JDK——HashMap实现
通过put方法来简单了解下JDK中HashMap的实现。
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value); #1
int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); #2
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { #3
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}把值通过制定的key存入这个map中。如果有相同的key保存的值,老的值会被替换掉。
通过#1看到,这个map可以用null当作key值。
#2是通过key的hashCode方法获取哈希值,然后通过hash方法再次进行一次hash计算。这个hsah方法源代码是:
/**
* Applies a supplemental hash function to a given hashCode, which
* defends against poor quality hash functions. This is critical
* because HashMap uses power-of-two length hash tables, that
* otherwise encounter collisions for hashCodes that do not differ
* in lower bits. Note: Null keys always map to hash 0, thus index 0.
*/
static int hash(int h) {
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}假设key.hashCode()的值为:0x7FFFFFFF,table.length为默认值16。
上面算法执行如下:
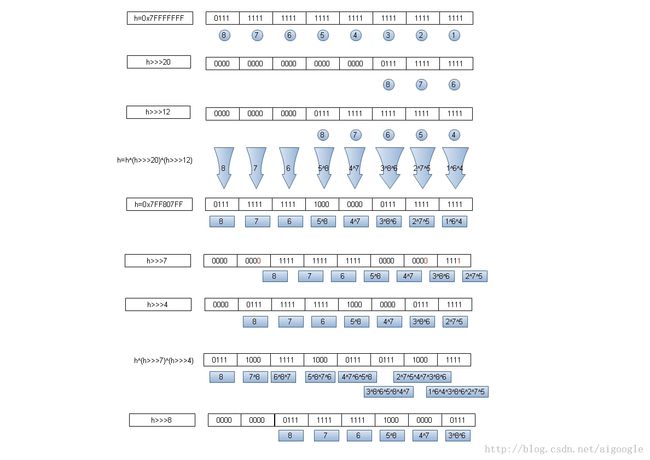
得到i=15
其中h^(h>>>7)^(h>>>4) 结果中的位运行标识是把h>>>7 换成 h>>>8来看。
即最后h^(h>>>8)^(h>>>4) 运算后hashCode值每位数值如下:
8=8
7=7^8
6=6^7^8
5=5^8^7^6
4=4^7^6^5^8
3=3^8^6^5^8^4^7
2=2^7^5^4^7^3^8^6
1=1^6^4^3^8^6^2^7^5
结果中的1、2、3三位出现重复位^运算
3=3^8^6^5^8^4^7 -> 3^6^5^4^7
2=2^7^5^4^7^3^8^6 -> 2^5^4^3^8^6
1=1^6^4^3^8^6^2^7^5 -> 1^4^3^8^2^7^5
算法中是采用(h>>>7)而不是(h>>>8)的算法,应该是考虑1、2、3三位出现重复位^运算的情况。使得最低位上原hashCode的8位都参与了^运算,所以在table.length为默认值16的情况下面,hashCode任意位的变化基本都能反应到最终hash table 定位算法中,这种情况下只有原hashCode第3位高1位变化不会反应到结果中,即:0x7FFFF7FF的i=15。
参考地址:http://www.iteye.com/topic/709945;
找到了hash码值之后用indexfor函数找到key在entity中的index。
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}就是取模运算。
#3循环是通过得到的index查找是否有entity存在,如果有则判断是不是相同的key,如果有相同的key替换掉老值并把老值返回掉。如果没有相同的key则用addEntry方法把这个key和value添加到这个bucketIndex中:
/**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}把新的元素放在队列的首位,然后之前的元素放在新加的元素的后面。通过给新元素的构造函数传递之前元素的对象引用实现的(e参数)。如果map中的元素总数量大于threshold的话,便会重新增加map大小。