表达式语言 2
表达式语言 ------ 在MVC中应用表达式语言
在之前讲解的MVC设计模式之中一直都有DAO 的存在,而且所有的对象都保存在VO 之中。那么这个时候如果将一个VO
传递到了JSP 文件中的话,则必须在JSP之中导入VO包,而如果现在使用了表达式语言的话,这个包导入就没用任何意义了。
package org.gz.el.vo;
public class Dept {
private int deptno;
private String dname;
private String loc;
public void setDeptno(int deptno) {
this.deptno = deptno;
}
public void setDname(String dname) {
this.dname = dname;
}
public void setLoc(String loc) {
this.loc = loc;
}
//
public int getDeptno() {
return this.deptno;
}
public String getDname() {
return this.dname;
}
public String getLoc() {
return this.loc;
}
}
//为了更好的理解,下面先在JSP中直接使用一下
<%@ page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<%@ page import="org.gz.le.vo.*"%>
<html>
<head> <title>欢迎光临</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
// 现在假设 这些代码是由Servlet 完成
Detp dept = new Dept();
dept.setDeptno(8);
dept.setDname("雪花神剑");
dept.setLoc("华山");
request.setAttribute("deptinfo",dept);
%>
<h3>部门编号: ${deptinfo.deptno}</h3>
<h3>部门名称: ${deptinfo.dname}</h3>
<h3>部门位置:${deptinfo.loc}</h3>
</body>
</html>
在JSP 文件之中并没用调用任何的getter() 方法就完成了输出,不用讲现在肯定还是依靠反射机制完成的。
但是,如果要想让这个程序发挥最好的效果,则一定要使用MVC
package org.gz.el.vo;
public class Dept {
private int deptno;
private String dname;
private String loc;
public void setDeptno(int deptno) {
this.deptno = deptno;
}
public void setDname(String dname) {
this.dname = dname;
}
public void setLoc(String loc) {
this.loc = loc;
}
//
public int getDeptno() {
return this.deptno;
}
public String getDname() {
return this.dname;
}
public String getLoc() {
return this.loc;
}
}
package org.gz.el.servlet;
import org.gz.el.vo.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class ElServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException,ServletException {
Dept dept = new Dept();
dept.setDeptno(8);
dept.setDname("雪花神剑");
dept.setLoc("华山");
request.setAttribute("deptinfo",dept);
request.getRequestDispatcher("dept_info.jsp").forward(request,response);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException,ServletException {
doGet(request,response);
}
}
<%@ page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<html>
<head> <title>欢迎光临</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("info","page属性范围");
request.setAttribute("info","request属性范围");
session.setAttribute("info","session属性范围");
application.setAttribute("info","application属性范围"); //getServletContext()
%>
<h3>${info}</h3>
</body>
</html>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>elservlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.gz.el.servlet.ElServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>elservlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/eldemo/ElServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
package org.gz.el.vo;
public class Dept {
private int deptno;
private String dname;
private String loc;
public void setDeptno(int deptno) {
this.deptno = deptno;
}
public void setDname(String dname) {
this.dname = dname;
}
public void setLoc(String loc) {
this.loc = loc;
}
public int getDeptno() {
return this.deptno;
}
public String getDname() {
return this.dname;
}
public String getLoc() {
return this.loc;
}
}
package org.gz.el.servlet;
import org.gz.el.vo.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
// org.gz.el.servlet.ElServlet
public class ElServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException,ServletException {
//HttpSession session = request.getSession();
Dept dept = new Dept();
dept.setDeptno(1);
dept.setDname("独孤求败");
dept.setLoc("火星");
request.setAttribute("info",dept);
request.getRequestDispatcher("deptinfo.jsp").forward(request,response);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException,ServletException {
doGet(request,response);
}
}
<servlet>
<servlet-name>el</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.gz.el.servlet.ElServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>el</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/eldemo/ElServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<%@ page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<html>
<head> <title>欢迎光临</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>部门编号: ${info.deptno}</h3>
<h3>部门名称: ${info.dname}</h3>
<h3>部门位置:${info.loc}</h3>
</body>
</html>
http://localhost:8080/demo/eldemo/ElServlet 路径一定要按照web.xml里面url走
可是在这里面还有一个问题,如果现在传递的到JSP 文件中的是 一个集合呢?
只是集合不管在何种情况下都要通过Iterator 输出,这是一个绝对的真理,可是现在是要通过EL 完成输出,而且EL 只能操作属性范围 所以
将集合通过Iterator 找到每一个,之后将每一个对象放在page 属性范围之中,再通过EL找到
在一个JSP 文件之中唯一允许导入的包就是java.util 包
现在充分发挥JSP 的特点: 接收、判断、输出。
集合永远是Iterator 而表达式永远只能操作一个属性范围
package org.gz.el.vo;
public class Dept {
private int deptno;
private String dname;
private String loc;
public void setDeptno(int deptno) {
this.deptno = deptno;
}
public void setDname(String dname) {
this.dname = dname;
}
public void setLoc(String loc) {
this.loc = loc;
}
public int getDeptno() {
return this.deptno;
}
public String getDname() {
return this.dname;
}
public String getLoc() {
return this.loc;
}
}
package org.gz.el.servletlist;
import org.gz.el.vo.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
// org.gz.el.servletlist.ElListServlet
public class ElListServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException,ServletException {
//HttpSession session = request.getSession();
List<Dept> list = new ArrayList<Dept>();
Dept dept = null;
dept = new Dept();
dept.setDeptno(1);
dept.setDname("独孤求败");
dept.setLoc("火星");
list.add(dept);
dept = new Dept();
dept.setDeptno(2);
dept.setDname("大刀王五");
dept.setLoc("太平洋");
list.add(dept);
request.setAttribute("infolist",list);
request.getRequestDispatcher("dept_list.jsp").forward(request,response);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException,ServletException {
doGet(request,response);
}
}
<%@ page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<%@ page import="java.util.*"%>
<html>
<head> <title>欢迎光临</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
List all = (List)request.getAttribute("infolist");
if(all != null) {
%>
<table border="1" width="90%">
<tr>
<td>部门编号</td>
<td>部门名称</td>
<td>部门位置</td>
</tr>
<%
Iterator iter = all.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
pageContext.setAttribute("dept",iter.next()); //通过pageContext 对象保存在当前的页面之中 (属性标记保存)
%>
<tr>
<td>${dept.deptno}</td>
<td>${dept.dname}</td>
<td>${dept.loc}</td>
</tr>
<%
}
%>
</table>
<%
}
%>
</body>
</html>
表达式语言可以方便的进行对象属性的输出
通过表达式语言输出集合时,需要使用page属性范围完成
表达式结合MVC设计模式将发挥更大的作用
掌握表达式各种运输符的使用。
在这之中需要重点掌握的就是三目运算符的使用
运算符
在表达式语言中为了方便用户的显示操作定义了许多数学运算符、关系运算符、逻辑运算符等,使用这些运算符将使得JSP页面更加简洁,但是对于复杂的操作还是应该在Servlet 或JavaBean 中完成,在使用这些运输符的时候,所有的操作内容也可以直接使用设置的属性,而不用考虑转型的问题。
一定要掌握好JSP 的主要作用,JSP 就是负责显示的,而所有的复杂的业务操作都应交给Servlet 完成
唯一的好处是可以直接使用属性名称完成操作
在jdk1.5 之后,增加了自动装箱操作,所有的数字会自动变成Integer对象 例如:pageContext.setAttribute("num",33);
<%@ page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<html>
<head> <title>欢迎光临</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("num1",10);
pageContext.setAttribute("num2",20);
%>
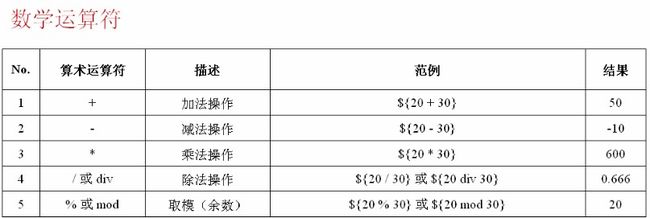
<h3>加法操作:${num1 + num2}</h3>
<h3>减法操作:${num1 - num2}</h3>
<h3>乘法操作: ${num1 * num2}</h3>
<h3>除法操作: ${num1 / num2} 和 ${num1 div num2}</h3>
<h3>取模操作:${num1 % num2} 和 ${num1 mod num2}</h3>
</body>
</html>
<%@ page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<html>
<head> <title>欢迎光临</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("num1",10);
pageContext.setAttribute("num2",20);
%>
<h3>等于判断:${num1 == num2} 和 ${num1 eq num2}</h3>
<h3>不等判断:${num1 != num2} 和 ${num1 ne num2}</h3>
<h3>小于判断:${num1 < num2} 和 ${num1 lt num2}</h3>
<h3>大于判断:${num1 > num2} 和 ${num1 gt num2}</h3>
<h3>小于等于判断:${num1 <= num2} 和 ${num1 le num2}</h3>
<h3>大于等于判断:${num1 >= num2} 和 ${num1 ge num2}</h3>
</body>
</html>
<%@ page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<html>
<head> <title>欢迎光临</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("flagA",true);
pageContext.setAttribute("flagB",false);
%>
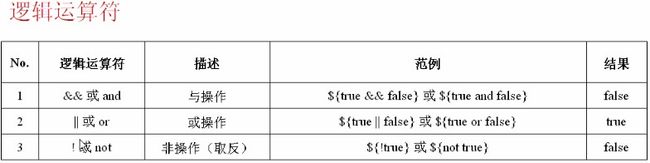
<h3>与操作: ${flagA && flagB} 和 ${flagA and flagB} </h3>
<h3>或操作: ${flagA || flagB} 和 ${flagA or flagB} </h3>
<h3>非操作: ${!flagA} 和 ${not flagA} </h3>
<h3>非操作: ${!flagB} 和 ${not flagB} </h3>
</body>
</html>
<%@ page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<html>
<head> <title>欢迎光临</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("num1",10);
pageContext.setAttribute("num2",20);
pageContext.setAttribute("num3",30);
%>
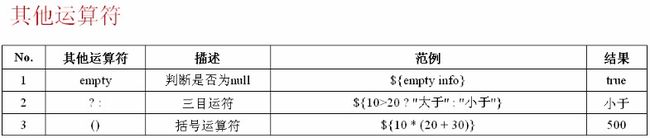
<h3>empty操作: ${empty info}</h3>
<h3>三目操作: ${num1 > num2 ? "大于" : "小于"}</h3>
<h3>括号操作: ${num1*(num2 + num3)}</h3>
</body>
</html> 小结:
使用表达式中的运算可以方便完成各种运算操作,从而避免使用转型所代码的麻烦
可以发现根本就不再考虑类型问题了