matlab中map工具箱(Mapping toolbox)使用
Mapping Toolbox是Matlab提供的,一整套包含许多函数跟图形用户界面的工具箱;它可以帮助用户分析几何空间方面的数据;并以地图的形式显示出来!
worldmap命令
help worldmap WORLDMAP 创建世界上给定区域的坐标 WORLDMAP 区域 或 WORLDMAP(区域名) 新建一个空的地图坐标,这个投影模型和限制与此区域相适应 . REGION 可能是一个字符串或则 cell array of strings. Permissible strings 包括大陆, 国家,岛屿,比如 'World', 'North Pole', 'South Pole', and 'Pacific'.
>> worldmap world
%绘制世界地图坐标或
>> worldmap ('world)
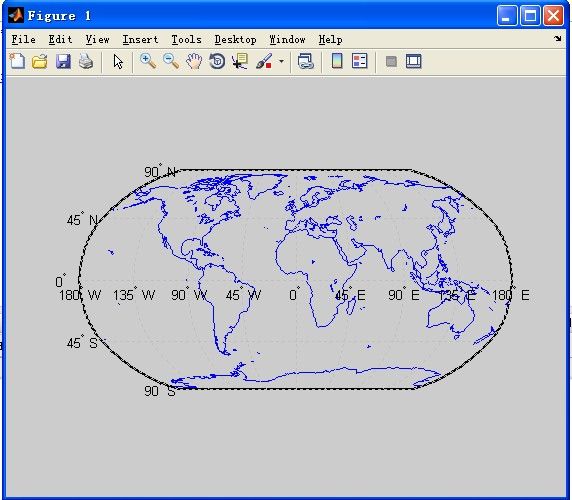
1、示例一:带有海岸线的世界地图
coast.m在目录D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2010a\toolbox\map\mapdemos
>> %
worldmap('World')
load coast
plotm(lat, long)coast中包含lat和long两个double型向量9865*1,9865*1
>> help plotm
PLOTM 投影二维直线和点到地图坐标
PLOTM(lat,lon)将线型对象投影到最近使用的地图坐标. 输入的维度(latitude)和经度(longitude)数据必须与最近使用地图坐标单位一致 。
PLOTM will clear the current map if the hold state is off.
>> help load
LOAD 从 MAT-file加载数据到工作空间.
S = LOAD(FILENAME) 加载来自a MAT-file 文件的变量到结构数组或来自ascii文件的数据到双精度数组.
2、实例二:带有陆地、主要湖泊河流和城市和人口密集区的世界地图
landareaslandareas.shp shx、dbf在D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2010a\toolbox\map\mapdemos目录下
>> % Worldmap with land areas, major lakes and rivers, and cities and
% populated places
ax = worldmap('World');
setm(ax, 'Origin', [0 180 0])
land = shaperead('landareas', 'UseGeoCoords', true);
geoshow(ax, land, 'FaceColor', [0.5 0.7 0.5])
lakes = shaperead('worldlakes', 'UseGeoCoords', true);
geoshow(lakes, 'FaceColor', 'blue')
rivers = shaperead('worldrivers', 'UseGeoCoords', true);
geoshow(rivers, 'Color', 'blue')
cities = shaperead('worldcities', 'UseGeoCoords', true);
geoshow(cities, 'Marker', '.', 'Color', 'red')
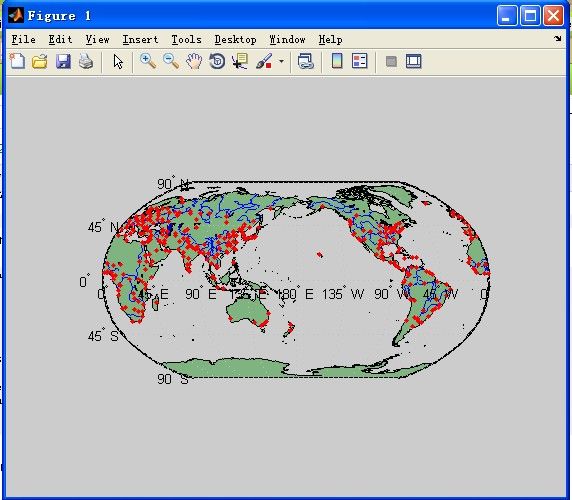
geoshow(ax, land, 'FaceColor', [0.5 0.7 0.5])
陆地的表面颜色
geoshow(cities, 'Marker', '.', 'Color', 'red')
城市用'.'标记
H = WORLDMAP(...)返回地图投影的句柄
>> help setm
SETM 设置地图坐标和图形对象的属性
SETM(H,'MapAxesPropertyName',PropertyValue,...)
H 有效的地图坐标句柄, sets the map properties specified in the input list. The
map properties must be recognized by AXESM.
SETM(H, 'MapPosition', POSITION)
H 为有效的地图 text object, uses a two or three element position vector specifying[维度,经度,海拔] [latitude, longitude, altitude]. 对于两个元素的向量, altitude = 0
is assumed.
SETM(H, 'Graticule', LAT, LON, ALT)
where H is a valid projected
surface object, uses LAT and LON 相同大小的矩阵specify the
格网点. The input ALT can be either a scalar to specify the
altitude plane, a matrix of the same size as LAT and LON, or an empty
matrix. If omitted, ALT = 0 is assumed.
>> help shaperead
SHAPEREAD 从shapefile中读取向量特征和属性
S = SHAPEREAD(FILENAME)
返回 N×1 结构数组, S,
containing one element for each non-null geographic feature in the shapefile. S is a "mapstruct" geographic data structure array and
combines coordinates/geometry, expressed in terms of map X and Y,
with non-spatial feature attributes.
Name Description of Value Purpose
Attributes Cell array of attribute Omit attributes that are
names not listed. Use {} to omit
all attributes. Also sets
the order of attributes in
the structure array.
UseGeoCoords Scalar logical 如果为true, 替换X和Y field names with 'Lon' and 'Lat', respectively.默认为 false.
>> help geoshow
GEOSHOW 显示地图纬度和经度数据
>> help geoshow
GEOSHOW Display map latitude and longitude data
GEOSHOW(LAT, LON) or
GEOSHOW(LAT, LON, ..., 'DisplayType', DISPLAYTYPE, ...)
投影并显示纬度和经度向量, LAT and LON, 使用存储在地图坐标系中的投影模型.如果无投影模型, 纬度和经度使用默认Plate Carree 投影.LAT and LON may contain embedded NaNs, delimiting individual lines or polygon parts. DISPLAYTYPE can be 'point', 'line', or 'polygon' anddefaults to 'line'.
projects and
displays the latitude and longitude vectors, LAT and LON, using the
projection stored in the axes. If there is no projection, the latitudes
and longitudes are projected using a default Plate Carree projection.
LAT and LON may contain embedded NaNs, delimiting individual lines or
polygon parts. DISPLAYTYPE can be 'point', 'line', or 'polygon' and
defaults to 'line'.