JSTL详解
JSTL支持常见的,结构性任务,如迭代和条件,标签为操纵XML文件,国际化标签和SQL标签。它还提供了一个框架,将现有的自定义标签和JSTL标签。
JSTL标签进行分类,根据其功能分为以下,可用于创建一个JSP页面时,JSTL标签库组:
-
核心标签(Core Tags)
-
格式化标签(Formatting tags)
-
SQL标签(SQL tags)
-
XML标签(XML tags)
-
JSTL函数(JSTL Functions)
安装JSTL库:
如果您使用的是Apache Tomcat容器,那么按照下面两个简单的步骤:
-
下载的二进制发行版,从Apache标准标记库和解压的压缩文件。
-
使用标准的标签库从Jakarta Taglibs分布,复制发行版'lib'目录到应用程序的JAR文件 webapps\ROOT\WEB-INF\lib 目录中。
要使用JSTL库,要在每一个JSP的顶部,使用该库必须包括一个<taglib>指令。
核心标签:
核心组的标签是最常用的JSTL标签。以下是在您的JSP的语法包括JSTL核心库:
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
有以下核心JSTL标签:
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| <c:out > | 和<%= ... >标签一样功能, 但对于表达式。 |
| <c:set > | 设置表达式求值的结果在一个'范围' |
| <c:remove > | 删除一个范围的变量(从一个特定的范围内,如果已指定)。 |
| <c:catch> | Catches any Throwable that occurs in its body and optionally exposes it. |
| <c:if> | Simple conditional tag which evalutes its body if the supplied condition is true. |
| <c:choose> | Simple conditional tag that establishes a context for mutually exclusive conditional operations, marked by <when> and <otherwise> |
| <c:when> | Subtag of <choose> that includes its body if its condition evalutes to 'true'. |
| <c:otherwise > | Subtag of <choose> that follows <when> tags and runs only if all of the prior conditions evaluated to 'false'. |
| <c:import> | Retrieves an absolute or relative URL and exposes its contents to either the page, a String in 'var', or a Reader in 'varReader'. |
| <c:forEach > | The basic iteration tag, accepting many different collection types and supporting subsetting and other functionality . |
| <c:forTokens> | Iterates over tokens, separated by the supplied delimeters. |
| <c:param> | Adds a parameter to a containing 'import' tag's URL. |
| <c:redirect > | Redirects to a new URL. |
| <c:url> | Creates a URL with optional query parameters |
格式化标签:
使用JSTL格式标签来格式化和显示文本,日期,时间和数字的,国际化的网站。以下是在您的JSP的语法,包括格式化库:
<%@ taglib prefix="fmt" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" %>
以下是格式化JSTL标签列表:
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| <fmt:formatNumber> | To render numerical value with specific precision or format. |
| <fmt:parseNumber> | Parses the string representation of a number, currency, or percentage. |
| <fmt:formatDate> | Formats a date and/or time using the supplied styles and pattern |
| <fmt:parseDate> | Parses the string representation of a date and/or time |
| <fmt:bundle> | Loads a resource bundle to be used by its tag body. |
| <fmt:setLocale> | Stores the given locale in the locale configuration variable. |
| <fmt:setBundle> | Loads a resource bundle and stores it in the named scoped variable or the bundle configuration variable. |
| <fmt:timeZone> | Specifies the time zone for any time formatting or parsing actions nested in its body. |
| <fmt:setTimeZone> | Stores the given time zone in the time zone configuration variable |
| <fmt:message> | To display an internationalized message. |
| <fmt:requestEncoding> | Sets the request character encoding |
SQL标签:
JSTL的SQL标签库标签可以交互关系型数据库(如Oracle,MySQL或Microsoft SQL Server的关系数据库管理系统)。
以下是在您的JSP语法包括JSTL SQL库:
<%@ taglib prefix="sql" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/sql" %>
以下是SQL JSTL标签的列表:
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| <sql:setDataSource> | Creates a simple DataSource suitable only for prototyping |
| <sql:query> | Executes the SQL query defined in its body or through the sql attribute. |
| <sql:update> | Executes the SQL update defined in its body or through the sql attribute. |
| <sql:param> | Sets a parameter in an SQL statement to the specified value. |
| <sql:dateParam> | Sets a parameter in an SQL statement to the specified java.util.Date value. |
| <sql:transaction > | Provides nested database action elements with a shared Connection, set up to execute all statements as one transaction. |
XML 标签:
JSTL XML标记提供了一种创建和操作XML文档的JSP为中心的方式。以下是在您的JSP的语法包括JSTL XML库。
JSTL XML标记库具有自定义标签与XML数据交互。这包括XML解析,转换XML数据,流控制,基于XPath表达式。
<%@ taglib prefix="x" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/xml" %>
在继续之前的例子中,将需要复制下面的两个XML和XPath相关的库到<Tomcat安装目录> 的\lib目录:
-
XercesImpl.jar: 下载地址 http://www.apache.org/dist/xerces/j/
-
xalan.jar: 下载地址 http://xml.apache.org/xalan-j/index.html
以下是XML JSTL标签列表:
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| <x:out> | Like <%= ... >, but for XPath expressions. |
| <x:parse> | Use to parse XML data specified either via an attribute or in the tag body. |
| <x:set > | Sets a variable to the value of an XPath expression. |
| <x:if > | Evaluates a test XPath expression and if it is true, it processes its body. If the test condition is false, the body is ignored. |
| <x:forEach> | To loop over nodes in an XML document. |
| <x:choose> | Simple conditional tag that establishes a context for mutually exclusive conditional operations, marked by <when> and <otherwise> |
| <x:when > | Subtag of <choose> that includes its body if its expression evalutes to 'true' |
| <x:otherwise > | Subtag of <choose> that follows <when> tags and runs only if all of the prior conditions evaluated to 'false' |
| <x:transform > | Applies an XSL transformation on a XML document |
| <x:param > | Use along with the transform tag to set a parameter in the XSLT stylesheet |
JSTL 函数:
JSTL包括一些标准功能,其中大部分是常见的字符串操作函数。以下是在JSP的语法包函JSTL函数库:
<%@ taglib prefix="fn" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions" %>
以下是JSTL函数列表:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| fn:contains() | Tests if an input string contains the specified substring. |
| fn:containsIgnoreCase() | Tests if an input string contains the specified substring in a case insensitive way. |
| fn:endsWith() | Tests if an input string ends with the specified suffix. |
| fn:escapeXml() | Escapes characters that could be interpreted as XML markup. |
| fn:indexOf() | Returns the index withing a string of the first occurrence of a specified substring. |
| fn:join() | Joins all elements of an array into a string. |
| fn:length() | Returns the number of items in a collection, or the number of characters in a string. |
| fn:replace() | Returns a string resulting from replacing in an input string all occurrences with a given string. |
| fn:split() | Splits a string into an array of substrings. |
| fn:startsWith() | Tests if an input string starts with the specified prefix. |
| fn:substring() | Returns a subset of a string. |
| fn:substringAfter() | Returns a subset of a string following a specific substring. |
| fn:substringBefore() | Returns a subset of a string before a specific substring. |
| fn:toLowerCase() | Converts all of the characters of a string to lower case. |
| fn:toUpperCase() | Converts all of the characters of a string to upper case. |
| fn:trim() | Removes white spaces from both ends of a string. |
<%@ taglib %>引入标签库
=========================================================================
1、以classPath中,加入jar包: standard-1.1.2.jar , jstl-1.1.2.jar
2、在相目\WEB-INF\tld\文件夹中放入常用的tld文件:c.tld,fmt.tld
3、在jsp文件的顶部加入以下内容:
<c:> 核心标签库
==========================================================================
JSTL 核心标签库(C标签)标签共有13个,功能上分为4类:
1.表达式控制标签:out、set、remove、catch
2.流程控制标签:if、choose、when、otherwise
3.循环标签:forEach、forTokens
4.URL操作标签:import、url、redirect
<c:forEach> 标签
-------------------------------------------------------------------
为循环控制,它可以将集合(Collection)中的成员循序浏览一遍。
<c:forEach> 标签的语法 说明 :
语法1:迭代一集合对象之所有成员
语法2:迭代指定的次数
<c:forEach> 标签的 属性说明 :
<c:forEach> 标签的 属性 : varStatus属性: 它的提供另外四个属性:index,count,fist和last,它们个自的意义如下:
- 属性 类型 意义
- index number 现在指到成员的索引
- count number 总共指到成员的总和
- first boolean 现在指到成员是否为第一个
- last boolean 现在指到成员是否为最后一个
<c:forEach> 遍历 List列表:
对于一个基本类型的数组,当前元素将作为相应包装类(Integer、Float等等)的一个实例提供。
<c:forEach> 遍历Map:
对于一个java.util.Map,当前元素则作为一个java.util.Map.Entry提供。
<c:forTokens> 标签
-------------------------------------------------------------------
用来浏览一字符串中所有的成员,其成员是由定义符号(delimiters)所分隔的。
<c:forTokens> 标签的语法 说明 :
<c:forTokens> 标签的 属性说明 :
<c:out> 标签
-------------------------------------------------------------------
主要用来显示数据的内容
<c:out> 标签的语法 说明 :
语法1:没有本体(body)内容
语法2:有本体内容
default value
</c:out>
<c:forEach> 标签的 属性说明 : 略
一般来说,<c:out>默认会将<、>、’、” 和 & 转换为 <、>、'、" 和&。假若不想转换时,只需要设定<c:out>的escapeXml属性为fasle就可以了。
<c:set> 标签
-------------------------------------------------------------------
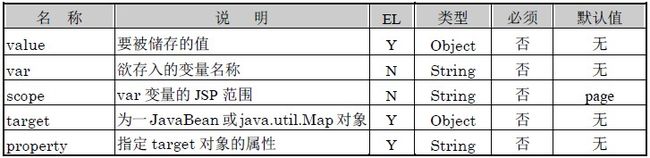
主要用来将变量储存至JSP范围中或是JavaBean的属性中。
<c:set> 标签的语法 说明 :
语法1:将value的值储存至范围为scope的 varName 变量之中
语法2:将本体内容的数据储存至范围为scope的 varName 变量之中
… 本体内容
</c:set>
语法3:将 value的值储存至 target 对象的属性中
语法4:将本体内容的数据储存至target 对象的属性中
… 本体内容
</c:set>
<c:set> 标签的 属性说明 :
<c:remove> 标签
-------------------------------------------------------------------
主要用来移除变量。
<c:remove> 标签的语法 说明 :
<c:remove var="varName" [scope="{ age|request|session|application }"] />
<c:catch> 标签
-------------------------------------------------------------------
主要用来处理产生错误的异常状况,并且将错误信息储存起来。
<c:catch> 标签的语法 说明 :
<c:catch [var="varName"] >… 欲抓取错误的部分</c:catch>
<c:if> 标签
-------------------------------------------------------------------
的用途就和我们一般在程序中用的if一样。
<c:if> 标签的语法 说明 :
语法1:没有本体内容(body)
<c:if test="testCondition" var="varName" [scope="{page|request|session|application}"]/>
语法2:有本体内容
<c:if test="testCondition" [var="varName"] [scope="{page|request|session|application}"]>本体内容</c:if>
示例:
<c:if test="${not empty item.publish_time}">内容</c:if>
<c:if test="${item['domain']!=null}">内容</c:if>
<c:if test="${!empty permissionMap}"> 内容</c:if>
c:choose> <c:when> <c:otherwise> 标签
-------------------------------------------------------------------
<c:choose when otherwise> 标签的语法 说明 :
<fmt:> 格式 化标签库
==========================================================================
一:JSTL格式化标签又称为I18N标签库,主要用来编写国际化的WEB应用,使用此功能可以对一个特定的语言请求做出合适的处理。
例如:中国内地用户将显示简体中文,台湾地区则显示繁体中文,使用I18N格式化标签库还可以格式化数字和日期,例如同一数字或日趋,在不同国家可能有不同的格式,使用I18N格式标签库可以将数字和日期格式为当地的格式。
在JSP页面中要使用到格式化标签,需要引入下面的语句:
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix="fmt"% >
二:概览
-------------------------------------------------------------------
格式化标签
<fmt:fromatNumber>
<fmt:formatDate>
<fmt:parseDate>
<fmt:parseNumber>
<fmt:setTimeZone>
<fmt:timeZone>
国际化标签
<fmt:setLocale>
<fmt:requestEncoding>
<fmt:bundle>
<fmt:message>
<fmt:param>
<fmt:setBundle>
三:<fmt:formatNumber>
-------------------------------------------------------------------
此标签会根据区域定制的方式将数字格式化成数字,货币,百分比。
此标签的属性:
value:要格式化的数字
type:按照什么类型格式化
pattern:自定义格式化样式
currencyCode:ISO-4721货币代码,只适用于按照货币格式化的数字
currencySymbol: 货币符号,如¥,只适用于按照货币格式化的数字
groupingUsed: 是否包含分隔符
maxIntegerDigits: 整数部分最多显示多少位
mixIntegerDigits: 整数部分最少显示多少位
maxFractionDigits: 小数部分最多显示多位位
minFractionDigits: 小数部分最少显示多位位
var:存储格式化后的结果
scope: 存储的范围
示例1:
注意:如果要实现国际化,那么编码格式要设置为utf-8.
从程序运行效果可以看出,设定的区域不同,格式化数字的显示也会不同.
四:type属性:可以是数字(number),货币(currency),百分比(percent)
示例2:
currencyCode为货币代码,例如美元为USD,人民币为CNY等
currencySymbol为货币符号例如,人民币为¥,美元为$。
如果不指定区域,则会根据语言区域自动选择currencySymbol
示例3:
currencySymbol属性还可以自定义要显示的头标识,但是一定得type="currency"才会生效,例如:
自定义数字样式
<fmt:formatNumber value="12.31" pattern=".0000"/><br/>
<fmt:formatNumber value="1234" pattern="###.##E0"/>
会显示:
12.3100
1.234E3
会四舍五入
var:定义一个变量,存储格式化后的结果,scope指定变量存储的范围.用法和前面讲的标签一致.
五:<fmt:parseNumber>
-------------------------------------------------------------------
此标签用来将字符串类型的数字,货币或百分比转换成数字类型,和<fmt:formatNumber>标签的作用正好相反.
value: 要转换的字符串
type: 指定要转换的字符串为什么类型,可取值:number,percent,currency
pattern: 自定义格式化样式
parseLocale: 指定区域来转换字符串
IntegerOnly: 转换后的数字是否只显示整数部分
var: 存储转换后的结果
scope: 存储的范围
示例1:
<fmt:parseNumber value="500,800,200"/>
显示: 500800200
示例2:
<fmt:parseNumber value="52%" type="percent" />
显示: 0.52 (52%在这里是一个字符串, type指定这个字符串是什么类型的值)
示例3:
<fmt:parseNumber value="¥123" type="currency" />
显示123, ¥123在这里是一个字符串, type指定这个字符串是什么类型的值
示例4:
<fmt:parseNumber value="123.333" type="number" /><br/>
<fmt:parseNumber value="123.333" type="number" integerOnly="true"/><br/>
显示:
123.333
123
integerOnly确定是否只显示整数部分.
示例5:
<fmt:parseNumber value="¥123.333" type="currency" parseLocale="zh_CN"/><br/>
<fmt:parseNumber value="$123.333" type="currency" parseLocale="en_US"/><br/>
parseLocale="en_US"主要是配合当type="currency"时用的,
如果要转换货币的字符串类型为value="¥123.333",不设置语言环境的话,会取当前浏览器的默认设置,否则就要加上parseLocale="zh_CN",指定环境为中文环境
如果要转换货币的字符串类型为value="$123.333",不设置语言环境的话,会取当前浏览器的默认设置,如果默认为zh_cn的话,程序会报错的,否则就要加上parseLocale="en_US",指定环境为英文美国环境
六:<fmt:formatDate />
-------------------------------------------------------------------
此标签可以将日期格式化.
属性介绍:
value 用来格式化的时间或日期
type 指定格式化的是日期还是时间,或者两者都是取值范围:date,time,both
pattern 自定义格式化样式
dateStyle 日期的格式化样式
timeStyle 时间的格式化样式
timeZone 指定使用的时区
var 存储格式化后的结果
scope 指定存储的范围
自定义格式:
--------------------------
注意这里小时 hh表示12小时制, HH代表24小时制
示例1:
--------------------------
大家可以看到大陆和台湾显示日期的格式是有区别的.
显示结果:
2009-12-7
2009/12/7
示例2:
--------------------------
显示结果:
14:59:28
下午 02:59:28
type可取值及意义:
date 格式化日期
time格式化时间
both格式化日期时间
示例3:
--------------------------
输出结果:
2009-12-7 21:24:26
2009/12/7 下午 09:24:26
dateStyle用来设定日期显示的样式,其值可以是default, short, medium, long, full,请看示例:
--------------------------
显示结果如下:
2009-12-7 21:30:49
09-12-7 21:30:49
2009-12-7 21:30:49
2009年12月7日 21:30:49
2009年12月7日 星期一 21:30:49
可以看到dateStyle属性只对日期部分起作用,时间部分没有作用.
timeStyle用来显示时间部分的样式,取值范围同上
--------------------------
输出:
2009-12-7 21:35:52
2009-12-7 下午9:35
2009-12-7 21:35:52
2009-12-7 下午09时35分52秒
2009-12-7 下午09时35分52秒 CST
timeZone用来设定时区,时区的意思类似于酒店里大堂放的几个时钟,比如现在时间会有北京时间,东京时间,纽约时间,伦墩时间,
取值范围为:EST, CST, MST, PST
--------------------------
输出结果:
下午09时41分37秒 CST
上午08时41分37秒 EST
上午07时41分37秒 CST
上午06时41分37秒 MST
上午05时41分37秒 PST
七:<fmt:parseDate>
-------------------------------------------------------------------
将字符串类型的时间转换为日期类型.
value 用来格式化的时间或日期的字符串
type 指定格式化的是日期还是时间,或者两者都是取值范围:date,time,both
pattern 自定义格式化样式
dateStyle 日期的格式化样式
timeStyle 时间的格式化样式
timeZone 指定使用的时区
var 存储格式化后的结果
scope 指定存储的范围
示例:
<fmt:setLocale value="zh_cn" />
<fmt:parseDate type="date" value="2008-4-5"/>
输出: Sat Apr 05 00:00:00 CST 2008,
这里已经将字符串” 2008-4-5”转换为了日期对象了.转换一定得注意,类似于2008-4-5这样的字符串,type必须为date,类似于12:34:56的字符串,type必须为time类似于2008-4-5 12:34:56这样的字符串,type必须为both还要注意浏览器的语言环境的设置,如果为zh_tw,那么字符串就必须得符合当地的标准,如为2009/12/7 下午 09:24:26就正确转换为日期对象,否则就会报错.
八:<fmt:setTimeZone>
-------------------------------------------------------------------
value 设定时区
var 存储设定的时区
scope 存储的范围
value用来设定时区,可以是EST,CST,MST,PST等,如果有var属性,则将结果存储在所设定的范围之内.在属性范围内的页面都会使用该时区为默认时区.
<fmt:setLocale value="zh_cn" />
<fmt:setTimeZone value="EST" />
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date()%>" type="time" timeStyle="full" /><br />
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date()%>" type="time" timeStyle="full" /><br />
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date()%>" type="time" timeStyle="full" /><br />
<fmt:setLocale value="zh_cn" />
<fmt:setTimeZone value="EST" />
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date()%>" type="time" timeStyle="full" /><br />
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date()%>" type="time" timeStyle="full" /><br />
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date()%>" type="time" timeStyle="full" /><br />
输出:
上午09时25分12秒 EST
上午09时25分12秒 EST
上午09时25分12秒 EST
此时区在该页面内都有效
九:<fmt:timeZone>
-------------------------------------------------------------------
用来暂时设置时区.
<fmt:setLocale value="zh_cn" />
<fmt:timeZone value="EST">
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date()%>" type="time" timeStyle="full" />
<br />
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date()%>" type="time" timeStyle="full" />
<br />
</fmt:timeZone>
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date()%>" type="time" timeStyle="full" />
<fmt:setLocale value="zh_cn" />
<fmt:timeZone value="EST">
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date()%>" type="time" timeStyle="full" />
<br />
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date()%>" type="time" timeStyle="full" />
<br />
</fmt:timeZone>
<fmt:formatDate value="<%=new Date()%>" type="time" timeStyle="full" />
此标签的时区只是部分,在标签开始至标签结束内有效,其它地方无效,其它地方还是会使用默认时区
<fn:> Function标签 库
==========================================================================
JSTL Functions 标签库中提供了一组常用的 EL 函数,主要用于处理字符串,在 JSP 中可以直接使用这些函数。
在 JSP 文件中使用 Functions 标签库,要先通过 taglib 指令引入该标签库:
<%@taglib uri=”http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions” prefix=”fn” %.
18.1fn:contains 函数
fn:contains 函数用于判断在源字符串中是否包含目标字符串,其语法为:
fn:contains(String source,String target) -------boolean;
以上 source 参数指定源字符串, target 参数指定目标字符串,返回类型为 boolean 。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
${fn:contains(“Tomcat”,”cat”)}
${fn:contains(“Tomcat”,”CAT”)}
第一个 EL 表达式的值为 true ,第二个 EL 表达式的值为 false 。
18.2fn:containsIgnoreCase 函数
fn:containsIgnoreCase 函数用于判断在源字符串中是否包含目标字符串,并且在判断时忽略大小写,其语法为:
fn: containsIgnoreCase (String source,String target) -------boolean;
以上 source 参数指定源字符串, target 参数指定目标字符串,返回类型为 boolean 。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
${fn: containsIgnoreCase (“Tomcat”,”CAT”)}
${fn: containsIgnoreCase (“Tomcat”,”Mike”)}
第一个 EL 表达式的值为 true ,第二个 EL 表达式的值为 false 。
18.3 fn:startsWith 函数
fn:startsWith 函数用于判断源字符串是否以指定的目标字符串开头,其语法为:
fn:startsWith(String source,String target) ----boolean
以上 source 参数指定源字符串, target 参数指定目标字符串,返回类型为 boolean 。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
${fn: startsWith (“Tomcat”,”Tom”)}
${fn: startsWith (“Tomcat”,”cat”)}
第一个 EL 表达式的值为 true ,第二个 EL 表达式的值为 false 。
18.4 fn:endsWith 函数
fn: endsWith 函数用于判断源字符串是否以指定的目标字符串结尾,其语法为:
fn: endsWith (String source,String target) ----boolean
以上 source 参数指定源字符串, target 参数指定目标字符串,返回类型为 boolean 。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
${fn: endsWith (“Tomcat”,”cat”)}
${fn: endsWith (“Tomcat”,”Tom”)}
第一个 EL 表达式的值为 true ,第二个 EL 表达式的值为 false 。
18.5 fn:indexOf 函数
fn:indexOf 函数用于在源字符串中查找目标字符串,并返回源字符串中最先与目标字符串匹配的第一个字符的索引,如果在源字符串中不包含目标字符串,就返回 -1 ,源字符串中的第一个字符的索引为 0 。 fn:indexOf 函数的语法为:
fn: indexOf (String source,String target) ----int
以上 source 参数指定源字符串, target 参数指定目标字符串,返回类型为 int 。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
1 ${fn: indexOf (“Tomcat”,”cat”)}<br/>
2 ${fn: indexOf (“2211221”,”21”)} <br/>
3 ${fn: indexOf (“Tomcat”,”Mike”)} <br/>
其输出结果为:
1 3
2 1
3 -1
18.6 fn:replace 函数
fn:replace 函数用于把源字符串中的一部分替换为另外的字符串,并返回替换后的字符串。 fn:replace 函数的语法为:
fn: replace (String source,String before,String after) ----String
以上 source 参数指定源字符串, before 参数指定源字符串中被替换的子字符串, after 参数指定用于替换的子字符串,返回类型为 String 。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
1 ${ fn: replace(“TomcAt”,”cAt”,”cat”)}<br/>
2 ${ fn: replace(“2008/1/9”,”/”,”-”)}<br/>
其输出结果为:
1 Tomcat
2 2008-1-9
18.7 fn:substring 函数
fn:substring 函数用于获取源字符串中的特定子字符串,它的语法为:
fn:substring(String source,int beginIndex,int endIndex) ------String
以上 source 参数指定源字符串, beginIndex 参数表示子字符串中的第一个字符在源字符串中的索引, endIndex 参数表示子字符串的最后一个字符在源字符串中的索引加 1 ,返回类型为 String ,源字符串中的第一个字符的索引为 0 。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
1 ${ fn: substring (“Tomcat”,0,3)}<br/>
2 ${ fn: substring (“Tomcat”,3,”6”)}<br/>
其输出结果为:
1 Tom
2 cat
18.8 fn:substringBefore 函数
fn:substringBefore 函数用于获取源字符串中指定子字符串之前的子字符串,其语法为:
fn:substringBefore(String source,String target) ----String
以上 source 参数指定源字符串, target 参数指定子字符串,返回类型为 String 。如果在源字符串中不包含特定子字符串,就返回空字符串。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
1 ${ fn: substringBefore (“Tomcat”,”cat”)}<br/>
2 ${ fn: substringBefore (“mydata.txt”,”.txt”)}<br/>
其输出结果为:
1 Tom
2 mydata
18.9 fn:substringAfter 函数
fn: substringAfter 函数用于获取源字符串中指定子字符串之后的子字符串,其语法为:
fn: substringAfter (String source,String target) ----String
以上 source 参数指定源字符串, target 参数指定子字符串,返回类型为 String 。如果在源字符串中不包含特定子字符串,就返回空字符串。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
1 ${ fn: substringAfter (“Tomcat”,”Tom”)}<br/>
2 ${ fn: substringAfter (“mydata.txt”,” mydata.”)}<br/>
其输出结果为:
1 cat
2 txt
18.10 fn:split 函数
fn:split 函数用于将源字符串拆分为一个字符串数组,其语法为:
fn: split (String source,String delimiter) ----String[]
以上 source 参数指定源字符串, delimiter 参数指定用于拆分源字符串的分隔符,返回类型为 String[] 。如果在源字符串中不包含 delimiter 参数指定的分隔符,或者 delimiter 参数为 null ,那么在返回的字符串数组中只有一个元素,为源字符串。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
<c:set value=’${ fn: split (“www.mywebsite.org”,”.”)}’ var=”strs”/>
<c:forEach var=”token” item=”${strs}”>
${token}<br/>
</c:forEach>
其输出结果为:
www
mywebsite
org
再例如对于以下代码:
<c:set value=’${ fn: split (“www.mywebsite.org”,”-”)}’ var=”strs”/>
${strs[0]}
其输出结果为:
www.mywebsite.org
18.11 fn:join 函数
fn:join 函数用于将源字符串数组中的所有字符串连接为一个字符串,其语法为:
fn:join(String source[],String separator) ----String
以上 source 参数指定源字符串数组, separator 参数指定用于连接源字符串数组中的各个字符串的分隔符,返回类型为 String 。
例如对于以下代码:
<%
String strs[] = {“www”,”mywebsite”,”org”};
%>
<c:set value=”<%=strs%>” var=”strs”/>
${fn:join(strs,”.”)}
其输出结果为:
www. mywebsite. org
18.12 fn:toLowerCase 函数
fn:toLowerCase 函数用于将源字符串中的所有字符改为小写,其语法为:
fn:toLowerCase(String source) -----String
以上 source 参数指定源字符串,返回类型为 String 。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
fn:toLowerCase(“TomCat”)
其输出结果为:
tomcat
18.13 fn:toUpperCase 函数
fn: toUpperCase 函数用于将源字符串中的所有字符改为大写,其语法为:
fn: toUpperCase (String source) -----String
以上 source 参数指定源字符串,返回类型为 String 。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
fn: toUpperCase (“TomCat”)
其输出结果为:
TOMCAT
18.14 fn:trim 函数
fn:trim 函数用于将源字符串中的开头和末尾的空格删除,其语法为:
fn:trim(String source) ----String
以上 source 参数指定源字符串,返回类型为 String 。
例如对于以下 EL 表达式:
fn:trim(“ Tomcat ”)
以上 EL 表达式的值为“ Tomcat ”。
18.15 fn:escapeXml 函数
fn:escapeXml 函数用于将源字符串中的字符“ < ”、“ > ”、“ ” ”和“ & ”等转换为转义字符,本书第 1 章的 1.2 节( HTML 简介)介绍了转义字符的概念。 fn:escapeXml 函数的行为与 <c:out> 标签的 escapeXml 属性为 true 时的转换行为相同, fn:escapeXml 函数的语法为:
fn:escapeXml(String source) ----String
以上 source 参数指定源字符串,返回类型为 String 。
例程 18-1 的 out.jsp 演示了 fn:escapeXml 函数的用法。
| <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions" prefix="fn"%> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" /> <title>out</title> </head> <body> 1.${fn:escapeXml("<b> 表示粗体字 </b>") }<br/> 2.<c:out value="<b> 表示粗体字 </b>" escapeXml="true"></c:out><br/> 3.${"<b> 表示粗体字 </b>"}<br/> </body> </html> |
对于 out.jsp 中的以下代码:
1.${fn:escapeXml("<b> 表示粗体字 </b>") }<br/>
2.<c:out value="<b> 表示粗体字 </b>" escapeXml="true"></c:out><br/>
3.${"<b> 表示粗体字 </b>"}<br/>
其输出结果为:
1.<b> 表示粗体字 </b><br/>
2.<b> 表示粗体字 </b><br/>
3.<b> 表示粗体字 </b><br/>
18.16 fn:length 函数
fn:length 函数用于返回字符串中的字符的个数,或者集合和数组的元素的个数,其语法为:
fn:length(source) ---- int
以上 source 参数可以为字符串、集合或者数组,返回类型为 int 。
| <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/functions" prefix="fn"%> <%@page import="java.util.ArrayList"%> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" /> <title>length</title> </head> <body> <% int[] array = {1,2,3,4}; ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); list.add("one"); list.add("two"); list.add("three"); %> <c:set value="<%=array%>" var="array"></c:set> <c:set value="<%=list%>" var="list"></c:set> 数组长度: ${fn:length(array)}<br/> 集合长度: ${fn:length(list)}<br/> 字符串长度: ${fn:length("Tomcat")}<br/> </body> </html> |
Functions 标签库概览
l fn:contains 函数 : 用于判断在源字符串中是否包含目标字符串。
l fn:containsIgnoreCase 函数 : 用于判断在源字符串中是否包含目标字符串 , 并且在判断时忽略大小写。
l fn:startsWith 函数 : 用于判断源字符串是否以指定的目标字符串开头。
l fn: endsWith 函数:用于判断源字符串是否以指定的目标字符串结尾。
l fn:indexOf 函数:用于在源字符串中查找目标字符串,并返回源字符串中最先与目标字符串匹配的第一个字符的索引。
l fn:replace 函数:用于把源字符串中的一部分替换为另外的字符串,并返回替换后的字符串。
l fn:substring 函数:用于获取源字符串中的特定子字符串。
l fn:substringBefore 函数:用于获取源字符串中指定子字符串之前的子字符串。
l fn: substringAfter 函数:用于获取源字符串中指定子字符串之后的子字符串
l fn:split 函数:用于将源字符串拆分为一个字符串数组。
l fn:join 函数:用于将源字符串数组中的所有字符串连接为一个字符串。
l fn:toLowerCase 函数:用于将源字符串中的所有字符改为小写。
l fn: toUpperCase 函数:用于将源字符串中的所有字符改为大写。
l fn:trim 函数:用于将源字符串中的开头和末尾的空格删除。
l fn:escapeXml 函数:用于将源字符串中的字符“ < ”、“ > ”、“ ” ”和“ & ”等转换为转义字符。
l fn:length 函数:用于返回字符串中的字符的个数,或者集合和数组的元素的个数