GCC-3.4.6源代码学习笔记(117)
5.12.4.1.1.2.1.3. 在当前作用域查找
来到这里,没有指定作用域,该名字应该在当前作用域中来查找。这里的当前域可以是类域、名字空间、函数域、局部域( FOR 循环、 WHILE 循环等)。
cp_parser_lookup_name (continue)
13832 else
13833 {
13834 decl = lookup_name_real (name, is_type, /*nonclass=*/ 0,
13835 is_namespace, flags);
13836 parser->qualifying_scope = NULL_TREE;
13837 parser->object_scope = NULL_TREE;
13838 }
注意参数 nonclass 的传入值是 0 ,这表示我们将要在类作用域中查找由参数 name 给出的名字;而 namespaces_only 则从 cp_parser_class_name 传入,其值来自 is_namespace 。
3912 tree
3913 lookup_name_real (tree name, int prefer_type, int nonclass, in name-lookup.c
3914 int namespaces_only, int flags)
3915 {
3916 cxx_binding *iter;
3917 tree val = NULL_TREE;
3918
3919 timevar_push (TV_NAME_LOOKUP);
3920 /* Conversion operators are handled specially because ordinary
3921 unqualified name lookup will not find template conversion
3922 operators. */
3923 if (IDENTIFIER_TYPENAME_P (name))
3924 {
3925 struct cp_binding_level *level;
3926
3927 for (level = current_binding_level ;
3928 level && level->kind != sk_namespace;
3929 level = level->level_chain)
3930 {
3931 tree class_type;
3932 tree operators;
3933
3934 /* A conversion operator can only be declared in a class
3935 scope. */
3936 if (level->kind != sk_class)
3937 continue ;
3938
3939 /* Lookup the conversion operator in the class. */
3940 class_type = level->this_entity;
3941 operators = lookup_fnfields (class_type, name, /*protect=*/ 0);
3942 if (operators)
3943 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, operators);
3944 }
3945
3946 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, NULL_TREE);
3947 }
这里首先处理转换操作符。其原因,上面的注释已经解释了,因为模板形式的转换操作符不是普通的非限定名字查找的候选(还记得吗,模板,除非具现,不进行域绑定,因此普通的非限定名字查找找不出来)。
5.12.4.1.1.2.1.3.1. 转换操作符
在 3923 行,如果 name 命名了一个类型转换操作符, IDENTIFIER_TYPENAME_P 返回 true 。转换操作符必须在类中定义。因此查找局限在类中并且从最里层的类开始向外(看到 level_chain 域显示了嵌套类的封闭类( enclosing class ),在嵌套类中找不到该名字就要沿着 level_chain 查找)。
1387 tree
1388 lookup_fnfields (tree xbasetype, tree name, int protect) in search.c
1389 {
1390 tree rval = lookup_member (xbasetype, name, protect, /*want_type=*/ false);
1391
1392 /* Ignore non-functions. */
1393 if (rval && !BASELINK_P (rval))
1394 return NULL_TREE;
1395
1396 return rval;
1397 }
具体做法实际上与在指定类中查找一致。
5.12.4.1.1.2.1.3.2. 其他名字
如果名字不是转换操作符名,首先调用 lookup_flags 来设置为后面查找所使用的标记。
3562 static int
3563 lookup_flags (int prefer_type, int namespaces_only) in name-lookup.c
3564 {
3565 if (namespaces_only)
3566 return LOOKUP_PREFER_NAMESPACES;
3567 if (prefer_type > 1)
3568 return LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES;
3569 if (prefer_type > 0)
3570 return LOOKUP_PREFER_BOTH;
3571 return 0;
3572 }
上面 LOOKUP_PREFER_NAMESPACES 表示不接受对象,结果可能是名字空间; LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES 表示不接受对象,结果可能是类型; LOOKUP_PREFER_BOTH 表示结果应该是类或名字空间名。
lookup_name_real (continue)
3949 flags |= lookup_flags (prefer_type, namespaces_only);
3650
3951 /* First, look in non-namespace scopes. */
3952
3953 if (current_class_type == NULL_TREE)
3954 nonclass = 1;
3955
3956 for (iter = IDENTIFIER_BINDING (name); iter; iter = iter->previous)
3957 {
3958 tree binding;
3959
3960 if (!LOCAL_BINDING_P (iter) && nonclass)
3961 /* We're not looking for class-scoped bindings, so keep going. */
3962 continue ;
3963
3964 /* If this is the kind of thing we're looking for, we're done. */
3965 if (qualify_lookup (iter->value, flags))
3966 binding = iter->value;
3967 else if ((flags & LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES)
3968 && qualify_lookup (iter->type, flags))
3969 binding = iter->type;
3970 else
3971 binding = NULL_TREE;
3972
3973 if (binding)
3974 {
3975 val = binding;
3976 break ;
3977 }
3978 }
节点 lang_identifier 的 binding 域指向一组非名字空间作用域,它是一个由 cxx_binding 节点构成的链表(参考图形: 内建类型的节点 作为例子)。 IDNEITIFIER_BINDING 访问这个 binding 域,并且通过每个节点的 previous 域来遍历整个链表。这个链表记录了该标识符声明目前已经出现的不同的作用域。而每个 cxx_binding 节点的 value 域记录了在该作用域中,该名字所绑定的非类型实体(通常是 TYPE_DECL 或 NAMESPACE_DECL ),而 type 域记录绑定的类型实体。
注意上面调用 qualify_lookup 的次序及参数;这个函数检查找到的是否就是目标。
3577 static tree
3578 qualify_lookup (tree val, int flags)
3579 {
3580 if (val == NULL_TREE)
3581 return val;
3582 if ((flags & LOOKUP_PREFER_NAMESPACES) && TREE_CODE (val) == NAMESPACE_DECL)
3583 return val;
3584 if ((flags & LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES)
3585 && (TREE_CODE (val) == TYPE_DECL || TREE_CODE (val) == TEMPLATE_DECL))
3586 return val;
3587 if (flags & (LOOKUP_PREFER_NAMESPACES | LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES))
3588 return NULL_TREE;
3589 return val;
3590 }
上面的 (LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES | LOOKUP_PREFER_NAMESPACES) 就是 LOOKUP_PREFER_BOTH 的对于。注意如果 flags 是 0 ,它接受任何东西(没有过滤)。
lookup_name_real (continue)
3980 /* Now lookup in namespace scopes. */
3981 if (!val)
3982 {
3983 tree t = unqualified_namespace_lookup (name, flags);
3984 if (t)
3985 val = t;
3986 }
3987
3988 if (val)
3989 {
3990 /* If we have a single function from a using decl, pull it out. */
3991 if (TREE_CODE (val) == OVERLOAD && ! really_overloaded_fn (val))
3992 val = OVL_FUNCTION (val);
3993 }
3994
3995 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, val);
3996 }
如果我们不能以这种快速的方式找到这个名字,该标识符一定被声明在某些名字空间或甚至是由 using 语句引入的名字空间里。我们不得不逐个查找这些名字空间。
3706 static tree
3707 unqualified_namespace_lookup (tree name, int flags) in name-lookup.c
3708 {
3709 tree initial = current_decl_namespace ();
3710 tree scope = initial;
3711 tree siter;
3712 struct cp_binding_level *level;
3713 tree val = NULL_TREE;
3714 cxx_binding binding;
3715
3716 timevar_push (TV_NAME_LOOKUP);
3717 cxx_binding_clear (&binding);
首先, current_decl_namespace 帮助找出最里层的封闭名字空间( enclosing namespace )。在下面,如果 decl_namespace_list 不是 NULL ,它保存所有封闭名字空间,越接近头部的封闭名字空间越靠近里层,因此最里面的名字空间在头部获得。
3039 tree
3040 current_decl_namespace (void) in name-lookup.c
3041 {
3042 tree result;
3043 /* If we have been pushed into a different namespace, use it. */
3044 if (decl_namespace_list )
3045 return TREE_PURPOSE (decl_namespace_list );
3046
3047 if (current_class_type )
3048 result = decl_namespace_context (current_class_type );
3049 else if (current_function_decl )
3050 result = decl_namespace_context (current_function_decl );
3051 else
3052 result = current_namespace ;
3053 return result;
3054 }
否则, decl_namespace_context 将不停进入上下文直到找到名字空间作用域。注意到名字空间总是可以找出来的,因为最顶层总是 global_namespace ,对于这个作用域将返回 NULL_TREE 。
1426 tree
1427 decl_namespace_context (tree decl) in tree.c
1428 {
1429 while (1)
1430 {
1431 if (TREE_CODE (decl) == NAMESPACE_DECL)
1432 return decl;
1433 else if (TYPE_P (decl))
1434 decl = CP_DECL_CONTEXT (TYPE_MAIN_DECL (decl));
1435 else
1436 decl = CP_DECL_CONTEXT (decl);
1437 }
1438 }
假定现在我们有以下的定义:
namespace C {
namespace B {
void func1() { … } // block scope A
void func2 () { // block scope D
using namespace Y;
using namespace X;
W w;
}
}
}
编译器准备查找 W 的定义。上面的作用域的层次结构如下图所示:
图 100 : unqualified_namespace_lookup 的例子
对于这些语句, current_decl_namespace 将返回 B 的 NAMESPACE_DECL 作为结果。然后在 3719 行外层的 FOR 循环,函数将沿着层次结构访问名字空间,直到到达全局名字空间,如果一直没有找到定义的话。
unqualified_namespace_lookup (continue)
3719 for (; !val; scope = CP_DECL_CONTEXT (scope))
3720 {
3721 cxx_binding *b =
3722 cxx_scope_find_binding_for_name (NAMESPACE_LEVEL (scope), name);
3723
3724 if (b)
3725 {
3726 if (b->value && DECL_P (b->value)
3727 && DECL_LANG_SPECIFIC (b->value)
3728 && DECL_ANTICIPATED (b->value))
3729 /* Ignore anticipated built-in functions. */
3730 ;
3731 else
3732 binding.value = b->value;
3733 binding.type = b->type;
3734 }
3735
3736 /* Add all _DECLs seen through local using-directives. */
3737 for (level = current_binding_level ;
3738 level->kind != sk_namespace;
3739 level = level->level_chain)
3740 if (!lookup_using_namespace (name, &binding, level->using_directives,
3741 scope, flags))
3742 /* Give up because of error. */
3743 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, error_mark_node);
而在 3737 行的内层的 FOR 循环, current_binding_level 将返回 D 的 cxx_scope (如果它是一个类域,因为 using 指示在类域是不被允许的, lookup_using_namespace 将立即返回)。因为在这些非名字空间作用域(类域除外)中,亦可以使用 using 指示来引入名字空间,使其在该域中可见,显然,这也是可见集的一部分,需要在其中查找,并进行二义性检查。
3809 static bool
3810 lookup_using_namespace (tree name, cxx_binding *val, tree usings, in name-lookup.c
3811 tree scope, int flags)
3812 {
3813 tree iter;
3814 timevar_push (TV_NAME_LOOKUP);
3815 /* Iterate over all used namespaces in current, searching for using
3816 directives of scope. */
3817 for (iter = usings; iter; iter = TREE_CHAIN (iter))
3818 if (TREE_VALUE (iter) == scope)
3819 {
3820 tree used = ORIGINAL_NAMESPACE (TREE_PURPOSE (iter));
3821 cxx_binding *val1 =
3822 cxx_scope_find_binding_for_name (NAMESPACE_LEVEL (used), name);
3823 /* Resolve ambiguities. */
3824 if (val1)
3825 val = ambiguous_decl (name, val, val1, flags);
3826 }
3827 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, val->value != error_mark_node);
3828 }
为了理解 lookup_using_namespace 的行为,假定名字空间 X 被封闭在名字空间 B 中,并且在名字空间 X 有指示“ using namespace Z ”;而名字空间 Y 则被封闭在名字空间 C 中:
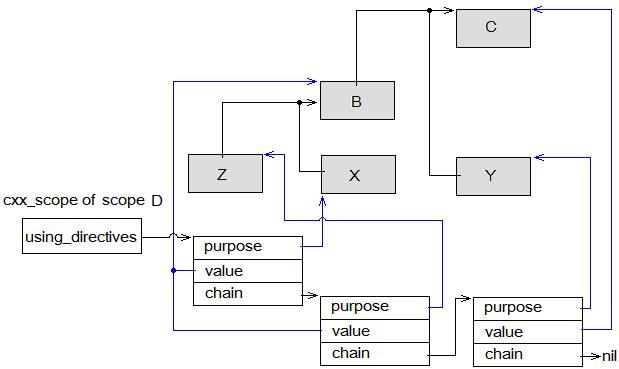
图 101 : using_directives 的例子
那么在作用域 D 的 cxx_scope 节点的 using_directives 域的链表中应该有 3 个节点(注意上面的链表反序了,不过这里的次序没有关系)。第一个节点是“ using namespace X ”加入的;第二个节点是由名字空间 X 里的“ using namespace Z ”加入的;第三个则是“ using namespace Y ”加入的。对于每个节点,其 value 域是被引入名字空间的上下文与作用域 D 的上下文的公共祖先, purpose 域则是引入的名字空间。
注意 lookup_using_namespace 的 3818 行,一开始 scope 是作用域 D 的最里层封闭名字空间。这句条件语句严格维护了名字空间的层次性,避免了名字空间之间的穿越。否则例子中的“ using namespace Y ”将在名字空间 B 中引入名字空间 Y ,这是不可以的。但是如果在名字空间 B 中没有找到, scope 将上升一级,指向名字空间 C ,这时“ using namespace X ”及间接的“ using namespace Z ”已经处理过,它们亦被 3818 行过滤掉;而“ using namespace Y ”这次得到处理。
unqualified_namespace_lookup (continue)
3745 /* Add all _DECLs seen through global using-directives. */
3746 /* XXX local and global using lists should work equally. */
3747 siter = initial;
3748 while (1)
3749 {
3750 if (!lookup_using_namespace (name, &binding,
3751 DECL_NAMESPACE_USING (siter),
3752 scope, flags))
3753 /* Give up because of error. */
3754 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, error_mark_node);
3755 if (siter == scope) break ;
3756 siter = CP_DECL_CONTEXT (siter);
3757 }
3758
3759 val = select_decl (&binding, flags);
3760 if (scope == global_namespace )
3761 break ;
3762 }
3763 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, val);
3764 }
在 3747 行, initial 就是最开始的封闭名字空间。而 DECL_NAMESPACE_USING 则是名字空间节点,用来记录其中的 using 指示所引入的名字空间,的链表。其结构与上面看到的 using_directive 相似。 lookup_using_namespace 依然坚定地维护着名字空间的层次,并忠实地查找名字。对于找到的结果, select_decl 从中选择最合适的实体。
3765 static tree
3766 select_decl (cxx_binding *binding, int flags) in name-lookup.c
3767 {
3768 tree val;
3769 val = binding->value;
3770
3771 timevar_push (TV_NAME_LOOKUP);
3772 if (LOOKUP_NAMESPACES_ONLY (flags))
3773 {
3774 /* We are not interested in types. */
3775 if (val && TREE_CODE (val) == NAMESPACE_DECL)
3776 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, val);
3777 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, NULL_TREE);
3778 }
3779
3780 /* If looking for a type, or if there is no non-type binding, select
3781 the value binding. */
3782 if (binding->type && (!val || (flags & LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES)))
3783 val = binding->type;
3784 /* Don't return non-types if we really prefer types. */
3785 else if (val && LOOKUP_TYPES_ONLY (flags) && TREE_CODE (val) != TYPE_DECL
3786 && (TREE_CODE (val) != TEMPLATE_DECL
3787 || !DECL_CLASS_TEMPLATE_P (val)))
3788 val = NULL_TREE;
3789
3790 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, val);
3791 }
看到如果找到的对象不合适, select_decl 将返回 NULL ,但是不会清除 binding ,因此在下一次循环时,如果找到新的定义,可以进行二义性检查。而如果返回了有效的 val ,我们将一直返回到 cp_parser_lookup_name 。
cp_parser_lookup_name (continue)
13840 /* If the lookup failed, let our caller know. */
13841 if (!decl
13842 || decl == error_mark_node
13843 || (TREE_CODE (decl) == FUNCTION_DECL
13844 && DECL_ANTICIPATED (decl)))
13845 return error_mark_node;
13846
13847 /* If it's a TREE_LIST, the result of the lookup was ambiguous. */
13848 if (TREE_CODE (decl) == TREE_LIST)
13849 {
13850 /* The error message we have to print is too complicated for
13851 cp_parser_error, so we incorporate its actions directly. */
13852 if (!cp_parser_simulate_error (parser))
13853 {
13854 error ("reference to `%D' is ambiguous", name);
13855 print_candidates (decl);
13856 }
13857 return error_mark_node;
13858 }
13859
13860 my_friendly_assert (DECL_P (decl)
13861 || TREE_CODE (decl) == OVERLOAD
13862 || TREE_CODE (decl) == SCOPE_REF
13863 || TREE_CODE (decl) == UNBOUND_CLASS_TEMPLATE
13864 || BASELINK_P (decl),
13865 20000619);
13866
13867 /* If we have resolved the name of a member declaration, check to
13868 see if the declaration is accessible. When the name resolves to
13869 set of overloaded functions, accessibility is checked when
13870 overload resolution is done.
13871
13872 During an explicit instantiation, access is not checked at all,
13873 as per [temp.explicit]. */
13874 if (DECL_P (decl))
13875 check_accessibility_of_qualified_id (decl, object_type, parser->scope);
13876
13877 return decl;
13878 }
记得对于重载函数,返回的节点是 OVERLOAD 类型的,而不是 TREE_LIST ——这个形式意味着出现了二义性(虽然从这里的调用路径来看,二义性应该在进入回到函数前就被发现了)。
如果找到的名字是有效的,这个时候要检查其可访问性。
1311 void
1312 check_accessibility_of_qualified_id (tree decl, in semantics.c
1313 tree object_type,
1314 tree nested_name_specifier)
1315 {
1316 tree scope;
1317 tree qualifying_type = NULL_TREE;
1318
1319 /* Determine the SCOPE of DECL. */
1320 scope = context_for_name_lookup (decl);
首先,我们要找出封闭这个名字的上下文。看到匿名 union 的定义是个例外,其成员被认为定义在该 union 所声明的作用域中。
600 tree
601 context_for_name_lookup (tree decl)
602 {
603 /* [class.union]
604
605 For the purposes of name lookup, after the anonymous union
606 definition, the members of the anonymous union are considered to
607 have been defined in the scope in which the anonymous union is
608 declared. */
609 tree context = DECL_CONTEXT (decl);
610
611 while (context && TYPE_P (context) && ANON_AGGR_TYPE_P (context))
612 context = TYPE_CONTEXT (context);
613 if (!context)
614 context = global_namespace ;
615
616 return context;
617 }
注意对于 NAMESPACE_DECL , TYPE_P 返回 false 。同时,对于名字空间,它永远是可访问的。
check_accessibility_of_qualified_id (continue)
1321 /* If the SCOPE is not a type, then DECL is not a member. */
1322 if (!TYPE_P (scope))
1323 return ;
1324 /* Compute the scope through which DECL is being accessed. */
1325 if (object_type
1326 /* OBJECT_TYPE might not be a class type; consider:
1327
1328 class A { typedef int I; };
1329 I *p;
1330 p->A::I::~I();
1331
1332 In this case, we will have "A::I" as the DECL, but "I" as the
1333 OBJECT_TYPE. */
1334 && CLASS_TYPE_P (object_type)
1335 && DERIVED_FROM_P (scope, object_type))
1336 /* If we are processing a `->' or `.' expression, use the type of the
1337 left-hand side. */
1338 qualifying_type = object_type;
1339 else if (nested_name_specifier)
1340 {
1341 /* If the reference is to a non-static member of the
1342 current class, treat it as if it were referenced through
1343 `this'. */
1344 if (DECL_NONSTATIC_MEMBER_P (decl)
1345 && current_class_ptr
1346 && DERIVED_FROM_P (scope, current_class_type ))
1347 qualifying_type = current_class_type ;
1348 /* Otherwise, use the type indicated by the
1349 nested-name-specifier. */
1350 else
1351 qualifying_type = nested_name_specifier;
1352 }
1353 else
1354 /* Otherwise, the name must be from the current class or one of
1355 its bases. */
1356 qualifying_type = currently_open_derived_class (scope);
1357
1358 if (qualifying_type)
1359 perform_or_defer_access_check (TYPE_BINFO (qualifying_type), decl);
1360 }
上面如果参数 decl 被命名为‘ A::B ’,那么参数 nested_name_specifier 是‘ A ’。显然,如果 object_type 或 nested_name_specifier 不是 NULL ,访问性检查应该根据该类型来进行。看到如果 object_type 不是类类型, qualifying_type 将保持为 NULL 。而如果这 2 个变量都是 NULL ,封闭域应该是当前打开的类的其中之一。它由 currently_open_derived_class 来确定。
5599 tree
5600 currently_open_derived_class (tree t) in class.c
5601 {
5602 int i;
5603
5604 /* The bases of a dependent type are unknown. */
5605 if (dependent_type_p (t))
5606 return NULL_TREE;
5607
5608 if (!current_class_type )
5609 return NULL_TREE;
5610
5611 if (DERIVED_FROM_P (t, current_class_type ))
5612 return current_class_type ;
5613
5614 for (i = current_class_depth - 1; i > 0; --i)
5615 if (DERIVED_FROM_P (t, current_class_stack [i].type))
5616 return current_class_stack [i].type;
5617
5618 return NULL_TREE;
5619 }
一旦封闭类型找到,对该声明的访问性检查由 perform_or_defer_access_check 执行。该声明被 cp_parser_lookup_name 返回。
5.12.4.1.1.2.2. 查找的结果
在经过名字查找,在这一点上,解析得到的参数及参数列表如图所示。
( 点此打开 )
图 102 :构建的参数及参数列表