杭电OJ--1021 Train Problem I
Train Problem I
Problem Description
As the new term comes, the Ignatius Train Station is very busy nowadays. A lot of student want to get back to school by train(because the trains in the Ignatius Train Station is the fastest all over the world ^v^). But here comes a problem, there is only one railway where all the trains stop. So all the trains come in from one side and get out from the other side. For this problem, if train A gets into the railway first, and then train B gets into the railway before train A leaves, train A can't leave until train B leaves. The pictures below figure out the problem. Now the problem for you is, there are at most 9 trains in the station, all the trains has an ID(numbered from 1 to n), the trains get into the railway in an order O1, your task is to determine whether the trains can get out in an order O2.
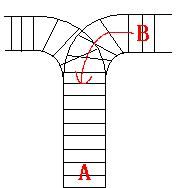
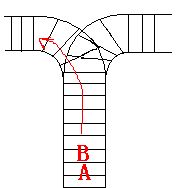
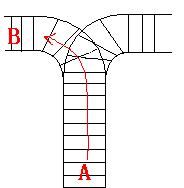



Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case consists of an integer, the number of trains, and two strings, the order of the trains come in:O1, and the order of the trains leave:O2. The input is terminated by the end of file. More details in the Sample Input.
Output
The output contains a string "No." if you can't exchange O2 to O1, or you should output a line contains "Yes.", and then output your way in exchanging the order(you should output "in" for a train getting into the railway, and "out" for a train getting out of the railway). Print a line contains "FINISH" after each test case. More details in the Sample Output.
Sample Input
3 123 321 3 123 312
Sample Output
Yes. in in in out out out FINISH No. FINISHFor the first Sample Input, we let train 1 get in, then train 2 and train 3. So now train 3 is at the top of the railway, so train 3 can leave first, then train 2 and train 1. In the second Sample input, we should let train 3 leave first, so we have to let train 1 get in, then train 2 and train 3. Now we can let train 3 leave. But after that we can't let train 1 leave before train 2, because train 2 is at the top of the railway at the moment. So we output "No.".HintHint
/*
很巧妙的一个出栈入栈模拟函数,要熟练地使用模版,
那么做起题来就很方便了!
1. v.push_back(t) 在容器的最后添加一个值为t的数据,容器的size变大。
另外list有push_front()函数,在前端插入,后面的元素下标依次增大。
2. v.size() 返回容器中数据的个数,size返回相应vector类定义的size_type的值。v.resize(2*v.size)或
v.resize(2*v.size, 99) 将v的容量翻倍(并把新元素的值初始化为99)
3. v.empty() 判断vector是否为空
4. v[n] 返回v中位置为n的元素
5. v.insert(pointer,number, content) 向v中pointer指向的位置插入number个content的内容。
还有v. insert(pointer, content),v.insert(pointer,a[2],a[4])将a[2]到a[4]三个元素插入。
6. v.pop_back() 删除容器的末元素,并不返回该元素。
7.v.erase(pointer1,pointer2) 删除pointer1到pointer2中间(包括pointer1所指)的元素。
vector中删除一个元素后,此位置以后的元素都需要往前移动一个位置,虽然当前迭代器位置没有自动加1,
但是由于后续元素的顺次前移,也就相当于迭代器的自动指向下一个位置一样。
8. v1==v2 判断v1与v2是否相等。
9. !=、<、<=、>、>= 保持这些操作符惯有含义。
10. vector<typeName>::iterator p=v1.begin( ); p初始值指向v1的第一个元素。*p取所指向元素的值。
对于const vector<typeName>只能用vector<typeName>::const_iterator类型的指针访问。
11. p=v1.end( ); p指向v1的最后一个元素的下一位置。
12.v.clear() 删除容器中的所有元素。
*/
//问题在于超时!!需要优化代码!
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num,i,k;
string in,out;
while(scanf("%d",&num)!=EOF)//认真读一下题目是很有必要的!
{
i=0;k=0;
cin>>in>>out;
stack<char> s;//构建一个栈
vector<string> pr;//建立string类型的数组
while(i<num)//一共要有n个元素进栈!
{
s.push(in[i]);//压栈
i++;
pr.push_back("in");//在尾部加入一个数据!
while(!s.empty())//栈不为空时循环
//可能会连续几个数出栈,同时栈如果空了,自然不能再出栈!
{
if(s.top()==out[k])//栈顶元素等于出栈序列的元素
{
s.pop();//出栈
k++;
pr.push_back("out");//在尾部加入一个数据
}
else break;
}
}
if(!s.empty())//栈不为空
cout<<"No."<<endl;
else
{
cout<<"Yes."<<endl;
for (i=0;i<pr.size();i++)//pr.size(),返回容器中实际数据的个数。
cout<<pr[i]<<endl;
}
cout<<"FINISH"<<endl;
// pr.clear();//c.clear()移除容器中所有数据!
//for (i=0;i<s.size();i++)
//s.pop();//出栈,清空!
}
return 0;
}