opencv实现车牌识别之字符分割
简介
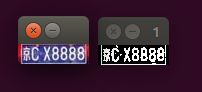
在前一篇中,我们已经定位出来了在图片中车牌号的位置,并且将车牌号图片复制成了新图片,并显示出来,本章在这些被截取出来的图片上继续处理。 截取出来的新图片如下:
图像灰阶/二值化
首先也是选择将图像进行灰阶,然后采用以255一遍开始,取占了总pixel为5%的地方作为阀值,进行二值化。 代码如下:
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <opencv/cv.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "lib/normal.h"
#include "lib/cutchar.h"
#define DEBUG
#ifdef DEBUG
#define DE(format, ...) printf(format, ## __VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define DE(format, ...) while(0)
#endif
int main(int argc, char** argv){
Mat img, img_2, img_3, img_4, img_5, img_w;
IplImage pI_1;
IplImage pI_2;
int width, reWidth=30, wWidth=20, pic_width;
int height, reHeight=100, wHeight = 20;
char str[2];
int i = 0, j = 0, k;
int threshold = 0, pic_ArrNumber, tmp;
int vArr[reHeight];
int **pic_Arr;
CvScalar s1;
float percentage = 0.0;
if(argc < 2){
DE("Please input argv[1]\n");
return -1;
}
img = cv::imread(argv[1]);
namedWindow(str);
imshow(str, img);
width = img.rows;
height = img.cols;
pic_gray(img, img_2);
threshold = histogram_Calculate(img_2, 5);
DE("threshold:%d\n",threshold);
pic_Thresholding(img_2, threshold);
sprintf(str, "%d", i+1);
namedWindow(str);
imshow(str, img_2);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}首先装载截取出来的车牌号图片到img,然后pic_gray进行灰阶化到img_2,接着计算出5%时候的pixel阀值threshold,最后对灰阶图像img_2进行二值化操作。 结果显示如下:
上下边缘分离
从图片和周围,我们知道车牌号的四周被白色的边框包围着,所以我们需要排除掉这部分干扰,这里我们首先来去除掉边框的上线边缘干扰。 代码如下:
int detectionChange(Mat& mat1, Mat& mat2, int number){
IplImage pI_1 = mat1, pI_2;
CvScalar s1, s2;
int width = mat1.rows;
int height = mat1.cols;
int sum = 0, sum_2 = 0, width_1 = 0, width_2 = 0;
int i, j;
for(i=0; i<width; i++){
sum = 0;
sum_2 = 0;
for(j=0; j<height-1; j++){
s1 = cvGet2D(&pI_1, i, j);
s2 = cvGet2D(&pI_1, i, j+1);
if(((int)s1.val[0]) != ((int)s2.val[0])){
sum += 1;
sum_2 = 0;
}else{
sum_2 += 1;
}
if(sum_2 != 0){
if(height / sum_2 < 5){
sum = 0;
break;
}
}
}
if(sum >= number){
width_1 = i;
break;
}else{
width_1 = i;
}
}
for(i=width-1; i> 0; i--){
sum = 0;
sum_2 = 0;
for(j=0; j<height-1; j++){
s1 = cvGet2D(&pI_1, i, j);
s2 = cvGet2D(&pI_1, i, j+1);
if(((int)s1.val[0]) != ((int)s2.val[0])){
sum += 1;
sum_2 = 0;
}else{
sum_2 += 1;
}
if(sum_2 != 0){
if(height / sum_2 < 1){
sum = 0;
break;
}
}
}
if(sum >= number){
width_2 = i;
break;
}else{
width_2 = i;
}
}
if(width_2 <= width_1){
width_2 = width;
}
mat2 = cv::Mat(width_2 - width_1 + 1, height, CV_8UC1, 1);
pI_2 = mat2;
for(i=width_1; i<= width_2; i++){
for(j=0; j<height; j++){
s1 = cvGet2D(&pI_1, i, j);
cvSet2D(&pI_2, i-width_1, j, s1);
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv){
pic_Thresholding(img_2, threshold);
sprintf(str, "%d", i+1);
namedWindow(str);
imshow(str, img_2);
detectionChange(img_2, img_3, 7);
sprintf(str, "%d", i+2);
namedWindow(str);
imshow(str, img_3);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
} 重点就是函数detectionChange,在这个函数中主要是进行那个判断,首先判断一行中,是否有连续的255像素大于了一定该行宽度的一定比例,
正常的牌照单个字符,它的字符宽度肯定小于整个车牌宽度的1/6;然后还判断一行中pixel从0到255或者从255到0的跳变有没有大于一定的数量,在
车牌号所在的行中,该跳变至少是7次。
detectionChange中首先将img_2从头开始扫描,找到车牌号真正开始的行头。然后反过来,从尾部开始扫描,找到车牌字符真正结束时候的尾部。
最后将这部分图像,复制到img_3中。
图像结果显示如下:
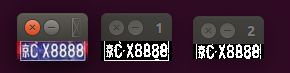
字符分割
经过如上之后,接着就是根据车牌图片的垂直投影宽度和积累的数值,进行字符分割。 具体代码如下:
void verProjection_calculate(Mat& mat1, int* vArr, int number){
IplImage pI_1 = mat1;
CvScalar s1;
int width = mat1.rows;
int height = mat1.cols;
int i, j;
for(i=0; i< number; i++){
vArr[i] = 0;
}
for(j=0; j<height; j++){
for(i=0; i<width; i++){
s1 = cvGet2D(&pI_1, i, j);
if(s1.val[0] > 20){
vArr[j] += 1;
}
}
}
}
int** verProjection_cut(int* vArr, int width, int* number){
int **a;
int i, flag = 0;
int num = 0;
int threshold = 2;
a = (int**)malloc(width / 2 * sizeof(int*));
for(i=0; i<width-1; i++){
if((vArr[i] <= threshold) && (vArr[i+1] > threshold)){
a[num] = (int* )malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
a[num][0] = i;
flag = 1;
}else if((vArr[i] > threshold) && (vArr[i+1] <= threshold) && (flag != 0)){
a[num][1] = i;
num += 1;
flag = 0;
}
}
*number = num;
return a;
int main(int argc, char** argv){
int width, reWidth=30, wWidth=20, pic_width;
int height, reHeight=100, wHeight = 20;
................
carCard_Resize(img_3, img_4, reWidth, reHeight);
pic_Thresholding(img_4, 60);
pI_1 = img_4;
verProjection_calculate(img_4, vArr, reHeight);
pic_Arr = verProjection_cut(vArr, reHeight, &pic_ArrNumber);
for(i=0; i< pic_ArrNumber; i++){
printf("pic_Arr[%d]:%d, %d\n", i, pic_Arr[i][0], pic_Arr[i][1]);
}
sprintf(str, "%d", i+3);
namedWindow(str);
imshow(str, img_4);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
} 这一步中,首先将消除了上下边缘的img_3,放大保存到img_4(reWidth=30,reHeight=100),接着将放大后图片img_4从新以阀值60来二值化,接着用
verProjection_calculate计算出img_4的垂直投影数据,保存到一维数组vArr中;然后verProjection_cut函数利用垂直投影数据vArr来分割出字符宽度。
在verProjection_cut中,到某一列的垂直投影数据小于等于2,就表示该位置不是字符。
打印出来的字符分割宽度位置和图像表现如下:
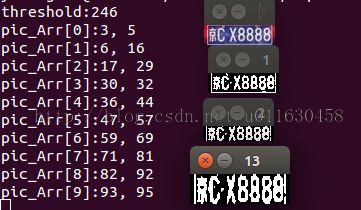
后续处理
在宽度分割出来之后,就可以在img_4上将对应的字符图片分割复制出来,然后在排除掉左右两边的边缘干扰和车牌的中间那一点的干扰,就获取到了合适的 车牌字符图片了。对应代码如下:
float pixelPercentage(Mat& mat1){
IplImage pI_1 = mat1;
CvScalar s1;
int width = mat1.rows;
int height = mat1.cols;
int i, j;
float sum = 0, allSum = 0, tmp;
for(i=0; i<width; i++){
for(j=0; j<height; j++){
s1 = cvGet2D(&pI_1, i, j);
if(s1.val[0] > 20){
sum += 1;
}
allSum += 1;
}
}
tmp = sum / allSum;
return tmp;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv){
......................
verProjection_calculate(img_4, vArr, reHeight);
pic_Arr = verProjection_cut(vArr, reHeight, &pic_ArrNumber);
for(i=0; i< pic_ArrNumber; i++){
pic_width = pic_Arr[i][1] - pic_Arr[i][0];
if(pic_width < 3){
continue;
}
img_5 = cv::Mat(reWidth, pic_Arr[i][1] - pic_Arr[i][0], CV_8UC1, 1);
pI_2 = img_5;
for(j=0; j<reWidth; j++){
for(k=pic_Arr[i][0]; k<pic_Arr[i][1]; k++){
s1 = cvGet2D(&pI_1, j, k);
cvSet2D(&pI_2, j, k-pic_Arr[i][0], s1);
}
}
percentage = pixelPercentage(img_5);
if(percentage < 0.1){
continue;
}
if(pic_width < 6){
printf("the %d is 1\n", i);
continue;
}
carCard_Resize(img_5, img_w, wWidth, wHeight);
pic_Thresholding(img_w, 60);
sprintf(str, "%d", i+10);
namedWindow(str);
imshow(str, img_w);
}
sprintf(str, "%d", i+3);
namedWindow(str);
imshow(str, img_4);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
} 在代码中,首先计算出分割出来的字符宽度pic_width,如果宽度小于3,表示不是正常的车牌字符,将该图片排除掉。如果满足大于2,则将分割字符图片
复制到img_5中,然后使用函数pixelPercentage计算出img_5中图片255的pixel占了总像素比例的比值,如果小于0.1,则表示该图像是车牌中的那个点。那么该
图片也排除掉,接着再宽度判断,如果宽度大于2而小于6,则表示该图片应该是1,因为1的垂直投影和其他字符相比,相差很多(注意:该方法很容易导致左右
边沿也被检测成了1)。最后在一次将筛选分割出来的字符img_5,归一化为wWidth=20,wHeight = 20的img_5,在以60为阀值的二值化后,将它们分别显示出来。
最后的显示效果如下:
效果演示
使用该方法做的效果并不好,如下是一些效果演示:
在这图片中,因为1之前已经判断筛选了,所以不会显示出1。
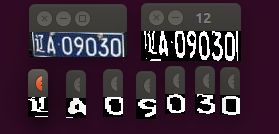 如图所示,该图片的效果就很差。
如图所示,该图片的效果就很差。
代码下载位置:http://download.csdn.net/detail/u011630458/8440123