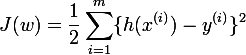最小均方算法(LMS Algorithm)理论及DSP实现
最小均方算法(LMS Algorithm)理论及DSP实现
本文主要对LMS(Least Mean Square)算法进行简单的整理,包括内容:
(1)理论上介绍基于LMS的梯度下降算法(包括BACH/STOCHASTIC),给出一个matlab的实现
(2)DSP上的实现,主要使用C语言
1. LMS算法理论
问题引出
因为本人感兴趣的领域为机器学习,因此这里先说明下学习的过程,给定这样一个问题:某地的房价与房地面积和卧室的数量之间成如下表的关系,
Living area (feet2) #bedrooms Price (1000$s)
2104 3 400
1600 3 330
2400 3 369
1416 2 232
3000 4 540
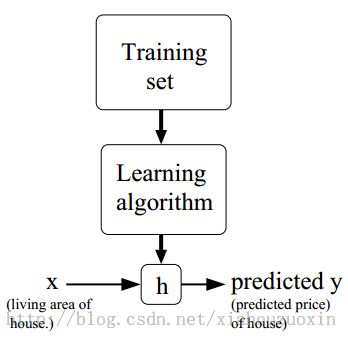
据此,我们要通过分析上面的数据学习出一个模型,用于预测其它情况(比如面积2000,卧室数5)的房价。这就是一个学习问题,更简洁的说,就是一个概率里的回归问题。这里固定几个符号:x表示输入([Living area,bedrooms]),y表示输出(Price),h表示要学习的模型,m表示输入每个数据维度(这里是2),n表示输入数据的个数(这里是5)。
该学习过程的可以描述如下图,
.
h必定与面积和卧室数相关,.这里不考虑复杂的情况,假设模型是线性的(实际其它问题中很可能是其它关系模型,比如exp)
.![]()
.令x1=1,则![]() 。这里,我们考虑上面的房价问题,还是将w0忽略。
。这里,我们考虑上面的房价问题,还是将w0忽略。
为了获得h(x),现在的问题是什么呢?那就是:怎样获得h(x)的w1~w2的值。
我们再对问题进行描述:
已知——上面的数据表格,线性模型(不知道参数)
求解——参数w1~w2
引入一个函数,叫损失函数
就是最小二乘法中计算误差的函数,只是前面添加了1/2,表示什么意思呢?损失函数越小,说明模型与当前已知数据的拟合程度越好,否则越差。因此,求解w1~w2的目标就是求解J(w)最小,这就用到了LMS算法。
LMS算法
LMS算法是一个搜索算法,假设w从某个给定的初始值开始迭代,逐渐使J(W)朝着最小的方向变化,直到达到一个值使J(w)收敛。考虑梯度下降算法(gradient descent algorithm),它通过给定的w值快速的执行如下的更新操作:
其中![]() 为学习率(Learning rate)。
为学习率(Learning rate)。
要对w更新,首先需要完成上面的求导,求导的结果参见下面的算法流程。
对一个单一的训练实例j,
![]()
按照上述的更新方法,对多个实例的更新规则为
Repeat until convergence {
for every j, exec
}
这种更新的梯度下降方法称为batch gradient descent。还有一种更新的方式:采用随机的样本数据实例,如下
Repeat until convergence {
for every j, exec
![]()
}
这种方法称为stochastic gradient descent (或者incremental gradient descent)。两种方法的明显区别是batch的训练时间要比stochastic常,但效果可能更好。实际问题中,因为我们只需要找到一个接近使J(w)最小的值即可,因此stochastic更常用。
说了这么久,LMS到底能用来干嘛,其实上面已经很清楚了:参数训练中的求极值。
在matlab上对stochastic gradient descent 的实现如下:
- function [test_targets, a, updates] = LMS(train_patterns, train_targets, test_patterns, params)
- % Classify using the least means square algorithm
- % Inputs:
- % train_patterns - Train patterns
- % train_targets - Train targets
- % test_patterns - Test patterns
- % param - [Maximum iteration Theta (Convergence criterion), Convergence rate]
- %
- % Outputs
- % test_targets - Predicted targets
- % a - Weights vector
- % updates - Updates throughout the learning iterations
- %
- % NOTE: Suitable for only two classes
- %
- [c, n] = size(train_patterns);
- [Max_iter, theta, eta] = process_params(params);
- y = [train_patterns ; ones(1,n)];
- train_zero = find(train_targets == 0);
- %Preprocessing
- processed_patterns = y;
- processed_patterns(:,train_zero) = -processed_patterns(:,train_zero);
- b = 2*train_targets - 1;
- %Initial weights
- a = sum(processed_patterns')';
- iter = 1;
- k = 0;
- update = 1e3;
- updates = 1e3;
- while ((sum(abs(update)) > theta) & (iter < Max_iter))
- iter = iter + 1;
- %k <- (k+1) mod n
- k = mod(k+1,n);
- if (k == 0),
- k = n;
- end
- % a <- a + eta*(b-a'*Yk)*Yk'
- update = eta*(b(k) - a'*y(:,k))*y(:,k);
- a = a + update;
- updates(iter) = sum(abs(update));
- end
- if (iter == Max_iter),
- disp(['Maximum iteration (' num2str(Max_iter) ') reached']);
- else
- disp(['Did ' num2str(iter) ' iterations'])
- end
- %Classify the test patterns
- test_targets = a'*[test_patterns; ones(1, size(test_patterns,2))];
- test_targets = test_targets > 0;
2. 基于LMS的梯度下降算法在DSP上的实现
下面是我在DSP6713上使用软件仿真实现的LMS算法,
- /*
- * zx_lms.h
- *
- * Created on: 2013-8-4
- * Author: monkeyzx
- */
- #ifndef ZX_LMS_H_
- #define ZX_LMS_H_
- /*
- * methods for @lms_st.method
- */
- #define STOCHASTIC (0x01) /* 随机梯度下降 */
- #define BATCH (0x02) /* BATCH梯度下降 */
- struct lms_st {
- short method; /* 0/1 */
- double *x; /* features, x0,...,x[n-1] */
- int n; /* dimension of features */
- double *y; /* given output, y0,..,y[m-1] */
- int m; /* number of data set */
- double *weight; /* weighs that want to train by using LMS, w0,w1,..,w[n-1] */
- double lrate; /* learning rate */
- double threshhold; /* if error < threshold, stop iteration */
- int max_iter; /* if iter numbers > max_iter, stop iteration,
- if max_iter<0, then max_iter is unused */
- };
- extern void zx_lms(void);
- #endif /* ZX_LMS_H_ */
- /*
- * zx_lms.c
- * Least Mean Squares Algorithm
- * Created on: 2013-8-4
- * Author: monkeyzx
- */
- #include "zx_lms.h"
- #include "config.h"
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- static double init_y[] = {4.00,3.30,3.69,2.32};
- static double init_x[] = {
- 2.104,3,
- 1.600,3,
- 2.400,3,
- 3.000,4
- };
- static double weight[2] = {0.1, 0.1};
- /*
- * Least Mean Square Algorithm
- * return value @error when stop iteration
- * use @lms_prob->method to choose a method.
- */
- double lms(struct lms_st *lms_prob)
- {
- double err;
- double error;
- int i = 0;
- int j = 0;
- int iter = 0;
- static double *h = 0; /* 加static,防止栈溢出*/
- h = (double *)malloc(sizeof(double) * lms_prob->m);
- if (!h) {
- return -1;
- }
- do {
- error = 0;
- if (lms_prob->method != STOCHASTIC) {
- i = 0;
- } else {
- /* i=(i+1) mod m */
- i = i + 1;
- if (i >= lms_prob->m) {
- i = 0;
- }
- }
- for ( ; i<lms_prob->m; i++) {
- h[i] = 0;
- for (j=0; j<lms_prob->n; j++) {
- h[i] += lms_prob->weight[j] * lms_prob->x[i*lms_prob->n+j]; /* h(x) */
- }
- if (lms_prob->method == STOCHASTIC) break; /* handle STOCHASTIC */
- }
- for (j=0; j<lms_prob->n; j++) {
- if (lms_prob->method != STOCHASTIC) {
- i = 0;
- }
- for ( ; i<lms_prob->m; i++) {
- err = lms_prob->lrate
- * (lms_prob->y[i] - h[i]) * lms_prob->x[i*lms_prob->n+j];
- lms_prob->weight[j] += err; /* Update weights */
- error += ABS(err);
- if (lms_prob->method == STOCHASTIC) break; /* handle STOCHASTIC */
- }
- }
- iter = iter + 1;
- if ((lms_prob->max_iter > 0) && ((iter > lms_prob->max_iter))) {
- break;
- }
- } while (error >= lms_prob->threshhold);
- free(h);
- return error;
- }
- #define DEBUG
- void zx_lms(void)
- {
- int i = 0;
- double error = 0;
- struct lms_st lms_prob;
- lms_prob.lrate = 0.01;
- lms_prob.m = 4;
- lms_prob.n = 2;
- lms_prob.weight = weight;
- lms_prob.threshhold = 0.2;
- lms_prob.max_iter = 1000;
- lms_prob.x = init_x;
- lms_prob.y = init_y;
- // lms_prob.method = STOCHASTIC;
- lms_prob.method = BATCH;
- // error = lms(init_x, 2, init_y, 4, weight, 0.01, 0.1, 1000);
- error = lms(&lms_prob);
- #ifdef DEBUG
- for (i=0; i<sizeof(weight)/sizeof(weight[0]); i++) {
- printf("%f\n", weight[i]);
- }
- printf("error:%f\n", error);
- #endif
- }
输入、输出、初始权值为
static double init_y[] = {4.00,3.30,3.69,2.32};
static double init_x[] = { /* 用一维数组保存 */
2.104, 3,
1.600, 3,
2.400, 3,
3.000, 4
};
static double weight[2] = {0.1, 0.1};
main函数中只需要调用zx_lms()就可以运行了,本文对两种梯度下降方法做了个简单对比,
| max_iter=1000 | w1 | w2 | error | CPU Cycles |
| batch | -0.6207369 | 1.419737 | 0.20947 | 2181500 |
| stochastic |
0.145440 | 0.185220 | 0.130640 | 995 |
需要说明的是:batch算法是达到最大迭代次数1000退出的,而stochastic是收敛退出的,因此这里batch算法应该没有对数据做到较好的拟合。stochastic算法则在时钟周期上只有995,远比batch更有时间上的优势。
注:这里的error没有太大的可比性,因为batch的error针对的整体数据集的error,而stochastic 的error是针对一个随机的数据实例。
LMS有个很重要的问题:收敛。开始时可以根据给定数据集设置w值,使h(x)尽可能与接近y,如果不确定可以将w设置小一点。
这里顺便记录下在调试过程中遇到的一个问题:在程序运行时发现有变量的值为1.#QNAN。
解决:QNAN是Quiet Not a Number简写,是常见的浮点溢出错误,在网上找到了解释
A QNaN is a NaN with the most significant fraction bit set. QNaN’s propagate freely through most arithmetic operations. These values pop out of an operation when the result is not mathematically defined.
在开始调试过程中因为迭代没有收敛,发散使得w和error等值逐渐累积,超过了浮点数的范围,从而出现上面的错误,通过修改使程序收敛后上面的问题自然而然解决了。
参考:
[1] Andrew Ng的机器学习课程
[2] Richard O.Duda 等,《模式分类》