C语言实现mencpy函数
memcpy copies count bytes from src to dest ; If the source and destination overlap, the behavior of memcpy is undefined. Use memmove to handle overlapping regions.
以上描述针对dest 和 src 所指的内存地址有重叠的情况,内存地址重叠情况,memcpy 函数处理步骤未定,而memmove 对重叠情况给予处理;
在winXP+visual c++2005 测试 memcpy 函数,程序如下:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <string.h>
int _tmain (int argc , _TCHAR * argv [])
{
char s [16] = "aabbcc" ;
char d [16] = {0};
memcpy (s +2, s , 4);
printf ("%s" , s );
return 0;
}
结果输出 “aaaabb”, 由此可见windows 平台的c 运行时MSVCRT 的memcpy 函数对重叠部分做了处理,同memmove 的实现。//notes: 如果重叠部分不做处理,应该输出”aaaaaa”
下面我们用c 语言来实现memcpy 函数, 首先我们写出不对内存重叠的处理函数,如下:
void *memcpy_no_handle_overlap (void *dest , void *src , unsigned int count )
{
if ((NULL ==dest ) || (NULL ==src ))
return NULL ;
char *d = (char *)dest ;
char *s = (char *)src ;
//Do normal (Upwards) Copy
while (count -- > 0)
*d ++ = *s ++;
return dest ;
}
测试程序如下:
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
char s[16] = "aabbcc";
char d[16] = {0};
memcpy_no_handle_overlap(s+2, s, 4);
printf("%s", s);
return 0;
}
输出结果”aaaaaa”
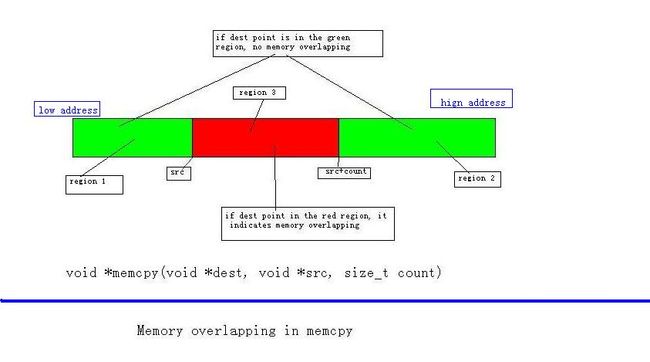
下面讨论处理memory overlapping 情况,如下图:
判断overlapping 条件如下:
If ( (dest <= src) || // green region 1
(dest >=src+count) ) // green region 2
{
// no memory overlapping
}
Else // red region 3
{
// there is overlapping
}
Overlapping 的处理:
我们可以看到memcpy_no_handle_overlap 函数,是从低地址依次赋值到高地址;在处理overlapping 时,如果我们采用同样的方法( 低地址到高地址) ,高地址的值将会被覆盖,所以我们应该从高地址依次到低地址赋值,如下图:
函数代码如下:
void *memcpy_handle_overlap(void *dest, void *src, unsigned int count)
{
if ((NULL==dest) || (NULL==src))
return NULL;
char *d = (char *)dest;
char *s = (char *)src;
//Check for overlapping buffers:
if ( (d<=s) || (d>=s+count) )
{
//Do normal (Upwards) Copy
while (count-- > 0)
*d++ = *s++;
}
else
{
//Do Downwards Copy to avoid propagation
while (count > 0)
{
*(d+count-1) = *(s+count-1);
--count;
}
}
return dest;
}
测试代码:
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
char s[16] = "aabbcc";
char d[16] = {0};
memcpy_handle_overlap(s+2, s, 4);
printf("%s", s);
return 0;
}
输出结果为: “aaaabb “
最后测试代码如下:
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
char s[16] = "aabbcc";
memcpy_no_handle_overlap(s+2, s, 4);
printf("memcpy(ignore memory overlapping): %s/n", s);
strcpy(s, "aabbcc");
memcpy_handle_overlap(s+2, s, 4);
printf("memcpy(handle memory overlapping): %s/n", s);
strcpy(s, "aabbcc");
memcpy(s+2, s, 4);
printf("memcpy( MSVCRT ): %s/n", s);
strcpy(s, "aabbcc");
memmove(s+2, s, 4);
printf("memmove( MSVCRT): %s/n", s);
return 0;
}
输出结果为:
memcpy(ignore memory overlapping): aaaaaa
memcpy(handle memory overlapping): aaaabb
memcpy( MSVCRT ): aaaabb
memmove( MSVCRT): aaaabb