积性函数
积性函数:对于正整数n的一个算术函数 f(n),若f(1)=1,且当a,b互质时f(ab)=f(a)f(b)
若对于某积性函数 f(n) ,就算a, b不互质,也有f(ab)=f(a)f(b),则称它为完全积性的
如果f是积性函数,那么其和是积性函数,其积也是积性函数
设有 , 那么其因子个数是 ,其因子和是
此外,欧拉函数,最大公约数gcd(a,b)=gcd(a1,b)*gcd(a2,b) [ a=a1a2 ],莫比乌斯函数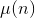 也是积性函数。
也是积性函数。
不过while部分可以这样写:
分析:(注:本题自己纯属乱搞,没有严格证明)
当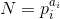 时, x(x-1)%N=0, 此时的结果是x=1或者x=0.
时, x(x-1)%N=0, 此时的结果是x=1或者x=0.
he[N]=2当N=pq时(p和q是互质的),x(x-1)%N=0, 此时(1) x=kp (2) x=kq 再加上x=1,x=0, 所以he[N]=he[p]he[q], 那么这是一个积性函数。
当 时,
那么hehe[N]就是:
若对于某积性函数 f(n) ,就算a, b不互质,也有f(ab)=f(a)f(b),则称它为完全积性的
如果f是积性函数,那么其和是积性函数,其积也是积性函数
设有 , 那么其因子个数是 ,其因子和是
此外,欧拉函数,最大公约数gcd(a,b)=gcd(a1,b)*gcd(a2,b) [ a=a1a2 ],莫比乌斯函数
献上两题:
POJ 2992 Divisors
http://poj.org/problem?id=2992
大意:求解C(n,k)的约数和,其中0 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 431。
不知道有多少数据,如果不预处理肯定是超时的。下面代码C++能过,但G++超时
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const LL N=500,M=500;
LL fac[N],cnt;
bool vis[M]; // care: RE
LL p[N][N],pow1[N];
void getfac(){
for(LL i=2;i<M;i++){
if(!vis[i]) fac[cnt++]=i;
for(LL j=0;j<cnt&&fac[j]*i<M;j++){
vis[fac[j]*i]=1;
if(i%fac[j]==0) break;
}
}
}
LL getpow(LL num,LL d){
LL ans=0;
while(num){
num=num/d;
ans=ans+num;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
getfac();
for(LL i=0;i<=431;i++){
for(LL j=0;fac[j]<=i;j++){
p[i][fac[j]]=getpow(i,fac[j]);
}
}
LL n,k;
while(cin>>n>>k){
memset(pow1,0,sizeof(pow1));
for(LL i=0;fac[i]<=n;i++){
pow1[i]+=p[n][fac[i]];
pow1[i]-=p[k][fac[i]];
pow1[i]-=p[n-k][fac[i]];
}
LL ans=1;
for(LL i=0;fac[i]<=n;i++){
ans=ans*(pow1[i]+1);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
不过while部分可以这样写:
while(cin>>n>>k){
LL ans=1;
for(LL i=0;fac[i]<=n;i++){
ans=ans*(p[n][fac[i]]-p[n-k][fac[i]]-p[k][fac[i]]+1);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
节省63Ms。嘿嘿
hdu 2879 hehe
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2879
In the equation X^2≡X(mod N) where x∈[0,N-1], we define He[N] as the number of solutions.
And furthermore, define HeHe[N]=He[1]*……*He[N]
Now here is the problem, write a program, output HeHe[N] modulo M for a given pair N, M.
And furthermore, define HeHe[N]=He[1]*……*He[N]
Now here is the problem, write a program, output HeHe[N] modulo M for a given pair N, M.
分析:(注:本题自己纯属乱搞,没有严格证明)
当
he[N]=2当N=pq时(p和q是互质的),x(x-1)%N=0, 此时(1) x=kp (2) x=kq 再加上x=1,x=0, 所以he[N]=he[p]he[q], 那么这是一个积性函数。
当 时,
那么hehe[N]就是:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N=1e7+10;
int pri[N],cnt;
bool vis[N];
void getpri(){
for(int i=2;i<N;i++){
if(!vis[i]) pri[cnt++]=i;
for(int j=0;j<cnt&&i*pri[j]<N;j++){
vis[i*pri[j]]=1;
if(i%pri[j]==0) break;
}
}
}
LL power(LL a,LL p,LL m){
LL ans=1;
while(p){
if(p&1) ans=ans*a%m;
a=a*a%m;
p>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
LL n,m;
getpri();
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m);
LL p=0;
for(int i=0;i<cnt&&pri[i]<=n;i++){
p+=n/pri[i];
}
printf("%lld\n",power(2,p,m));
}
return 0;
}