (*key++);
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % SIZE;
}
hash_insert(struct hash_table *ht, char *key, char *value)
{
unsigned int h;
struct hash_node *node,*pnode;
node=pnode=(struct hash_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct hash_node));
memset(node,0,sizeof(struct hash_node));
node->next=NULL;
h = hash(key);
pnode=ht[h].ht;
while(pnode->next!=NULL)
{
pnode=pnode->next;
}
pnode->key=key;
pnode->value=value;
pnode->next=node;
}
int main() {
int i;char *a1;char *a2;
struct hash_table *h=(struct hash_table *)malloc(sizeof(struct hash_table)*SIZE);
struct hash_node *node=NULL;
memset(h,0,sizeof(struct hash_table)*SIZE);
for(i=0;i<SIZE;i++)
{
node=(struct hash_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct hash_node));
memset(node,0,sizeof(struct hash_node));
node->next=NULL;
h[i].ht=node;
}
a1="aaa";
a2="abc";
hash_insert(h,a1,a2);
a1="bbb";
a2="jkjhk";
hash_insert(h,a1,a2);
a1="ccc";
a2="reew";
hash_insert(h,a1,a2);
a1="ddd";
a2="hyte";
hash_insert(h,a1,a2);
a1="eee";
a2="wwq";
hash_insert(h,a1,a2);
a1="fff";
a2="fd4";
hash_insert(h,a1,a2);
return 0;
}
hash.h
struct hash_node{
struct hash_node* next;
char * key;
char * value;
};
struct hash_table{
struct hash_node *ht;
};
#define SIZE 1
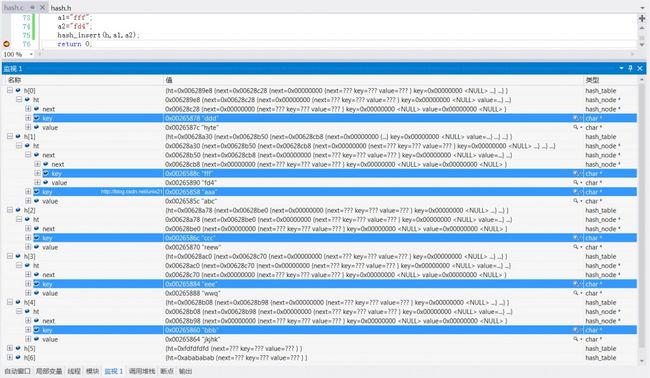
SIZE就是哈希表数组的大小,现在故意设置其为1,则哈希表退化为普通链表,这里只是为了演示所有的数据应该链接在一起
扩大SIZE为5,因为我们有6对数据,所以必然最少会有2个数据冲突,冲突的放一起: