QT分析之网络编程
原文地址:http://blog.163.com/net_worm/blog/static/127702419201002842553382/
首先对Windows下的网络编程总结一下:
如果是服务器,其WinSDK调用分别为:
1 WSAStartup() -> socket() -> htons() / htonl() -> bind() -> listen() -> accept() -> recv() / send() -> closesocket() -> WSACleanup()
如果是客户端程序,其调用序列为:
1 WSAStartup() -> socket() -> htons() / htonl() -> connect() -> recv() / send() -> closesocket() -> WSACleanup()
前面转贴的客户端(WinSocket温习)程序中,收到信息就在console打印出来然后退出了;在一般的应用中,通常是要一直等待收发消息的,直到程序确认退出才关闭socket。如果用一个轮询就会占用很多的CPU资源,所以很多嵌入式设计中会用一个WaitForMultiObject调用,等待退出命令或者超时,然后退出或进行下一轮信息接受。在Windows平台下也有一些比较高明的设计,使用异步socket,然后用异步选择的办法,实现多线程和事件的并发。在WinSocket中,同样也有一套异步Socket函数,那就是使用WSAAsyncSelect()及其配合函数。具体可以参考MSDN。QT在Windows平台上的实现,肯定也跟这些SDK调用有关。
按照这个思路,果然在QT代码里面找到了Qnativesocketengine_win.cpp,WSAStartup(),WSASocket()等序列WSA函数都有。QNativeSocketEnginePrivate类把这些SDK封装成:createNewSocket()、option()、setOption()、nativeConnect()、nativeBind()、nativeListen()、nativeAccept()、nativeWrite()、nativeRead()、nativeSelect()、nativeClose()等。按照QT的设计,QPrivate类是数据类;Q类应该是主类。接着看QNativeSocket类的继承:
1 QNativeSocketEngine : public QAbstractSocketEngine : public QObject
QAbstractSocketEngine类是使用了大量纯虚函数的定义。继续深入查看,发现大量有关的类:QAbstractSocket,SocketAsyncHandler,QTcpSocket,QUdpSocket等,看来我要先了解下QT网络编程体系再进一步分析之
之前没有看QT自带的文档,看了doc之后对QT的网络体系有一个大致的了解:
QNatvieSocketEnginePrivate是OS相关的API封装,和QNativeSocketEngine一起构成具体平台SOCKET实现;
QTcpSocket、QUdpSocket、QTcpServer构成底层的应用API;QSslSocket是SSL加密相关API;
QHttp、QFtp构成高层次应该API;
QNetworkAccessManager、QNetworkRequest、QNetworkReply是高度抽象的网络层。
分析TCP的例子fortuneclient,运行起来按了[Get
Fortune]按钮之后,调用的是Client::requestNewFortune()。
1 void Client::requestNewFortune() 2 { 3 getFortuneButton->setEnabled(false); 4 blockSize = 0; 5 tcpSocket->abort(); 6 tcpSocket->connectToHost(hostLineEdit->text(), portLineEdit->text().toInt()); 7 }
具体看QTcpSocket::connectToHost()的代码
1 void QAbstractSocket::connectToHost(const QString &hostName, quint16 port, 2 OpenMode openMode) 3 { 4 QMetaObject::invokeMethod(this, "connectToHostImplementation", 5 Qt::DirectConnection, 6 Q_ARG(QString, hostName), 7 Q_ARG(quint16, port), 8 Q_ARG(OpenMode, openMode)); 9 }
调用的是QAbstractSocket::connectToHostImplementation()。
1 void QAbstractSocket::connectToHostImplementation(const QString &hostName, quint16 port, 2 OpenMode openMode) 3 { 4 Q_D(QAbstractSocket); 5 if (d->state == ConnectedState || d->state == ConnectingState || d->state == ClosingState) { 6 qWarning("QAbstractSocket::connectToHost() called when already connecting/connected to \"%s\"", qPrintable(hostName)); 7 return; 8 } 9 10 d->hostName = hostName; 11 d->port = port; 12 d->state = UnconnectedState; 13 d->readBuffer.clear(); 14 d->writeBuffer.clear(); 15 d->abortCalled = false; 16 d->closeCalled = false; 17 d->pendingClose = false; 18 d->localPort = 0; 19 d->peerPort = 0; 20 d->localAddress.clear(); 21 d->peerAddress.clear(); 22 d->peerName = hostName; 23 if (d->hostLookupId != -1) { 24 QHostInfo::abortHostLookup(d->hostLookupId); 25 d->hostLookupId = -1; 26 } 27 28 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY 29 // Get the proxy information 30 d->resolveProxy(hostName, port); 31 if (d->proxyInUse.type() == QNetworkProxy::DefaultProxy) { 32 // failed to setup the proxy 33 d->socketError = QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError; 34 setErrorString(QAbstractSocket::tr("Operation on socket is not supported")); 35 emit error(d->socketError); 36 return; 37 } 38 #endif 39 40 if (!d_func()->isBuffered) 41 openMode |= QAbstractSocket::Unbuffered; 42 QIODevice::open(openMode); // ?? 43 d->state = HostLookupState; 44 emit stateChanged(d->state); 45 46 QHostAddress temp; 47 if (temp.setAddress(hostName)) { 48 QHostInfo info; 49 info.setAddresses(QList<QHostAddress>() << temp); 50 d->_q_startConnecting(info); 51 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY 52 } else if (d->proxyInUse.capabilities() & QNetworkProxy::HostNameLookupCapability) { 53 // the proxy supports connection by name, so use it 54 d->startConnectingByName(hostName); 55 return; 56 #endif 57 } else { 58 if (d->threadData->eventDispatcher) 59 d->hostLookupId = QHostInfo::lookupHost(hostName, this, SLOT(_q_startConnecting(QHostInfo))); 60 } 61 }
继续调用QAbstractSocket::_q_startConnecting(),是QAbstractSocket的私有信号。简单来说,_q_startConnecting()就是调用了_q_connectToNextAddress()而已。
1 void QAbstractSocketPrivate::_q_connectToNextAddress() 2 { 3 Q_Q(QAbstractSocket); 4 do { 5 // Check for more pending addresses 6 if (addresses.isEmpty()) { 7 state = QAbstractSocket::UnconnectedState; 8 if (socketEngine) { 9 if ((socketEngine->error() == QAbstractSocket::UnknownSocketError 10 ) && socketEngine->state() == QAbstractSocket::ConnectingState) { 11 socketError = QAbstractSocket::ConnectionRefusedError; 12 q->setErrorString(QAbstractSocket::tr("Connection refused")); 13 } else { 14 socketError = socketEngine->error(); 15 q->setErrorString(socketEngine->errorString()); 16 } 17 } else { 18 // socketError = QAbstractSocket::ConnectionRefusedError; 19 // q->setErrorString(QAbstractSocket::tr("Connection refused")); 20 } 21 emit q->stateChanged(state); 22 emit q->error(socketError); 23 return; 24 } 25 26 // Pick the first host address candidate 27 host = addresses.takeFirst(); 28 29 #if defined(QT_NO_IPV6) 30 if (host.protocol() == QAbstractSocket::IPv6Protocol) { 31 // If we have no IPv6 support, then we will not be able to 32 // connect. So we just pretend we didn't see this address. 33 continue; 34 } 35 #endif 36 37 if (!initSocketLayer(host.protocol())) { 38 // hope that the next address is better 39 continue; 40 } 41 42 // Tries to connect to the address. If it succeeds immediately 43 // (localhost address on BSD or any UDP connect), emit 44 // connected() and return. 45 if (socketEngine->connectToHost(host, port)) { 46 //_q_testConnection(); 47 fetchConnectionParameters(); 48 return; 49 } 50 51 // cache the socket descriptor even if we're not fully connected yet 52 cachedSocketDescriptor = socketEngine->socketDescriptor(); 53 54 // Check that we're in delayed connection state. If not, try 55 // the next address 56 if (socketEngine->state() != QAbstractSocket::ConnectingState) { 57 continue; 58 } 59 60 // Start the connect timer. 61 if (threadData->eventDispatcher) { 62 if (!connectTimer) { 63 connectTimer = new QTimer(q); 64 QObject::connect(connectTimer, SIGNAL(timeout()), 65 q, SLOT(_q_abortConnectionAttempt()), 66 Qt::DirectConnection); 67 } 68 connectTimer->start(QT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT); 69 } 70 71 // Wait for a write notification that will eventually call 72 // _q_testConnection(). 73 socketEngine->setWriteNotificationEnabled(true); 74 break; 75 } while (state != QAbstractSocket::ConnectedState); 76 }
上面关键的三句,实际是把WinSocket编程中的简单过程分成三个阶段:socket初始化;connect到远程目标;设定Timer定时查看并处理Select的情况(收发数据或者关闭socket)。这里主要看前面两个:初始化和连接,select的处理放到明天分析。
1、初始化
1 bool QAbstractSocketPrivate::initSocketLayer(QAbstractSocket::NetworkLayerProtocol protocol) 2 { 3 #ifdef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY 4 // this is here to avoid a duplication of the call to createSocketEngine below 5 static const QNetworkProxy &proxyInUse = *(QNetworkProxy *)0; 6 #endif 7 8 Q_Q(QAbstractSocket); 9 10 resetSocketLayer(); 11 socketEngine = QAbstractSocketEngine::createSocketEngine(q->socketType(), proxyInUse, q); 12 if (!socketEngine) { 13 socketError = QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError; 14 q->setErrorString(QAbstractSocket::tr("Operation on socket is not supported")); 15 return false; 16 } 17 if (!socketEngine->initialize(q->socketType(), protocol)) { 18 socketError = socketEngine->error(); 19 q->setErrorString(socketEngine->errorString()); 20 return false; 21 } 22 23 if (threadData->eventDispatcher) 24 socketEngine->setReceiver(this); 25 26 return true; 27 } 28 29 QAbstractSocketEngine *QAbstractSocketEngine::createSocketEngine(QAbstractSocket::SocketType socketType, const QNetworkProxy &proxy, QObject *parent) 30 { 31 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY 32 // proxy type must have been resolved by now 33 if (proxy.type() == QNetworkProxy::DefaultProxy) 34 return 0; 35 #endif 36 37 QMutexLocker locker(&socketHandlers()->mutex); 38 for (int i = 0; i < socketHandlers()->size(); i++) { 39 if (QAbstractSocketEngine *ret = socketHandlers()->at(i)->createSocketEngine(socketType, proxy, parent)) 40 return ret; 41 } 42 43 return new QNativeSocketEngine(parent); 44 }
上面可以知道socketEngine->initialize()实际调用的是QNativeSocketEngine::initialize()
1 bool QNativeSocketEngine::initialize(QAbstractSocket::SocketType socketType, QAbstractSocket::NetworkLayerProtocol protocol) 2 { 3 Q_D(QNativeSocketEngine); 4 if (isValid()) 5 close(); 6 7 #if defined(QT_NO_IPV6) 8 if (protocol == QAbstractSocket::IPv6Protocol) { 9 d->setError(QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError, 10 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::NoIpV6ErrorString); 11 return false; 12 } 13 #endif 14 15 // Create the socket 16 if (!d->createNewSocket(socketType, protocol)) { 17 return false; 18 } 19 20 // Make the socket nonblocking. 21 if (!setOption(NonBlockingSocketOption, 1)) { 22 d->setError(QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError, 23 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::NonBlockingInitFailedErrorString); 24 close(); 25 return false; 26 } 27 28 // Set the broadcasting flag if it's a UDP socket. 29 if (socketType == QAbstractSocket::UdpSocket 30 && !setOption(BroadcastSocketOption, 1)) { 31 d->setError(QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError, 32 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::BroadcastingInitFailedErrorString); 33 close(); 34 return false; 35 } 36 37 // Make sure we receive out-of-band data 38 if (socketType == QAbstractSocket::TcpSocket 39 && !setOption(ReceiveOutOfBandData, 1)) { 40 qWarning("QNativeSocketEngine::initialize unable to inline out-of-band data"); 41 } 42 43 // Set the send and receive buffer sizes to a magic size, found 44 // most optimal for our platforms. 45 setReceiveBufferSize(49152); 46 setSendBufferSize(49152); 47 48 d->socketType = socketType; 49 d->socketProtocol = protocol; 50 return true; 51 }
至此,初始化过程完成,socket被设定为非阻塞模式(也就是Select会超时方式)。
2、connect到远程目标
1 bool QNativeSocketEngine::connectToHost(const QHostAddress &address, quint16 port) 2 { 3 Q_D(QNativeSocketEngine); 4 Q_CHECK_VALID_SOCKETLAYER(QNativeSocketEngine::connectToHost(), false); 5 6 #if defined (QT_NO_IPV6) 7 if (address.protocol() == QAbstractSocket::IPv6Protocol) { 8 d->setError(QAbstractSocket::UnsupportedSocketOperationError, 9 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::NoIpV6ErrorString); 10 return false; 11 } 12 #endif 13 if (!d->checkProxy(address)) 14 return false; 15 16 Q_CHECK_STATES(QNativeSocketEngine::connectToHost(), 17 QAbstractSocket::UnconnectedState, QAbstractSocket::ConnectingState, false); 18 19 d->peerAddress = address; 20 d->peerPort = port; 21 bool connected = d->nativeConnect(address, port); 22 if (connected) 23 d->fetchConnectionParameters(); 24 25 return connected; 26 }
连接相对简单。
3、读取信息
在QAbstractSocket中,有两个成员是收发数据用的:readData()、writeData()
readData()有两种读取方式:有缓冲和无缓冲方式。基本原理是一致的,简单其见只分析无缓冲直接读取方式。
1 qint64 QAbstractSocket::readData(char *data, qint64 maxSize) 2 { 3 Q_D(QAbstractSocket); 4 if (d->socketEngine && !d->socketEngine->isReadNotificationEnabled() && d->socketEngine->isValid()) 5 d->socketEngine->setReadNotificationEnabled(true); 6 7 if (!d->isBuffered) { 8 if (!d->socketEngine) 9 return -1; // no socket engine is probably EOF 10 qint64 readBytes = d->socketEngine->read(data, maxSize); 11 if (readBytes < 0) { 12 d->socketError = d->socketEngine->error(); 13 setErrorString(d->socketEngine->errorString()); 14 } 15 if (!d->socketEngine->isReadNotificationEnabled()) 16 d->socketEngine->setReadNotificationEnabled(true); 17 return readBytes; 18 } 19 20 if (d->readBuffer.isEmpty()) 21 // if we're still connected, return 0 indicating there may be more data in the future 22 // if we're not connected, return -1 indicating EOF 23 return d->state == QAbstractSocket::ConnectedState ? qint64(0) : qint64(-1); 24 25 // If readFromSocket() read data, copy it to its destination. 26 if (maxSize == 1) { 27 *data = d->readBuffer.getChar(); 28 return 1; 29 } 30 31 qint64 bytesToRead = qMin(qint64(d->readBuffer.size()), maxSize); 32 qint64 readSoFar = 0; 33 while (readSoFar < bytesToRead) { 34 const char *ptr = d->readBuffer.readPointer(); 35 int bytesToReadFromThisBlock = qMin(int(bytesToRead - readSoFar), 36 d->readBuffer.nextDataBlockSize()); 37 memcpy(data + readSoFar, ptr, bytesToReadFromThisBlock); 38 readSoFar += bytesToReadFromThisBlock; 39 d->readBuffer.free(bytesToReadFromThisBlock); 40 } 41 42 return readSoFar; 43 }
从前面(二)可以知道,socketEngine->read()实际调用的是QNativeSocketEngine::read()
1 qint64 QNativeSocketEngine::read(char *data, qint64 maxSize) 2 { 3 Q_D(QNativeSocketEngine); 4 Q_CHECK_VALID_SOCKETLAYER(QNativeSocketEngine::read(), -1); 5 Q_CHECK_STATES(QNativeSocketEngine::read(), QAbstractSocket::ConnectedState, QAbstractSocket::BoundState, -1); 6 7 qint64 readBytes = d->nativeRead(data, maxSize); 8 9 // Handle remote close 10 if (readBytes == 0 && d->socketType == QAbstractSocket::TcpSocket) { 11 d->setError(QAbstractSocket::RemoteHostClosedError, 12 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::RemoteHostClosedErrorString); 13 close(); 14 return -1; 15 } 16 return readBytes; 17 }
除了一些相关的检查,就是调用QNativeSocketPrivate::nativeRead()
1 qint64 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::nativeRead(char *data, qint64 maxLength) 2 { 3 qint64 ret = -1; 4 WSABUF buf; 5 buf.buf = data; 6 buf.len = maxLength; 7 DWORD flags = 0; 8 DWORD bytesRead = 0; 9 #if defined(Q_OS_WINCE) 10 WSASetLastError(0); 11 #endif 12 if (::WSARecv(socketDescriptor, &buf, 1, &bytesRead, &flags, 0,0) == SOCKET_ERROR) { 13 int err = WSAGetLastError(); 14 WS_ERROR_DEBUG(err); 15 switch (err) { 16 case WSAEWOULDBLOCK: 17 ret = -2; 18 break; 19 case WSAEBADF: 20 case WSAEINVAL: 21 setError(QAbstractSocket::NetworkError, ReadErrorString); 22 break; 23 case WSAECONNRESET: 24 case WSAECONNABORTED: 25 // for tcp sockets this will be handled in QNativeSocketEngine::read 26 ret = 0; 27 break; 28 default: 29 break; 30 } 31 } else { 32 if (WSAGetLastError() == WSAEWOULDBLOCK) 33 ret = -2; 34 else 35 ret = qint64(bytesRead); 36 } 37 38 return ret; 39 }
至此,调用Windows API读取数据。
4、发送数据
同样分有缓存与无缓存方式,对无缓存方式:
1 qint64 QAbstractSocket::writeData(const char *data, qint64 size) 2 { 3 Q_D(QAbstractSocket); 4 if (d->state == QAbstractSocket::UnconnectedState) { 5 d->socketError = QAbstractSocket::UnknownSocketError; 6 setErrorString(tr("Socket is not connected")); 7 return -1; 8 } 9 10 if (!d->isBuffered) { 11 qint64 written = d->socketEngine->write(data, size); 12 if (written < 0) { 13 d->socketError = d->socketEngine->error(); 14 setErrorString(d->socketEngine->errorString()); 15 } else if (!d->writeBuffer.isEmpty()) { 16 d->socketEngine->setWriteNotificationEnabled(true); 17 } 18 if (written >= 0) 19 emit bytesWritten(written); 20 return written; 21 } 22 23 char *ptr = d->writeBuffer.reserve(size); 24 if (size == 1) 25 *ptr = *data; 26 else 27 memcpy(ptr, data, size); 28 29 qint64 written = size; 30 31 if (d->socketEngine && !d->writeBuffer.isEmpty()) 32 d->socketEngine->setWriteNotificationEnabled(true); 33 return written; 34 }
查看QNativeSocketEngine::write():
1 qint64 QNativeSocketEngine::write(const char *data, qint64 size) 2 { 3 Q_D(QNativeSocketEngine); 4 Q_CHECK_VALID_SOCKETLAYER(QNativeSocketEngine::write(), -1); 5 Q_CHECK_STATE(QNativeSocketEngine::write(), QAbstractSocket::ConnectedState, -1); 6 return d->nativeWrite(data, size); 7 } 8 9 qint64 QNativeSocketEnginePrivate::nativeWrite(const char *data, qint64 len) 10 { 11 Q_Q(QNativeSocketEngine); 12 qint64 ret = 0; 13 // don't send more than 49152 per call to WSASendTo to avoid getting a WSAENOBUFS 14 for (;;) { 15 qint64 bytesToSend = qMin<qint64>(49152, len - ret); 16 WSABUF buf; 17 buf.buf = (char*)data + ret; 18 buf.len = bytesToSend; 19 DWORD flags = 0; 20 DWORD bytesWritten = 0; 21 22 int socketRet = ::WSASend(socketDescriptor, &buf, 1, &bytesWritten, flags, 0,0); 23 24 ret += qint64(bytesWritten); 25 26 if (socketRet != SOCKET_ERROR) { 27 if (ret == len) 28 break; 29 else 30 continue; 31 } else if (WSAGetLastError() == WSAEWOULDBLOCK) { 32 break; 33 } else { 34 int err = WSAGetLastError(); 35 WS_ERROR_DEBUG(err); 36 switch (err) { 37 case WSAECONNRESET: 38 case WSAECONNABORTED: 39 ret = -1; 40 setError(QAbstractSocket::NetworkError, WriteErrorString); 41 q->close(); 42 break; 43 default: 44 break; 45 } 46 break; 47 } 48 } 49 return ret; 50 }
至此分析完毕。
前面分析中,一个问题一直没有解决:新生成的SOCKET是什么时候加入WSASelect()的?另外还有一个不是很大的问题,close流程。
在
1 QEventDispatcherWin32Private::doWsaAsyncSelect()
中WSAAsyncSelect()设置一个断点,观察call stack:
1 QtCored4.dll!QEventDispatcherWin32Private::doWsaAsyncSelect(int socket=0x00001628) 行633 C++ 2 QtCored4.dll!QEventDispatcherWin32::registerSocketNotifier(QSocketNotifier * notifier=0x00c6f248) 行829 C++ 3 QtCored4.dll!QSocketNotifier::QSocketNotifier(int socket=0x00001628, QSocketNotifier::Type type=Write, QObject * parent=0x00c66228) 行185 C++ 4 QtNetworkd4.dll!QWriteNotifier::QWriteNotifier(int fd=0x00001628, QNativeSocketEngine * parent=0x00c66228) 行1053 + 0x1a 字节 C++ 5 QtNetworkd4.dll!QNativeSocketEngine::setWriteNotificationEnabled(bool enable=true) 行1118 + 0x2d 字节 C++ 6 QtNetworkd4.dll!QAbstractSocketPrivate::_q_connectToNextAddress() 行996 C++ 7 QtNetworkd4.dll!QAbstractSocketPrivate::_q_startConnecting(const QHostInfo & hostInfo={...}) 行890 C++ 8 QtNetworkd4.dll!QAbstractSocket::qt_metacall(QMetaObject::Call _c=InvokeMetaMethod, int _id=0x0000000a, void * * _a=0x00c6e510) 行104 + 0x16 字节 C++ 9 QtNetworkd4.dll!QTcpSocket::qt_metacall(QMetaObject::Call _c=InvokeMetaMethod, int _id=0x00000012, void * * _a=0x00c6e510) 行58 + 0x14 字节 C++ 10 QtCored4.dll!QMetaCallEvent::placeMetaCall(QObject * object=0x00c4f790) 行478 C++ 11 QtCored4.dll!QObject::event(QEvent * e=0x00c4d8a0) 行1102 + 0x14 字节 C++ 12 QtGuid4.dll!QApplicationPrivate::notify_helper(QObject * receiver=0x00c4f790, QEvent * e=0x00c4d8a0) 行4065 + 0x11 字节 C++ 13 QtGuid4.dll!QApplication::notify(QObject * receiver=0x00c4f790, QEvent * e=0x00c4d8a0) 行3605 + 0x10 字节 C++ 14 QtCored4.dll!QCoreApplication::notifyInternal(QObject * receiver=0x00c4f790, QEvent * event=0x00c4d8a0) 行610 + 0x15 字节 C++ 15 QtCored4.dll!QCoreApplication::sendEvent(QObject * receiver=0x00c4f790, QEvent * event=0x00c4d8a0) 行213 + 0x39 字节 C++ 16 QtCored4.dll!QCoreApplicationPrivate::sendPostedEvents(QObject * receiver=0x00000000, int event_type=0x00000000, QThreadData * data=0x00bc8890) 行1247 + 0xd 字节 C++ 17 QtCored4.dll!QEventDispatcherWin32::processEvents(QFlags<enum QEventLoop::ProcessEventsFlag> flags={...}) 行679 + 0x10 字节 C++ 18 QtGuid4.dll!QGuiEventDispatcherWin32::processEvents(QFlags<enum QEventLoop::ProcessEventsFlag> flags={...}) 行1182 + 0x15 字节 C++ 19 QtCored4.dll!QEventLoop::processEvents(QFlags<enum QEventLoop::ProcessEventsFlag> flags={...}) 行150 C++ 20 QtCored4.dll!QEventLoop::exec(QFlags<enum QEventLoop::ProcessEventsFlag> flags={...}) 行201 + 0x2d 字节 C++ 21 QtGuid4.dll!QDialog::exec() 行499 C++ 22 fortuneclient.exe!main(int argc=0x00000001, char * * argv=0x00bc8750) 行51 + 0x9 字节 C++ 23 fortuneclient.exe!WinMain(HINSTANCE__ * instance=0x00400000, HINSTANCE__ * prevInstance=0x00000000, char * __formal=0x001520e2, int cmdShow=0x00000001) 行137 + 0x12 字节 C++ 24 fortuneclient.exe!__tmainCRTStartup() 行574 + 0x35 字节 C 25 fortuneclient.exe!WinMainCRTStartup() 行399 C 26 kernel32.dll!7c82f23b()
[下面的框架可能不正确和/或缺失,没有为 kernel32.dll 加载符号]
看QNativeSocketEngine::setWriteNotificationEnabled()的代码实现:
1 void QNativeSocketEngine::setWriteNotificationEnabled(bool enable) 2 { 3 Q_D(QNativeSocketEngine); 4 if (d->writeNotifier) { 5 d->writeNotifier->setEnabled(enable); 6 } else if (enable && d->threadData->eventDispatcher) { 7 d->writeNotifier = new QWriteNotifier(d->socketDescriptor, this); 8 d->writeNotifier->setEnabled(true); 9 } 10 }
在QWriteNotifier对象新建的时候,引起其父类的构建:QSocketNotifier
1 QSocketNotifier::QSocketNotifier(int socket, Type type, QObject *parent) 2 : QObject(parent) 3 { 4 if (socket < 0) 5 qWarning("QSocketNotifier: Invalid socket specified"); 6 sockfd = socket; 7 sntype = type; 8 snenabled = true; 9 10 Q_D(QObject); 11 if (!d->threadData->eventDispatcher) { 12 qWarning("QSocketNotifier: Can only be used with threads started with QThread"); 13 } else { 14 d->threadData->eventDispatcher->registerSocketNotifier(this); 15 } 16 }
原来是通过获取当前线程数据得到Dispatcher的指针(QEventDispatcherWin32),通过其注册QNativeSocketEngine对象自己本身。
1 void QEventDispatcherWin32::registerSocketNotifier(QSocketNotifier *notifier) 2 { 3 Q_ASSERT(notifier); 4 int sockfd = notifier->socket(); 5 int type = notifier->type(); 6 7 Q_D(QEventDispatcherWin32); 8 QSNDict *sn_vec[3] = { &d->sn_read, &d->sn_write, &d->sn_except }; 9 QSNDict *dict = sn_vec[type]; 10 11 if (QCoreApplication::closingDown()) // ### d->exitloop? 12 return; // after sn_cleanup, don't reinitialize. 13 14 if (dict->contains(sockfd)) { 15 const char *t[] = { "Read", "Write", "Exception" }; 16 /* Variable "socket" below is a function pointer. */ 17 qWarning("QSocketNotifier: Multiple socket notifiers for " 18 "same socket %d and type %s", sockfd, t[type]); 19 } 20 21 QSockNot *sn = new QSockNot; 22 sn->obj = notifier; 23 sn->fd = sockfd; 24 dict->insert(sn->fd, sn); 25 26 if (d->internalHwnd) 27 d->doWsaAsyncSelect(sockfd); 28 }
在这里跟前面分析的QEventDispatcherWin32消息处理搭上关系了,把QWriteNotifier对象加入到系统的列表中;在QApplication::exec()的消息循环中,就能够获取目标对象了。
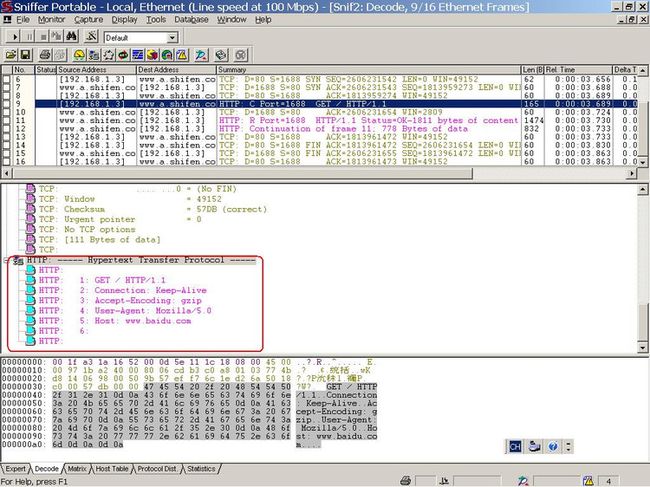
分析QNetworkAccessManager的时候,有一段设定HTTP的请求包的Header,当时没进行深入的分析。
1 void QHttpNetworkConnectionPrivate::prepareRequest(HttpMessagePair &messagePair) 2 { 3 QHttpNetworkRequest &request = messagePair.first; 4 QHttpNetworkReply *reply = messagePair.second; 5 6 // add missing fields for the request 7 QByteArray value; 8 // check if Content-Length is provided 9 QIODevice *data = request.data(); 10 if (data && request.contentLength() == -1) { 11 if (!data->isSequential()) 12 request.setContentLength(data->size()); 13 else 14 bufferData(messagePair); // ### or do chunked upload 15 } 16 // set the Connection/Proxy-Connection: Keep-Alive headers 17 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY 18 if (networkProxy.type() == QNetworkProxy::HttpCachingProxy) { 19 value = request.headerField("proxy-connection"); 20 if (value.isEmpty()) 21 request.setHeaderField("Proxy-Connection", "Keep-Alive"); 22 } else { 23 #endif 24 value = request.headerField("connection"); 25 if (value.isEmpty()) 26 request.setHeaderField("Connection", "Keep-Alive"); 27 #ifndef QT_NO_NETWORKPROXY 28 } 29 #endif 30 31 // If the request had a accept-encoding set, we better not mess 32 // with it. If it was not set, we announce that we understand gzip 33 // and remember this fact in request.d->autoDecompress so that 34 // we can later decompress the HTTP reply if it has such an 35 // encoding. 36 value = request.headerField("accept-encoding"); 37 if (value.isEmpty()) { 38 #ifndef QT_NO_COMPRESS 39 request.setHeaderField("Accept-Encoding", "gzip"); 40 request.d->autoDecompress = true; 41 #else 42 // if zlib is not available set this to false always 43 request.d->autoDecompress = false; 44 #endif 45 } 46 // set the User Agent 47 value = request.headerField("user-agent"); 48 if (value.isEmpty()) 49 request.setHeaderField("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0"); 50 // set the host 51 value = request.headerField("host"); 52 if (value.isEmpty()) { 53 QByteArray host = QUrl::toAce(hostName); 54 55 int port = request.url().port(); 56 if (port != -1) { 57 host += ':'; 58 host += QByteArray::number(port); 59 } 60 61 request.setHeaderField("Host", host); 62 } 63 64 reply->d_func()->requestIsPrepared = true; 65 }
如果想模拟IE浏览器,或者想修改成任何你希望的信息,就是在这里修改。
在设定了这些请求信息之后,发送的请求信息包是什么样子的呢?我把工具拦截的信息包具体情况贴出来