SQL Server 2005的XML数据修改语言(XML DML)
作为对XQuery语言的扩展,XML DML为XML数据操作提供了更大的灵活性,而不再仅仅是对XML数据进行一些查询操作。通过XML DML,用户可以像操作关系表一样对XML中的节点内容进行插入、更新和删除操作。XML DML需要通过xml数据类型的modify方法进行调用。
1.insert
insert用于将Expression1标识的一个或多个节点作为Expression2标识的节点的子节点或同级节点插入。语法格式如下:
insert
Expression1 (
{as first | as last} into | after | before
Expression2
)
Expression1和Expression2
标识要插入的一个或多个节点。它可以是常量XML实例,也可以是XQuery表达式。该表达式可以得出节点、文本节点或一组有序的节点,但它无法解得根节点。如果该表达式得出一个值或一组值,则这些值作为单个文本节点插入,各值之间以空格分隔开。如果将多个节点指定为常量,则这些节点用括号括住,并以逗号分隔开。但无法插入异构序列(如一组元素、属性或值)。如果Expression1解得一个空序列,则不会发生插入操作,并且不会返回任何错误。
into
Expression1标识的节点作为Expression2标识的节点的子节点插入。如果Expression2中的节点已有一个或多个子节点,则必须使用as first或as last来指定所需的新节点添加位置。
after
Expression1标识的节点作为Expression2标识的节点的同级节点直接插入在其后面,after关键字不能用于插入属性。
before
Expression1标识的节点作为Expression2标识的节点的同级节点直接插入在其前面,before关键字不能用于插入属性。
(1)插入元素文档中
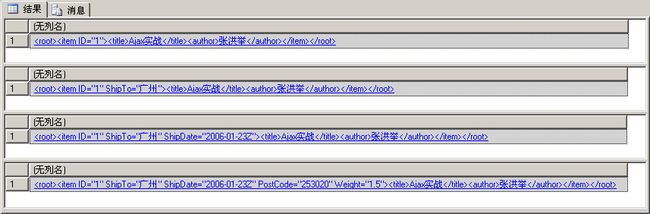
在下面的示例中,首先将XML文档分配给xml类型的变量。然后使用几个insert XML DML语句说明如何将元素节点插入文档中。注意在示例中为各种路径表达式都指定了“[1]”,以要求每次只返回单个目标,这样就确保了只有单个目标节点。每次插入后,SELECT语句都会显示结果。最终执行结果如图1所示。
DECLARE @myDoc xml
SET @myDoc = '<root>
<item ID="1">
</item>
</root>'
SELECT @myDoc
-- 插入item的第1个子节点,此时不需要指定as first或as last
SET @myDoc.modify('
insert <author>张洪举</author>
into (/root/item)[1]')
SELECT @myDoc
-- 插入item的第2个子节点,as first指定插入到同级子节点的前面
SET @myDoc.modify('
insert <title>SQL Server 2005开发宝典</title>
as first into (/root/item)[1]')
SELECT @myDoc
-- 插入第2个item节点
SET @myDoc.modify('
insert <item ID="2"></item>
into (/root)[1]')
SELECT @myDoc
-- 向第2个item中插入第1个子节点
SET @myDoc.modify('
insert <title>SQL Server 2005的新增功能</title>
as first into (/root/item)[2]')
SELECT @myDoc
GO
图1 向XML中插入节点
(2)插入多个元素到文档中
在下面的示例中,将<title>和<author>元素插入到了item节点中。元素之间使用逗号分隔,并包含在括号中。
DECLARE @myDoc xml
SET @myDoc = '<root>
<item ID="1">
</item>
</root>'
SELECT @myDoc
SET @myDoc.modify('
insert (
<title>SQL Server 2005开发宝典</title>,
<author>张洪举</author>
)
into (/root/item)[1]');
SELECT @myDoc
GO
(3)插入属性到文档中
在下面的示例中,向XML文档中插入了多个属性。每次插入属性后,SELECT语句都会显示结果,最终执行结果如图2所示。
DECLARE @myDoc xml
SET @myDoc = '<root>
<item ID="1">
<title>Ajax实战</title>
<author>张洪举</author>
</item>
</root>'
SELECT @myDoc
SET @myDoc.modify('
insert attribute ShipTo {"广州"}
into (/root/item[@ID=1])[1]');
SELECT @myDoc
-- 通过一个sql变量指定要插入属性ShipDate的值
DECLARE @ShipDate char(11)
SET @ShipDate='2006-01-23Z'
SET @myDoc.modify('
insert attribute ShipDate {sql:variable("@ShipDate") cast as xs:date ?}
into (/root/item[@ID=1])[1]') ;
SELECT @myDoc
-- 插入多个属性,属性之间使用逗号分隔,并包含在括号内
SET @myDoc.modify('
insert (
attribute PostCode {"253020" },
attribute Weight {"1.5"}
)
into (/root/item[@ID=1])[1]');
SELECT @myDoc
GO
图2插入属性到XML中
(4)插入注释节点
在下面的示例中,将注释节点插入到ID为2的item节点中<title>元素的后面。
DECLARE @myDoc xml
SET @myDoc = '<root>
<item ID="1">
<title>Ajax实战</title>
<author>张洪举</author>
</item>
<item ID="2">
<title>ASP.NET实战</title>
<author>卢桂章</author>
</item>
</root>'
SET @myDoc.modify('
insert <!-- 注释 -->
after (/root/item[@ID=2]/title)[1]');
SELECT @myDoc
GO
插入注释后XML的内容如下:
<root>
<item ID="1">
<title>Ajax实战</title>
<author>张洪举</author>
</item>
<item ID="2">
<title>ASP.NET实战</title>
<!-- 注释 -->
<author>卢桂章</author>
</item>
</root>
(5)使用CDATA部分插入数据
当插入的文本中包含有XML无效字符(如“<”或“>”)时,可以使用CDATA部分插入数据。参考下面的示例:
DECLARE @myDoc xml
SET @myDoc = '<root>
<item ID="1">
<title>Ajax实战</title>
<author>张洪举</author>
</item>
<item ID="2">
<title>ASP.NET实战</title>
<author>卢桂章</author>
</item>
</root>'
SET @myDoc.modify('
insert <desc><![CDATA[ <送货方式>上门<价款>未收]]></desc>
into (/root/item[@ID=2])[1] ') ;
SELECT @myDoc
GO
被插入部分中的XML无效字符,会被转换成实体,如“<”保存为<。下面的插入CDATA部分后XML文档的内容:
<root>
<item ID="1">
<title>Ajax实战</title>
<author>张洪举</author>
</item>
<item ID="2">
<title>ASP.NET实战</title>
<author>卢桂章</author>
<desc> <送货方式>上门<价款>未收</desc>
</item>
</root>
(6)插入文本节点
要将文件插入到XML中,需要使用text函数构造文本,参考下面的示例:
DECLARE @myDoc xml
SET @myDoc = '<root>
<item ID="1">
<title>Ajax实战</title>
<author>张洪举</author>
</item>
</root>'
SET @myDoc.modify('
insert text{"订单列表"}
as first into (/root)[1]');
SELECT @myDoc
GO
得到的XML结果如下:
<root>订单列表<item ID="1"><title>Ajax实战</title><author>张洪举</author></item></root>
(7)将节点插入类型化的xml列中
在下面的示例中,首先创建了一个架构集合,并建立了一个使用该架构集合的表。在使用Transact-SQL INSERT语句向表中插入一个符合架构约束的XML后,再使用XML DML insert向该XML中插入一个item节点。
-- 创建XML架构集合
CREATE XML SCHEMA COLLECTION MySchemas
AS
N'<?xml version = "1.0"?>
<xsd:schema targetNamespace="http://schemas.mybook.com/customerschemas"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xsd:element name="customer">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element maxOccurs="unbounded" name="item">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="customername" type="xsd:string"/>
<xsd:element name="address" type="xsd:string"/>
<xsd:element name="phone" type="xsd:string"/>
<xsd:element name="contact" type="xsd:string"/>
</xsd:sequence>
<xsd:attribute name="ID" type="xsd:int"/>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:schema>';
GO
-- 创建包含xml数据类型列的表
CREATE TABLE MyCustomer
(CustomerID int IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerItem xml(MySchemas));
GO
-- 向表中插入XML,该XML应当符合http://schemas.mybook.com/customerschemas命名空间架构的定义
INSERT INTO MyCustomer
VALUES
(N'<C:customer xmlns:C="http://schemas.mybook.com/customerschemas">
<item ID="1">
<customername>北方书城</customername>
<address>北京市海淀区知春路22号</address>
<phone>2222222</phone>
<contact>刘先生</contact>
</item>
</C:customer>');
-- 使用XML DML insert插入另一个item节点到XML中
UPDATE MyCustomer
SET CustomerItem.modify('
declare namespace CS="http://schemas.mybook.com/customerschemas";
insert (<item ID="2">
<customername>东图大厦</customername>
<address>长春市朝阳大街99号</address>
<phone>1111111</phone>
<contact>孙小姐</contact>
</item>)
into (/CS:customer)[1] ')
WHERE CustomerID=1;
SELECT CustomerItem
FROM Mycustomer;
GO
执行上面的SELECT查询后,可以看到CustomerItem中的XML内容,如下所示:
<C:customer xmlns:C="http://schemas.mybook.com/customerschemas">
<item ID="1">
<customername>北方书城</customername>
<address>北京市海淀区知春路22号</address>
<phone>2222222</phone>
<contact>刘先生</contact>
</item>
<item ID="2">
<customername>东图大厦</customername>
<address>长春市朝阳大街99号</address>
<phone>1111111</phone>
<contact>孙小姐</contact>
</item>
</C:customer>
2.delete
delete用于删除XML实例的节点。其语法格式如下:
delete Expression
Expression是要删除的节点的XQuery表达式。删除该表达式选择的所有节点,以及所选节点中的所有节点或值。表达式不能是根(/)节点。如果表达式返回空序列,则不进行删除,不返回错误。
下面的示例演示了从非类型化的xml变量中删除指令、注释、属性、元素和节点的方法。在每次删除后都会显示XML,结果如图3所示。
DECLARE @myDoc xml
SET @myDoc = '<?Instructions for=TheWC.exe ?>
<root>
<!-- 这里是注释 -->
<item ID="1" ShipTo="广州">这里是文本
<title>Ajax实战</title>
<author>张洪举</author>
</item>
<item ID="2">
<title>ASP.NET实战</title>
<author>卢桂章</author>
</item>
</root>'
SELECT @myDoc
-- 删除注释
SET @myDoc.modify('
delete /root/comment()
')
SELECT @myDoc
-- 删除所有指令
SET @myDoc.modify('
delete //processing-instruction()
')
SELECT @myDoc
-- 删除ID为1的item中的文本节点
SET @myDoc.modify('
delete /root/item[@ID=1]/text()
')
SELECT @myDoc
-- 删除一个属性
SET @myDoc.modify('
delete /root/item[@ID=1]/@ShipTo
')
SELECT @myDoc
-- 删除一个元素
SET @myDoc.modify('
delete /root/item[@ID=2]/author
')
SELECT @myDoc
-- 删除ID为2的item节点
SET @myDoc.modify('
delete /root/item[@ID=2]
')
SELECT @myDoc
GO
图3从非类型化xml变量中删除注释、指令、属性、元素和节点
下面的语句演示从类型化XML中删除节点的方法,其中的MyCustomer是前面在“将节点插入类型化的xml列中”部分中创建的。
UPDATE MyCustomer
SET CustomerItem.modify('
declare namespace CS="http://schemas.mybook.com/customerschemas";
delete /CS:customer/item[@ID=2]
');
SELECT CustomerItem FROM MyCustomer;
GO
3.replace
replace用于更新文档中的值。其语法格式如下:
replace value of
Expression1
with
Expression2
Expression1
标识其值要更新的节点。它必须仅标识一个单个节点。如果XML已类型化,则节点的类型必须是具有简单类型内容(列表或原子类型)的单个元素、文本节点或属性节点,不能是联合类型、复杂类型、处理指令、文档节点或注释节点。否则,将返回错误。
Expression2
标识节点的新值。在修改类型化的XML实例中,Expression2与Expression1必须是相同类型。
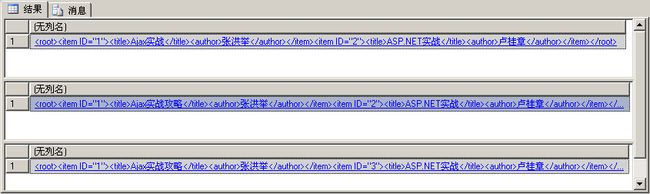
下面的示例演示了更新XML中元素的文本和属性值的方法。每次更改时,都会显示XML,如图4所示。
DECLARE @myDoc xml
SET @myDoc = '<root>
<item ID="1">
<title>Ajax实战</title>
<author>张洪举</author>
</item>
<item ID="2">
<title>ASP.NET实战</title>
<author>卢桂章</author>
</item>
</root>'
SELECT @myDoc
-- 更新ID为1的item中的title元素的文本
SET @myDoc.modify('
replace value of (/root/item[@ID=1]/title/text())[1]
with "Ajax实战攻略"
')
SELECT @myDoc
-- 更新属性值
SET @myDoc.modify('
replace value of (/root/item[@ID=2]/@ID)[1]
with "3"
')
SELECT @myDoc
图4 更改XML中元素的文本和属性值