java ------ IO(从基础到加强)
IO基础到加强
基础篇
一、一些基础知识概念
1、文件的逻辑结构
流式文件
记录式文件
2、文件的存取方法
顺序存取
随机存取
3、文件的使用
操作接口
应用程序接口
4、流的定义和作用
流的定义、方向性和读/写操作
流采用缓冲区技术
流的作用:简单的说就是控制文件的输入和输出
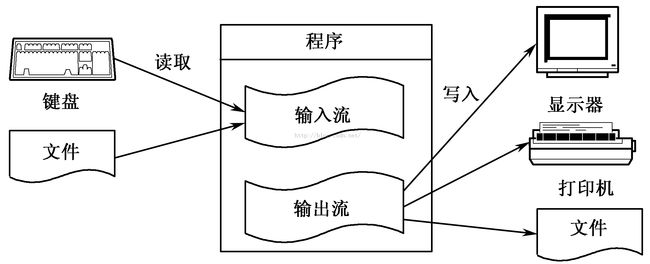
5、流的存在
通过这个图,就可以很好的理解输入流和输出流,它们的命名是以程序为参展点,写进程序来,就是要用输入流,写出程序(写到文件中)就是要用输出流。
二、输入、输出流
主要分为两大类:字节流和字符流
1、字节流
(1)InputStream 抽象字节输入流类
public abstract class InputStream extends Object implements Closeable
{
public abstract int read() throws IOException; //返回读取的一个字节,抽象方法
public int read(byte[] b) throws IOException
//从输入流中读取若干字节到指定缓冲区,返回实际读取的字节数
public void close() throws IOException {} //关闭输入流,空方法
}
a、文件字节输入流 FileInputSream类
public class FileInputStream extends InputStream
{
public FileInputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException
public FileInputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException
}
b、数据字节输入流 DataInputStream类
public class DataInputStream extends FilterInputStream implements DataInput
{
public DataInputStream(InputStream in) //构造方法
public final short readShort() throws IOException
public final byte readByte() throws IOException
public final int readInt() throws IOException //读取整型
public final long readLong() throws IOException
public final float readFloat() throws IOException
public final double readDouble() throws IOException
public final char readChar() throws IOException //读取字符
public final boolean readBoolean() throws IOException
}
c、对象字节输入流
ObjectInputStream类
public class ObjectInputStream extends InputStream implements ObjectInput, ObjectStreamConstants
{
public ObjectInputStream(InputStream in) throws IOException //构造方法
public final Object readObject() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException //读取一个对象
}
(2)OuputStream 抽象字节输出流类
public abstract class OutputStream extends Object implements Closeable, Flushable
{
public abstract void write(int b) throws IOException; //写入一个字节,抽象方法
public void write(byte[] b) throws IOException //将缓冲区中的若干字节写入输出流
public void flush() throws IOException {} //立即传输
public void close() throws IOException {} //关闭输出流,空方法
}
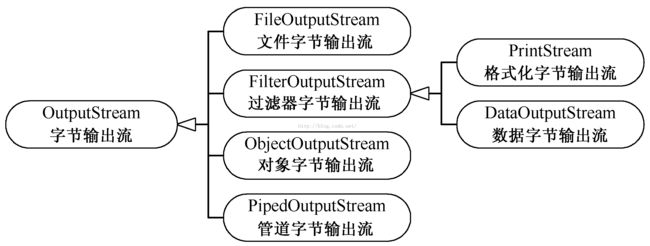
a、文件字节输出流 FileOutputStream类
public class FileOutputStream extends OutputStream
{
public FileOutputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException
public FileOutputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException
public FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) throws FileNotFoundException
}
b、数据字节输出流 DataOutputStream类
public class DataOutputStream extends FilterOutputStream implements DataOutput
{
public DataOutputStream(OutputStream out) //构造方法
public final void writeByte(int v) throws IOException
public final void writeShort(int v) throws IOException
public final void writeInt(int v) throws IOException //写入一个整型
public final void writeLong(long v) throws IOException
public final void writeFloat(float v) throws IOException
public final void writeDouble(double v) throws IOException
public final void writeChar(int v) throws IOException //写入一个字符
public final void writeBoolean(boolean v) throws IOException
public final void writeChars(String s) throws IOException //写入一个字符串
public final int size() //返回实际写入的字节数
}c、对象字节输出流
ObjectOutputStream类
public class ObjectOutputStream extends OutputStream implements ObjectOutput, ObjectStreamConstants
{
public ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out) throws IOException //构造方法
public final void writeObject(Object obj) throws IOException //写入一个对象
}
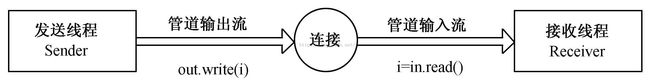
(3)管道字节流
a、PipedInputStream类
b、PipedOutputStream类
PipedInputStream in = new PipedInputStream();
try
{
PipedOutputStream out= new PipedOutputStream(in);
}
catch(IOException ioe) {}
用这个做发牌器就很方便:
2、字符流
(1)抽象字符流
a、Reader类
public abstract class Reader extends Object implements Readable, Closeable
{
public int read() throws IOException
public int read(char cbuf[]) throws IOException
abstract public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
abstract public void close() throws IOException;
}
b、Writer类
public abstract class Writer implements Appendable, Closeable, Flushable
{
public void write(int c) throws IOException
public void write(char[] cbuf) throws IOException
public void write(String str) throws IOException //将字符串写入输出流
public Writer append(CharSequence csq) throws IOException
public Writer append(char c) throws IOException
public abstract void flush() throws IOException //将缓冲区内容写入输出流
public abstract void close() throws IOException
}(2)文件字符流
a、FileReader类
public class FileReader extends InputStreamReader
{
public FileReader(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException //构造方法
public FileReader(File file) throws FileNotFoundException
}
b、 FileWriter类
public class FileWriter extends OutputStreamWriter
{
public FileWriter(String fileName) throws IOException //构造方法
public FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append) throws IOException
public FileWriter(File file) throws IOException
public FileWriter(File file, boolean append) throws IOException
}
(3)缓冲字符流
a、BufferedReader类
public class BufferedReader extends Reader
{
public BufferedReader(Reader in) //构造方法
public String readLine() throws IOException //读取一行字符串,输入流结束时返回null
}
b、BufferedWriter类
public class BufferedWriter extends Writer
{
public BufferedWriter(Writer out) //构造方法
public BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz) //sz指定字符缓冲区长度
public void newLine() throws IOException //写入一个换行符
}
3、文件操作
(1)文件操作类
a、File类的构造方法
public class File extends Object implements Serializable, Comparable<File>
{
public File(String pathname)
public File(String parent, String child)
public File(File parent, String child)
}例如:
File file = new File("myfile.txt");
File dir = new File(".",""); //创建一个目录文件对象,表示当前目录
File dir = new File("C:","");
b、File类提供的方法
public String getName() //返回文件名,不包含路径名 public String getPath() //返回相对路径名,包含文件名 public String getAbsolutePath() //返回绝对路径名,包含文件名 public String getParent() //返回父文件对象的路径名 public File getParentFile() //返回父文件对象
(2)文件过滤器接口
a、FileFilter和FilenameFilter接口
public interface FileFilter
{
public boolean accept(File pathname)
}
public interface FilenameFilter
{
public boolean accept(File dir, String name)
}b、获得文件列表时使用过滤器
public String[] list(FilenameFilter filter) //过滤显示文件清单 public File[] listFiles(FilenameFilter filter) public File[] listFiles(FileFilter filter)(3)文件对话框组件
a、JFileChooser类
public class JFileChooser extends JComponent implements Accessible
{
public static final int APPROVE_OPTION = 0; //单击“打开”或“保存”按钮
public static final int CANCEL_OPTION = 1; //单击“撤消”按钮
public static final int ERROR_OPTION = -1; //出错
public JFileChooser()
public JFileChooser(String currentDirectoryPath) //初始路径
public JFileChooser(File currentDirectory)
public void setFileFilter(FileFilter filter) //设置文件过滤器
public int showOpenDialog(Component parent) throws HeadlessException
//显示打开文件对话框
public int showSaveDialog(Component parent) throws HeadlessException
//显示保存文件对话框
public File getSelectedFile() //返回选中文件
}
b、JFileChooser的文件过滤器
public abstract class FileFilter extends Object
{
public abstract boolean accept(File f)
//过滤操作,f指定待过滤文件
public abstract String getDescription() //文件类型描述字符串
}
ex
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FilenameFilter;
import javax.swing.JFileChooser;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class DirFilter implements FilenameFilter{ //2
private String prefix="";
private String extension="";
public DirFilter(String filterstr, File dir) {
filterstr = filterstr.toLowerCase();
//取前缀
int i= filterstr.indexOf('*');
if(i>0){
this.prefix = filterstr.substring(0,i);
}
//取后缀
int j= filterstr.lastIndexOf('.');
this.extension = filterstr.substring(j+1);
if(this.extension.equals("*")){
this.extension="";
}
System.out.println(dir.getAbsolutePath()+"目录中,"+"的文件如下:");
String fileNames[] = dir.list(this); //1
for(String fName:fileNames){
System.out.println(fName);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new DirFilter("*.Java",new File(".","src/cn/hncu/inOut/p29"));
JFileChooser jf = new JFileChooser();
jf.showOpenDialog( new JFrame() );
}
public boolean accept(File dir, String fileName) {
fileName = fileName.toLowerCase();
return fileName.startsWith(this.prefix) && fileName.endsWith(extension);
}
}
(4)随机存取文件类
public class RandomAccessFile extends Object implements DataOutput, DataInput, Closeable
{
public RandomAccessFile(String name, String mode) throws FileNotFoundException
public RandomAccessFile(File file, String mode) throws FileNotFoundException
public final int readInt() throws IOException
//读一个整数类型值,当读到文件尾时,抛出EOFException异常
public final void writeInt(int v) throws IOException //写入一个整型值
public long length() throws IOException //返回文件长度
public long getFilePointer() throws IOException //获取文件指针位置
public void seek(long pos) throws IOException //设置文件指针位置
public void close() throws IOException //关闭文件
}
4、各种输入/输出流及其读/写方法
数据字节流ex
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class MyDataInOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// writeToFile();
readFromFile();
}
private static void writeToFile() {
OutputStream fout = null;
DataOutputStream dout = null;
try {
fout = new FileOutputStream("d:\\ex\\a\\a.txt");//目录必须已存在
dout = new DataOutputStream(fout);
for(int i=1;i<=100;i++){
dout.writeInt(i);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (Exception e) {
}finally{
try {
fout.close();
dout.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件无法关闭");
}
}
}
private static void readFromFile() {
FileInputStream fin = null;
DataInputStream din = null;
try {
fin = new FileInputStream("d:\\ex\\a\\a.txt");
din = new DataInputStream(fin);
while(din.available()>0){
System.out.print( din.readInt() +" ");
}
System.out.println();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (Exception e) {
}finally{
try {
fin.close();
din.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件无法关闭");
}
}
}
}
对象字节流ex
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class MyObjectOutputStream extends ObjectOutputStream {
//定义成静态的好处
private static File f;
public static MyObjectOutputStream newInstance(File file, OutputStream out)
throws IOException {
f = file;//本方法最重要的地方:构建文件对象,是两个文件对象属于同一个
return new MyObjectOutputStream(out, f);
}
@Override
protected void writeStreamHeader() throws IOException {
if (!f.exists() || (f.exists() && f.length() == 0)) {
super.writeStreamHeader();
} else {
super.reset();
}
}
public MyObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out, File f) throws IOException {
super(out);
}
}
文件字节流ex
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyFileInOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//readFromFile();
writeToFile();
}
private static void readFromFile() {
byte buffer[] = new byte[512];
int num=0;
try {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\\ex\\a\\a.txt");
num = in.read(buffer);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
//System.out.print(buffer[i]+" ");
System.out.print((char)buffer[i]+" ");
}
//System.out.println();
}
private static void writeToFile(){
try {
//FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("d:/ex/a/b.dat");//覆盖
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("d:/ex/a/b.dat",true);//追加
byte[] buffer = {13,10,97,98,99,100,101,102,49,55};
out.write(buffer);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
管道字节流(模拟发牌器)ex
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PipedInputStream;
import java.io.PipedOutputStream;
public class SendCard {
PipedInputStream[] in;
PipedOutputStream[] out;
int data[][]; //data[n][max/n],保存n个接收线程分别保存的牌
public SendCard(int max, int n) throws IOException{
in = new PipedInputStream[n];
out = new PipedOutputStream[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
in[i] = new PipedInputStream();
out[i] = new PipedOutputStream(in[i]);
}
Sender s = new Sender(out,max);
s.start();
data = new int[n][max/n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
new Receiver(in[i],data[i]).start();
}
}
public void print(){
System.out.println();
for(int i=0;i<data.length; i++){
System.out.print("Receiver"+(i+1)+": ");
for(int j=0; j<data[i].length; j++){
System.out.print(data[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
SendCard sc = new SendCard(52,4);
Thread.sleep(1);
sc.print();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
结果:Sender:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
Receiver1: 1 5 9 13 17 21 25 29 33 37 41 45 49
Receiver2: 2 6 10 14 18 22 26 30 34 38 42 46 50
Receiver3: 3 7 11 15 19 23 27 31 35 39 43 47 51
Receiver4: 4 8 12 16 20 24 28 32 36 40 44 48 52
文件拷贝ex
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileCopyStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//fileCopy0("b.dat","d:/ex/a/","d:/ex/b/");
//fileCopy1("b.dat","d:/ex/a/","d:/ex/b/");
//fileCopy2("b.dat","d:/ex/a/","d:/ex/b/");
fileCopy3("1.mp3","d:/ex/a/","d:/ex/b/");
//fileCopy3("c.mp3","d:/ex/a/","d:/ex/b/");
//fileCopy3("d.txt","d:/ex/a/","d:/ex/b/");
}
private static void fileCopy0(String fileName, String dir1,String dir2){
try {
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(dir1+fileName);
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dir2+fileName);
byte[] buffer = new byte[512];
in.read(buffer);
out.write(buffer);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
//学习关流
private static void fileCopy1(String fileName, String dir1,String dir2){
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream(dir1+fileName);
out = new FileOutputStream(dir2+fileName);
byte[] buffer = new byte[512];
in.read(buffer);
out.write(buffer);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally{
try {
in.close();
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("文件无法关闭");
}
}
}
//能够拷贝大文件
private static void fileCopy2(String fileName, String dir1,String dir2){
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream(dir1+fileName);
out = new FileOutputStream(dir2+fileName);
byte[] buffer = new byte[512];
int num = 0;
do{
num = in.read(buffer);
out.write(buffer,0,num);
}while(num>=0);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
in.close();
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("文件无法关闭");
}
}
}
//能够拷贝大文件
private static void fileCopy3(String fileName, String dir1,String dir2){
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream(dir1+fileName);
out = new FileOutputStream(dir2+fileName);
byte[] buffer = new byte[512];
int num=0;
while(in.available()>0){
num = in.read(buffer);
//最简单的加密
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
buffer[i] = (byte)(buffer[i]+1);
}
out.write(buffer,0,num);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
}finally{
try {
in.close();
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("文件无法关闭");
}
}
}
}
字符流ex
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyReaderWriter {
private static final String LINE_SEPARATOR = System
.getProperty("line.separator");
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// writeToFile();
//readFromFile();
copyFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// writeToFile2();
}
private static void writeToFile() throws IOException {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("aw.txt");
fw.write("abcdkk");
// fw.write("\n");
// fw.write("\r\n");
fw.write(LINE_SEPARATOR);
fw.write("城市海陆空");
// fw.flush();
fw.close();
}
/* 用字符流写文件,模板 */
private static void writeToFile2() {
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter("aw.txt");
fw.write("abcdkk");
fw.write(LINE_SEPARATOR);
fw.write("城市海陆空");
fw.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fw != null) {
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("关闭失败!");
}
}
}
}
private static void readFromFile() throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("aw.txt");
//char c = (char) fr.read();
//System.out.println(c);
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
int num;
while((num=fr.read(buffer))!=-1){
System.out.println( new String(buffer,0,num) );
}
}
//用字符流拷贝,是不能拷非文本文件,会失真!
private static void copyFile() throws IOException{
FileReader fr = new FileReader("d:/ex/a/a.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("d:/ex/a/b.txt");
char[] buffer = new char[512];
int len=0;
while((len=fr.read(buffer))!=-1){
fw.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
}
强化篇
一、RandomAccessFile
1、随机访问文件,自身具备读写的方法
new RandomAccessFile()之后,若文件不存在会自动创建,存在则不创建。——该类其实内部既封装了字节输入流,又封装了字节输出流。
该类若用write()方法写整数,每次只写它的最后一个字节。而采用writeInt()方法,则可把一个整数完整地写入。
2、通过skipBytes(int x),seek(int x)来达到随机访问
通过seek方法设置数据的指针就可以实现对文件数据的随机读写。InputStream中的skip()方法只能从头往后跳,不能反向;而seek()方法可双向随便定位。
3、数据修改方面的特点
用RandomAccessFile类可以实现数据的修改,当然文件中的数据一般要有规律,以方便在编程时能够进行定位,让数据写对地方。 而用“流”实现数据修改时,则通常需要把数据从流读到数组当中,在数组中进行数据修改,然后再把修改后的数组
再重新写到流中。
/*
* 用IO流读取数据时,游标是会自动走的。
* 而RandomAccessFile的游标是不会自动向前移动的,要自己控制的
*
* 1)用RandomAccessFile类访问数据表记录的速度比Object流更快,因为后者查找匹配的是一个对象
* 2)InputStream类中的skip()方法只能从头往后跳,不能反向。而RandomAccessFile类中的seek()定位,可以双向随意定位。
* 3)如果存储的数据有规律(比如,数据库表中的数据),应该采用RandomAccessFile
*/
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
public class RandomAcessFileDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
write2File();
readFromFile();
}
private static void write2File() {
RandomAccessFile rf = null;
try {
rf = new RandomAccessFile("d:/ex/a/r4.txt", "rw");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
rf.writeDouble(3.14f*i);
}
rf.seek(16);//绝对定位
rf.writeDouble(0);
rf.seek(rf.length());
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
rf.writeInt(15*i);
rf.writeByte(5*i);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (rf != null) {
try {
rf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("关流失败");
}
}
}
}
private static void readFromFile() {
RandomAccessFile rf = null;
try {
rf = new RandomAccessFile("d:/ex/a/r4.txt", "r");
// long pointer = 0;//自己控制游标
// long len = rf.length();
// //rf.skipBytes(2);//写入的是浮点,不需要跳
// while (pointer < len) {
// double d = rf.readDouble();
// System.out.println(d);
// pointer = rf.getFilePointer();
// }
// rf.seek(48);
// double d = rf.readDouble();
// System.out.println(d);
rf.seek(85);
int x = rf.readInt();
System.out.println(x);
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (rf != null) {
try {
rf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("关流失败");
}
}
}
}
}
二、序列化
1、序列化
将一个对象存放到某种类型的永久存储器上称为保持。如果一个对象可以被存放到磁盘或磁带上,或者可以发送到另外一台机器并存放到存储器或磁盘上,那么这个对象就被称为可保持的。(在Java中,序列化、持久化、串行化是一个概念。)
java.io.Serializable接口没有任何方法,它只作为一个“标记者”,用来表明实现了这个接口的类可以考虑串行化。类中没有实现Serializable的对象不能保存或恢复它们的状态。
2、对象图
当一个对象被串行化时,只有对象的数据被保存;方法和构造函数不属于串行化流。如果一个数据变量是一个对象,那么这个对象的数据成员也会被串行化。树或者对象数据的结构,包括这些子对象,构成了对象图。
3、瞬时 transient
防止对象的属性被序列化。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class TestSerializable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//序列化---写(输出)到永久存储器
FileOutputStream fout = null;
try {
fout = new FileOutputStream("a.txt");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fout);
//Address类必须要实现Serializable接口,否则不能序列化
// out.writeObject(new Address("aa",11,"12345678908"));
// out.writeObject(new Address("bb",22,"12345888888"));
// out.writeObject(new Address("cc",33,"12345666666"));
// out.writeObject(new Address("dd",44,"12345777777"));
out.writeObject(new Address(1,"aa",11,"12345678908"));
out.writeObject(new Address(5,"bb",22,"12345888888"));
//线程Thread本身是没有实现Serializable接口的,因此不能序列化
//Thread t1 = new Thread();
//out.writeObject(t1);
//如果自定义线程类实现了Serializable接口,则可以序列化
MyThread mt1 = new MyThread();
out.writeObject(mt1);
//反序列化----从永久存储器读取(输入)数据
FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(fin);
System.out.println(in.readObject());
System.out.println(in.readObject());
System.out.println(in.readObject());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(fout!=null){
try {
fout.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("关流失败!");
}
}
}
}
}
class Address implements Serializable{
transient int num; //瞬时变量,不会被序列化
String name;
int age;
String tel;
public Address(int num, String name, int age, String tel) {
this.num = num;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.tel = tel;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address [num=" + num + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age
+ ", tel=" + tel + "]";
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread implements Serializable{
}
三、缓冲输入输出流(BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream)
方式1:(方案1是最优的)
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("Test.txt") );
方式2:
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(
new FileInputStream("Test.txt") );
方式3:
BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(
new DataInputStream(
new FileInputStream("Test.java") );1)有buffer比没有更快;
2)buffer放在中间层包装比放在外层更快;
3)按行或按块操作 比 按字节或字符操作更快(用Object流操作的速度 比 字节字符方式 更快)
4)缓冲区要结合流才可以使用,在流的基础上对流的功能进行了增强。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class BufferedStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//testRead1();
//testRead2();
testRead3();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void testRead1() throws Exception{
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();//起始时间
DataInputStream din = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("test.xyz")));
String strLine="";
while((strLine=din.readLine())!=null ){
System.out.println(strLine);
}
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();//终止时间
System.out.println("case1-time:"+(t2-t1));
}
public static void testRead2() throws Exception{
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();//起始时间
DataInputStream din = new DataInputStream(
new FileInputStream("test.xyz"));
String strLine="";
while((strLine=din.readLine())!=null ){
System.out.println(strLine);
}
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();//终止时间
System.out.println("case2-time:"+(t2-t1));
}
public static void testRead3() throws Exception{
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();//起始时间
BufferedInputStream din = new BufferedInputStream(
new DataInputStream(
new FileInputStream("test.xyz")));
byte bs[] = new byte[din.available()];
din.read(bs);
System.out.println(new String(bs));
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();//终止时间
System.out.println("case3-time:"+(t2-t1));
}
}
四、转换流(InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter)
1、转换流功能1:充当字节流与字符流之间的桥梁
例:需求:模拟英文聊天程序,要求:
(1) 从键盘录入英文字符,每录一行就把它转成大写输出到控制台;
(2) 保存聊天记录到字节流文件。
要求1的设计分析:a)需要从键盘接收录入,得用System.in,它是字节输入流InputStream;
b)需要处理字符,可以自己把字节强转成字符,也可以用字符流;
c)需要类似readLine的功能,而这个方法在字符流BufferedReader中有(而且该类有缓冲增速)。
综上,采用转换流把字节流转成字符流处理比较合理,即使用InputStreamReader
要求2的设计分析:
a)需要把字符数据按行保存到字节流文件 ;
b)字符流采用BufferedWriter比较合适,因为它有newLine方法且能实现高效;
c)字节流文件,得采用FileOutputStream。
综上,采用转换流把字符流转成字节流处理比较合理,即使用OutputStreamWriter
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class TransStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//输入
InputStream in = System.in;
//System.out.println(in.read());
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(in);
BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(isr);
//String str =bufr.readLine();
//输出
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream("files\\out.txt",true);
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fout);
BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
//聊天
String line=null;
while( (line=bufr.readLine())!=null){
// if(line.equals("over")){
// break;
// }
if("over".equals(line)){//一个好的习惯:把字符串常量放在前面
break;
}
System.out.println(line.toUpperCase());
bufw.write(line.toUpperCase());
bufw.newLine();
bufw.flush();
}
//关流
bufw.close();
osw.close();
fout.close();
bufr.close();
isr.close();
}
}
2、转换流功能2:字符编码转换
a)采用FileWriter以默认方式编码
FileOutputStream+默认编码表
b)采用转换流以默认方式编码
OutputStreamWriter + FileOutputStream + 默认编码表
c)采用转换流以指定编码方式编码
OutputStreamWriter + FileOutputStream +指定编码表
d)采用转换流以指定编码方式解码
InputStreamReader + FileInputStream +指定编码表
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class TransStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//readTestDecoding();
writeTextEncoding();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void readTestDecoding() throws IOException{
//FileReader fr = new FileReader("files\\utf8.txt");//采用默认编码表来解码(而且在MyEclipse中可以更改默认编码)
//FileReader fr = new FileReader("files\\gbk.txt");
// char cbuf[] = new char[50];
// int len = fr.read(cbuf);
// String str = new String(cbuf,0,len);
// System.out.println(str);
// fr.close();
//通过转换流解决乱码
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("files\\gbk.txt"), "gbk");
//InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("files\\utf8.txt"), "utf-8");
char buf[] = new char[50];
int len2 = isr.read(buf);
String str2 = new String(buf,0,len2);
System.out.println(str2);
isr.close();
}
//输出流,字符流的编码解决方案
public static void writeTextEncoding() throws IOException{
//第一种 (使用默认编码表 )
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("files\\gbk-1.txt");
fw.write("每天进步一点点...");
fw.close();//内部含flush()的功能
//第二种(相当于 FileOutputStream+默认编码表 )
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("files\\gbk-2.txt"));
osw.write("每天进步一点点22222...");
osw.close();//内部含flush()的功能
//第三种(既明确字节输出流,又明确编码表 )
OutputStreamWriter osw2 = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("files\\wutf8-1.txt"),"utf-8");
osw2.write("每天进步一点点22222...");
osw2.close();//内部含flush()的功能
}
}
五、打印流(PrintStream和PrintWriter)
1、打印流的特点
1)只有输出没有输入。PrintStream是字节打印流,PrintWriter是字符打印流。
2)能够方便地打印各种数据“值表示形式”,提供了一系列的打印功能(只有它有,其它流都没有。)
3)和其他输出流不同,它永远不会抛出IOException异常(构造方法除外),异常内部解决且设置了内部标志。
4)可创建具有自动刷新的功能,可使用带换行符的println()方法。
5)(在构造方法中)可以指定字符集编码的。
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class PrintStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
try {
printStreamDemo();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
*/
PrintStream outBak = System.out;
changeOut(null);
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
changeOut(outBak);
for(int i=100;i<=110;i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
public static void printStreamDemo()throws IOException{
PrintStream out = new PrintStream("aa.txt");
//out.write(97);//输出该整数的最后一个字节 :97
//out.write(353);//只输出该整数的最后一个字节 : 97 用于计算机内部处理的
out.print(97);//输出该整数的值的表现形式:'9'和'7' 用于给人看的
//out.print(35378332);
}
/*
void print(int i){
out.write(String.valueOf(i));
}
*/
public static void changeOut(PrintStream out0){
PrintStream out=null;
if(out0!=null){
System.setOut(out0);
}else{
try {
out = new PrintStream("aa2.log");
System.setOut(out);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2、关于打印流的自动刷新
只有遇到结束字符(换行符)时才会自动刷新,如在调用其中一个println方法或写入换行符或字节('\n)时会自动刷新输出缓冲区。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class PrintWriterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//encodingDemo();
//autoFlushDemo();
autoFlushDemo2();
}
private static void encodingDemo() throws IOException {
//PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter("gbk.txt");//用默认编码表
//PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter("gbk.txt","utf-8");//指定编码表
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("gbk.txt"),"utf-8"));//要指定编码表,建议最好采用转换流,因为它就是专门用来指定编码的
out.print("中国人民共和国");
out.close(); //字符输出流,一定要刷新flush()。close()方法中带有flush()
}
private static void autoFlushDemo(){
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(System.out,true);//(1)默认不自动刷新,因此下面还是要手动写flush()
out.print("Hello World!");
out.flush();
PrintWriter out2 = new PrintWriter(System.out,true);//(2)默认不自动刷新,因此下面还是要手动写flush()
out2.print("Hello World2!");//不会自动刷新
out2.print("Hello World2!\n");//还是不会自动刷新
out2.println("Hello World3!");//“会”自动刷新
//println,pringf,format会自动刷新
}
//需求:将键盘录入的英文字符转成大写并按行存储到文件中,且带自动刷新功能
private static void autoFlushDemo2()throws IOException{
BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
//PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("recod.txt"));//默认不带自动刷新
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("recod.txt"),true);//默认不带自动刷新
String line = null;
while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null){
if("over".equalsIgnoreCase(line)){
break;
}
//out.write(line.toUpperCase()+"\r\n");
//out.flush();
out.println(line.toUpperCase());
}
}
}
六、序列流、字节数组流
1、SequenceInputStream ——对多个流进行合并
将多个流进行逻辑串联(合并变成一个流,操作起来很方便,因为多个源变成了一个源)
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.SequenceInputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Enumeration;
public class SequenceInputStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
FileInputStream fis1 = new FileInputStream("filesequences\\seq1.txt");
FileInputStream fis2 = new FileInputStream("filesequences\\seq2.txt");
FileInputStream fis3 = new FileInputStream("filesequences\\seq3.txt");
//需要枚举对象,通过Collections.enumeration(Collection t)来实现
ArrayList<FileInputStream> v = new ArrayList<FileInputStream>();
v.add(fis1);
v.add(fis2);
v.add(fis3);
Enumeration<FileInputStream> en = Collections.enumeration(v);
SequenceInputStream sis = new SequenceInputStream(en);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("filesequences\\merge.txt");
byte buf[] = new byte[1024];
int len=0;
while((len=sis.read(buf))!=-1){
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
fos.close();
sis.close();
}
}
2、字节数组流
ByteArrayInputStream与ByteArrayOutputStream
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
public class ByteArrayStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream("dssd2323232".getBytes());
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int ch=0;
while((ch=bis.read())!=-1){
bos.write(ch);
}
System.out.println( bos.toString() );
}
}
七、IO流知识点小结
1、知识点
a、流是用来处理数据的。
b、处理数据时,一定要先明确数据源与数据目的地(数据汇)。
c、数据源可以是文件、键盘或者其他流。
d、数据目的地可以是文件、显示器或者其他流。
e、流只是在帮助数据进行传输,并对传输的数据进行处理,比如过滤处理、转换处理等。
2、 IO流体系
使用要点:看顶层(父类共性功能),用底层(子类具体对象)。
命名规律:每个子类的后缀名都是所属体系的父类的名称,很容易区分所属的体系。
而且每一个子类前缀名都是该子类对象的功能体现。
(掌握IO流体系的要点和规律,开发时设计与查找相应的类就容易多了)
八、IO流的操作规律
1、明确源和目的。
源:InputStream Reader 一定是被读取的。
目的:OutputStream Writer 一定是被写入的。
2、处理的数据是否是纯文本的数据?
是:使用字符流。Reader Writer
否:使用字节流。 InputStream OutputStream
(到这里,两个明确确定完,就可以确定出要使用哪个体系。接下来,就应该明确具体这个体系要使用哪个具体的对象。【所谓的看顶层】)
3、明确数据所在的设备。
源设备:
键盘(System.in)
硬盘(FileXXX)FileReader FileInputStream
内存(数组)ByteArrayInputStream CharArrayReader StringReader
网络(Socket)
目的设备:
显示器(控制台System.out)
硬盘(FileXXX)FileWriter FileOutputStream
内存(数组)ByteArrayOutputStream CharArrayWriter StringWriter
网络(Socket)
(到这里,具体使用哪个对象就可以明确了。【所谓的用底层】)
4、明确是否需要额外功能?
1) 是否需要高效?缓冲区Buffered (字符与字节各两个)
2) 是否需要转换?转换流 InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter
3) 是否操作基本数据类型? DataInputStream DataOutputStream
4) 是否操作对象(对象序列化)? ObjectInputStream ObjectOutputStream
5) 需要对多个源合并吗? SequenceInputStream
6) 需要保证数据的表现形式到目的地吗? PrintStream 或 PrintWriter
(到这里,具体的设计方案就可以明确了。【套接与功能加强】)
IO流的操作规律之设计方案练习
需求1:复制一个文本文件。
1、明确源和目的。
源:InputStream Reader
目的:OutputStream Writer
2、处理的数据是否是纯文本的数据?
源:Reader
目的:Writer
3、明确数据所在的设备。
源:file(硬盘) FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");
目的:file(硬盘) FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("b.txt");
4、明确是否需要额外功能?
BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt"));
BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("b.txt"));
需求2:复制一个图片文件。
1、明确源和目的。
源:InputStream Reader
目的:OutputStream Writer
2、处理的数据是否是纯文本的数据?
源:Reader
目的:Writer
3、明确数据所在的设备。
源:file(硬盘) FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");
目的:file(硬盘) FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("b.txt");
4、明确是否需要额外功能?
BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt"));
BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("b.txt"));
需求3:读取键盘录入,存储到一个文件中。
1、明确源和目的。
源:InputStream Reader
目的:OutputStream Writer
2、处理的数据是否是纯文本的数据?
源:Reader
目的:Writer
3、明确数据所在的设备。
源:file(硬盘) InputStream in = System.in; 原因:必须要将键盘录入的字节转成字符。需要将字节-->字符的转换流。InputStreamReader
目的:file(硬盘) FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("b.txt");
4、明确是否需要额外功能?
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("a.txt");
高效:BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader( isr);
BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter( fw );
需求4:读取一个文本文件,显示到显示器上。
1、明确源和目的。
源:InputStream Reader
目的:OutputStream Writer
2、处理的数据是否是纯文本的数据?
源:Reader
目的:Writer
3、明确数据所在的设备。
源:file(硬盘) FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");
目的:显示器 OutputStream out = System.out; 原因:要将字符数据转换成字节输出。输出转换流:OutputStreamWriter
4、明确是否需要额外功能?
FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(System.out);
高效:BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader( fr);
BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter( osw );
需求5:读取一个文本文件,将文本按照指定的编码表UTF-8写入到另一个文件中
1、明确源和目的。
源:InputStream Reader
目的:OutputStream Writer
2、处理的数据是否是纯文本的数据?
源:Reader
目的:Writer
3、明确数据所在的设备。
源:file(硬盘) FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");
目的:file(硬盘) FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream("b.txt")原因:假定输出时要为字符数据指定编码表。转换流中的参数需要字节流,因此用转换流:FileOutputStream。
4、明确是否需要额外功能?
FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fout,”utf-8”);
高效:BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader( fr);
BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter( osw );
九、两大例题
1、文件切割与合并
点击打开链接
2、字符串截取
点击打开链接
虽然看上去很多,其实仔细看看也没什么,无非是看懂加强片中的八中所讲的内容,就可以随手写io了。