网络编程常用接口的内核实现----sys_socket()
最近在开发一个内核模块,主要的功能是在集群的节点之间迁移TCP连接,从而实现基于内容的调用。因此,花了很多时间和精力研究linux的网络协议栈,但是还是有很多地方没有串起来。网络协议栈是为用户层的应用开发服务的,因此决定从用户层常用的编程接口入手,通过学习这些接口的实现,来理清整个过程,加深对网络协议栈的理解。
网络编程通常是基于客户端-服务端模型。首先启动服务器,稍后的某个时刻启动客户,它要连接到此服务器上。假设客户给服务器发送一个请求,服务器处理这个请求,并且给客户发送一个响应。为了执行网络I/O,第一件事情就是调用socket()函数来创建套接字。socket()函数对应的系统调用时sys_socket(),其源码及分析如下所示:
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(socket, int, family, int, type, int, protocol)
{
int retval;
struct socket *sock;
int flags;
/* Check the SOCK_* constants for consistency. */
/*
* 下面的检查是在编译的时候进行的,如果这些
* 变量的值不一致,编译时会报错。
*/
BUILD_BUG_ON(SOCK_CLOEXEC != O_CLOEXEC);
BUILD_BUG_ON((SOCK_MAX | SOCK_TYPE_MASK) != SOCK_TYPE_MASK);
BUILD_BUG_ON(SOCK_CLOEXEC & SOCK_TYPE_MASK);
BUILD_BUG_ON(SOCK_NONBLOCK & SOCK_TYPE_MASK);
/*
* 从linux 2.6.27开始,参数type除了指定套接字类型外,还
* 可以通过或运算来指定SOCK_CLOEXEC和SOCK_NONBLOCK标志
* 来改变套接字的行为。可以通过man socket命令查看详情。
* 首先通过SOCK_TYPE_MASK掩码来获取type中设置的标志(当然
* 也可能没有设置)。如果type中有标志设置,但是不是
* SOCK_CLOEXEC和SOCK_NONBLOCK对应的位,则返回EINVAL错误。
*/
flags = type & ~SOCK_TYPE_MASK;
if (flags & ~(SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK))
return -EINVAL;
/*
* 获取套接字类型
*/
type &= SOCK_TYPE_MASK;
/*
* 如果SOCK_NONBLOCK不等于O_NONBLOCK并且设置了SOCK_NONBLOCK
* 标志,则将flags中的SOCK_NONBLOCK替换为O_NONBLOCK。
*/
if (SOCK_NONBLOCK != O_NONBLOCK && (flags & SOCK_NONBLOCK))
flags = (flags & ~SOCK_NONBLOCK) | O_NONBLOCK;
/*
* 根据协议族类型和套接字类型创建套接字。
*/
retval = sock_create(family, type, protocol, &sock);
if (retval < 0)
goto out;
/*
* 创建一个新的文件描述符,将新创建的
* socket实例关联上去。
*/
retval = sock_map_fd(sock, flags & (O_CLOEXEC | O_NONBLOCK));
if (retval < 0)
goto out_release;
out:
/* It may be already another descriptor 8) Not kernel problem. */
return retval;
out_release:
sock_release(sock);
return retval;
}
sys_socket()的代码流程图如下所示:
从上面的代码及流程图中,可以看到sys_socket()主要调用sock_create()和sock_map_fd()来完成创建套接字的工作,在讨论这两个函数之前,要强调一下type参数。从linux 2.6.27开始,参数type除了指定套接字类型外,还可以通过或运算来指定SOCK_CLOEXEC和SOCK_NONBLOCK标志来改变套接字的行为。可以通过man socket命令来查看,原文是:
Since Linux 2.6.27, the type argument serves a second purpose: in addition to specifying a
socket type, it may include the bitwise OR of any of the following values, to modify the
behavior of socket():
SOCK_NONBLOCK Set the O_NONBLOCK file status flag on the new open file description. Using
this flag saves extra calls to fcntl(2) to achieve the same result.
SOCK_CLOEXEC Set the close-on-exec (FD_CLOEXEC) flag on the new file descriptor. See the
description of the O_CLOEXEC flag in open(2) for reasons why this may be
useful.
一、sock_create()函数
sock_create()函数时对__sock_create()函数的简单封装,__sock_create()函数的代码流程图如下所示:
__sock_create()调用sock_alloc()分配一个新的inode和socket对象,并设置套接字的权限位及套接字所属的用户和用户组。如果要创建的是TCP套接字,pf->create()中的pf是inet_family_ops变量,该变量的类型是net_proto_family结构,在net/ipv4/if_inet.c文件中定义。inet_family_ops的create成员设置的是inet_create()函数,因此如果是创建TCP套接字,pf->create()调用的实际是inet_create()函数。
inet_create()用来创建inet套接字,其源码及分析如下:
/*
* Create an inet socket.
*/
static int inet_create(struct net *net, struct socket *sock, int protocol)
{
struct sock *sk;
struct inet_protosw *answer;
struct inet_sock *inet;
struct proto *answer_prot;
unsigned char answer_flags;
char answer_no_check;
int try_loading_module = 0;
int err;
/*
* inet_ehash_secret用于在将除原始套接字和UDP套接字外的套接字,
* 哈希计算后插入到系统时用到的哈希因子,只设置一次。
*/
if (unlikely(!inet_ehash_secret))
if (sock->type != SOCK_RAW && sock->type != SOCK_DGRAM)
build_ehash_secret();
/*
* 设置套接字的初始状态。
*/
sock->state = SS_UNCONNECTED;
/* Look for the requested type/protocol pair. */
lookup_protocol:
err = -ESOCKTNOSUPPORT;
rcu_read_lock();
/*
* TCP套接字、UDP套接字、原始套接字的inet_protosw实例都
* 在inetsw_array数组中定义,这些实例会调用inet_register_protosw()
* 注册到inetsw中。
* 根据protocol查找要创建的套接字对应的四层传输协议。
*/
list_for_each_entry_rcu(answer, &inetsw[sock->type], list) {
err = 0;
/* Check the non-wild match. */
if (protocol == answer->protocol) {
if (protocol != IPPROTO_IP)
break;
} else {
/* Check for the two wild cases. */
if (IPPROTO_IP == protocol) {
protocol = answer->protocol;
break;
}
if (IPPROTO_IP == answer->protocol)
break;
}
err = -EPROTONOSUPPORT;
}
/*
* 如果没有找到,则调用request_module()来尝试加载
* 协议所属的模块,正常情况下不会发生。
*/
if (unlikely(err)) {
if (try_loading_module < 2) {
rcu_read_unlock();
/*
* Be more specific, e.g. net-pf-2-proto-132-type-1
* (net-pf-PF_INET-proto-IPPROTO_SCTP-type-SOCK_STREAM)
*/
if (++try_loading_module == 1)
request_module("net-pf-%d-proto-%d-type-%d",
PF_INET, protocol, sock->type);
/*
* Fall back to generic, e.g. net-pf-2-proto-132
* (net-pf-PF_INET-proto-IPPROTO_SCTP)
*/
else
request_module("net-pf-%d-proto-%d",
PF_INET, protocol);
goto lookup_protocol;
} else
goto out_rcu_unlock;
}
err = -EPERM;
/*
* 检查用户是否有创建指定协议类型的套接字的权限,
* 如果是TCP套接字,capability为-1,表示没有权限限制。
*/
if (answer->capability > 0 && !capable(answer->capability))
goto out_rcu_unlock;
err = -EAFNOSUPPORT;
/*
* 检查网络命名空间,检查指定的协议类型
* 是否已经添加,参见init_inet(),tcp协议对应
* 的net_protocol实例是tcp_protocol。
*/
if (!inet_netns_ok(net, protocol))
goto out_rcu_unlock;
/*
* 设置套接字的操作接口,如果是TCP协议,
* answer->ops的值为inet_stream_ops。
*/
sock->ops = answer->ops;
/*
* 获取套接字对应的proto实例,如果是TCP协议,
* 值为tcp_prot。
*/
answer_prot = answer->prot;
answer_no_check = answer->no_check;
answer_flags = answer->flags;
rcu_read_unlock();
WARN_ON(answer_prot->slab == NULL);
err = -ENOBUFS;
/*
* 分配sock实例并初始化,如果是TCP协议,
* 则实际分配的大小为sizeof(tcp_sock)。
*/
sk = sk_alloc(net, PF_INET, GFP_KERNEL, answer_prot);
if (sk == NULL)
goto out;
err = 0;
/*
* 设置是否需要计算校验和的值
*/
sk->sk_no_check = answer_no_check;
if (INET_PROTOSW_REUSE & answer_flags)
sk->sk_reuse = 1;
inet = inet_sk(sk);
/*
* 设置是否是基于连接的套接字
*/
inet->is_icsk = (INET_PROTOSW_ICSK & answer_flags) != 0;
if (SOCK_RAW == sock->type) {
inet->num = protocol;
if (IPPROTO_RAW == protocol)
inet->hdrincl = 1;
}
/*
* 后面都是对一些成员的初始化,不作过多的
* 分析。
*/
if (ipv4_config.no_pmtu_disc)
inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_DONT;
else
inet->pmtudisc = IP_PMTUDISC_WANT;
inet->id = 0;
sock_init_data(sock, sk);
/*
* 在释放传输控制块之前释放资源。
*/
sk->sk_destruct = inet_sock_destruct;
sk->sk_protocol = protocol;
/*
* 在TCP中,用于接收预备队列和后备队列中的
* TCP段,实际的函数时tcp_v4_do_rcv()。
*/
sk->sk_backlog_rcv = sk->sk_prot->backlog_rcv;
inet->uc_ttl = -1;
inet->mc_loop = 1;
inet->mc_ttl = 1;
inet->mc_all = 1;
inet->mc_index = 0;
inet->mc_list = NULL;
sk_refcnt_debug_inc(sk);
if (inet->num) {
/* It assumes that any protocol which allows
* the user to assign a number at socket
* creation time automatically
* shares.
*/
inet->sport = htons(inet->num);
/* Add to protocol hash chains. */
sk->sk_prot->hash(sk);
}
if (sk->sk_prot->init) {
/*
* TCP协议调用的tcp_v4_init_sock()。
*/
err = sk->sk_prot->init(sk);
if (err)
sk_common_release(sk);
}
out:
return err;
out_rcu_unlock:
rcu_read_unlock();
goto out;
}
二、sock_map_fd()函数
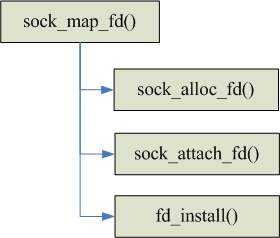
sock_map_fd()主要是创建一个文件描述符,然后将socket实例附加到文件描述符对应的file实例中,其代码流程图如下所示:
sock_alloc_fd()用来分配一个空闲的文件描述符,d_install()将新分配的文件描述添加到存储当前进程所有打开的文件描述符的数组中,sock_attach_fd()将分配的文件描述符对应的file实例和新分配的socket实例关联起来。sock_map_fd()中主要涉及的是文件操作,不作过多的分析,如果对文件系统感兴趣的可以研究一下。
socket实例、文件描述符fd、file实例的关系如下图所示: