深入解析开源项目之Universal-Image-Loader(一)框架篇
珍惜作者劳动成果,如需转载,请注明出处。
http://blog.csdn.net/zhengzechuan91/article/details/50281835
Universal-Image-Loader (Github地址) 是一个优秀的图片加载开源项目,很多童鞋都在自己的项目中用到了。优秀的项目从来都是把简单留给开发者,把复杂封装在框架内部。ImageLoader作为Github上Star数过万的项目,备受开发者青睐,所以我们有必要搞清楚它的内部实现。
我们要研究一个框架,要顺着它的脉络去分析。先要搞清楚这个框架大概的思路是什么,这样我们才能顺着这个思路去对这个框架进行进一步的分析。
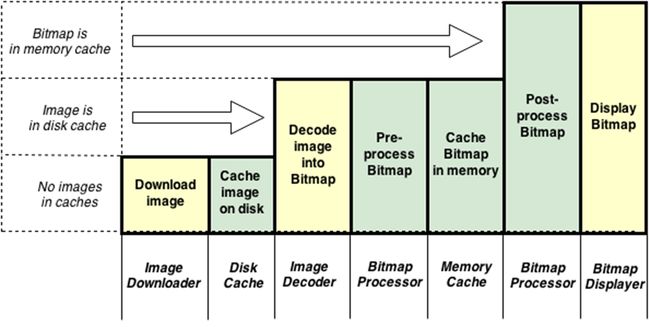
ImageLoader加载图片原理
首先来说说ImageLoader框架的整体思路:通过ImageLoader#displayImage()将Task加载到ImageLoaderEngine的线程池中,然后通过ImageDownloader缓存到Cache,再经过BitmapProcessor加工Bitmap,最后BitmapDisplayer显示Bitmap。
ImageLoader
ImageLoader类是一个单例,使用它之前首先要在应用的Application里调用ImageLoader#init(ImageLoaderConfiguration configuration)方法初始化,这个方法是配置自定义的ImageLoaderConfiguration,并实例化ImageLoaderEngine。
/* ImageLoader.java */
public synchronized void init(ImageLoaderConfiguration configuration) {
engine = new ImageLoaderEngine(configuration);
this.configuration = configuration;
}而ImageLoaderEngine构造方法如下:
/* ImageLoaderEngine.java */
ImageLoaderEngine(ImageLoaderConfiguration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
taskExecutor = configuration.taskExecutor;
taskExecutorForCachedImages = configuration.taskExecutorForCachedImages;
taskDistributor = DefaultConfigurationFactory.createTaskDistributor();
}ImageLoaderEngine中有3个线程池:
taskDistributor使用了Executors#newCachedThreadPool(),
负责加载跟图片无关的任务;如果是首次加载图片,使用taskExecutor。
而如果是缓存过的图片,使用taskExecutorForCachedImages执行图片相关任务;
接下来先来看看一些配置相关的类:
DisplayImageOptions默认配置
首先是用于显示图片的配置类DisplayImageOptions,这里用到了Build模式,内部类Builder的默认值如下:
/* DisplayImageOptions$Builder.java */
//默认加载过程中的默认图都为空,需要手动配置
private int imageResOnLoading = 0;
private int imageResForEmptyUri = 0;
private int imageResOnFail = 0;
private Drawable imageOnLoading = null;
private Drawable imageForEmptyUri = null;
private Drawable imageOnFail = null;
//默认加载前不需要重置ImageViewAware
private boolean resetViewBeforeLoading = false;
//默认不缓存在内存中,需要手动配置
private boolean cacheInMemory = false;
//默认不缓存在磁盘上,需要手动配置
private boolean cacheOnDisk = false;
//默认Image的ScaleType为IN_SAMPLE_POWER_OF_2,在
//BaseImageDecoder#decode()时使用
//prepareDecodingOptions()方法对尺寸做处理时用到
private ImageScaleType imageScaleType = ImageScaleType.IN_SAMPLE_POWER_OF_2;
private Options decodingOptions = new Options();
//默认加载前无延时
private int delayBeforeLoading = 0;
//默认不接收EXIF参数
private boolean considerExifParams = false;
//下载参数
private Object extraForDownloader = null;
//缓存前处理
private BitmapProcessor preProcessor = null;
//缓存后处理
private BitmapProcessor postProcessor = null;
//默认显示图片为SimpleBitmapDisplayer,实现了display()
//方法,通过给imageAware使用setImageBitmap(bitmap)方法
//显示图片。
private BitmapDisplayer displayer = DefaultConfigurationFactory.createBitmapDisplayer();
//Handler
private Handler handler = null;
//默认为异步加载
private boolean isSyncLoading = false;ImageLoaderConfiguration默认配置
另一个类为用于图片加载缓存的配置类ImageLoaderConfiguration,还是使用的Build模式,默认值如下:
/* ImageLoaderConfiguration$Builder.java */
private Context context;
//图片内存缓存的宽度
private int maxImageWidthForMemoryCache = 0;
//图片内存缓存的高度
private int maxImageHeightForMemoryCache = 0;
//图片磁盘缓存的宽度
private int maxImageWidthForDiskCache = 0;
//图片磁盘缓存的高度
private int maxImageHeightForDiskCache = 0;
//默认磁盘缓存不处理图片
private BitmapProcessor processorForDiskCache = null;
private Executor taskExecutor = null;
private Executor taskExecutorForCachedImages = null;
private boolean customExecutor = false;
private boolean customExecutorForCachedImages = false;
//默认的线程池容量为3
private int threadPoolSize = DEFAULT_THREAD_POOL_SIZE;
//默认线程优先级为3,正常为5
private int threadPriority = DEFAULT_THREAD_PRIORITY;
//默认同一Uri的图片在内存中可以有多个尺寸
private boolean denyCacheImageMultipleSizesInMemory = false;
//默认队列为先进先出
private QueueProcessingType tasksProcessingType = DEFAULT_TASK_PROCESSING_TYPE;
//内存缓存
private int memoryCacheSize = 0;
//磁盘缓存
private long diskCacheSize = 0;
//磁盘缓存数量
private int diskCacheFileCount = 0;
//内存缓存
private MemoryCache memoryCache = null;
//磁盘缓存
private DiskCache diskCache = null;
//文件命名规则,有Hash和MD5两种方式
private FileNameGenerator diskCacheFileNameGenerator = null;
//通过Uri获取输入流
private ImageDownloader downloader = null;
//通过图片加载ImageDecodingInfo实体获取Bitmap
private ImageDecoder decoder;
//图片显示配置
private DisplayImageOptions defaultDisplayImageOptions = null;另外,在build()的时候,对一些空的配置赋予了一些默认的值。
/* ImageLoaderConfiguration$Builder.java */
public ImageLoaderConfiguration build() {
initEmptyFieldsWithDefaultValues();
return new ImageLoaderConfiguration(this);
}
private void initEmptyFieldsWithDefaultValues() {
//默认的线程池为自定义的corePoolSize和
//maximumPoolSize都为threadPoolSize的线程池,
//而阻塞队列会根据tasksProcessingType分为
//LIFOLinkedBlockingDeque和LinkedBlockingQueue。
if (taskExecutor == null) {
taskExecutor = DefaultConfigurationFactory
.createExecutor(threadPoolSize, threadPriority, tasksProcessingType);
} else {
customExecutor = true;
}
//创建的线程池同上
if (taskExecutorForCachedImages == null) {
taskExecutorForCachedImages = DefaultConfigurationFactory
.createExecutor(threadPoolSize, threadPriority, tasksProcessingType);
} else {
customExecutorForCachedImages = true;
}
if (diskCache == null) {
//默认根据hashcode生成磁盘缓存文件名称
if (diskCacheFileNameGenerator == null) {
diskCacheFileNameGenerator = DefaultConfigurationFactory.createFileNameGenerator();
}
//磁盘缓存路径分为备用目录和首选目录,默认的
//备用目录为'context.getCacheDir()+
//"uil-images"'这个路径,而首选目录要根据设
//置的diskCacheSize和diskCacheFileCount
//来决定,如果这两个为有效值,路径为'cache路径
//+"uil-images"',而cache路径的选择为先外部
//后内部,外部路径为
//\Android\data\packageName\cache,内部路
//径为context.getCacheDir()。diskCache实
//例为LruDiskCache,而为无效值时,路径为
//路径',diskCache实例为
//UnlimitedDiskCache。
diskCache = DefaultConfigurationFactory
.createDiskCache(context, diskCacheFileNameGenerator, diskCacheSize, diskCacheFileCount);
}
if (memoryCache == null) {
//默认创建内存为可用内存1/8的LruMemoryCache实例
memoryCache = DefaultConfigurationFactory.createMemoryCache(context, memoryCacheSize);
}
if (denyCacheImageMultipleSizesInMemory) {
//如果设置不允许一个key缓存多个尺寸的cache,
//创建FuzzyKeyMemoryCache实例,
//FuzzyKeyMemoryCache是对MemoryCache的装
//饰,在put()的时候还先删除此key已有的
//cache。
memoryCache = new FuzzyKeyMemoryCache(memoryCache, MemoryCacheUtils.createFuzzyKeyComparator());
}
if (downloader == null) {
//默认downloader为BaseImageDownloader,
//实现了基本Uri的输入流的获取。
downloader = DefaultConfigurationFactory.createImageDownloader(context);
}
if (decoder == null) {
//默认decoder为BaseImageDecoder的实例
decoder = DefaultConfigurationFactory.createImageDecoder(writeLogs);
}
if (defaultDisplayImageOptions == null) {
//默认DisplayImageOptions配置
defaultDisplayImageOptions = DisplayImageOptions.createSimple();
}
}
}看看BaseImageDecoder的decode(ImageDecodingInfo decodingInfo)方法的实现:
/* BaseImageDecoder.java */
@Override
public Bitmap decode(ImageDecodingInfo decodingInfo) {
Bitmap decodedBitmap;
ImageFileInfo imageInfo;
//通过decodingInfo的ImageDownloader实例获取到输入流
InputStream imageStream = getImageStream(decodingInfo);
if (imageStream == null) {
return null;
}
try {
//获取输入流图片的长和宽,如果为本地的jpeg格式的图片
//获取exif参数
imageInfo = defineImageSizeAndRotation(imageStream, decodingInfo);
//重置输入流到上次mark位置
imageStream = resetStream(imageStream, decodingInfo);
//根据decodingInfo设置的Image的ScaleType将输入
//流图片尺寸调整到一个合适的尺寸。
Options decodingOptions = prepareDecodingOptions(imageInfo.imageSize, decodingInfo);
//加载输入流图片
decodedBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(imageStream, null, decodingOptions);
} finally {
IoUtils.closeSilently(imageStream);
}
if (decodedBitmap == null) {
} else {
//如果Image的ScaleType为EXACTLY或
//EXACTLY_STRETCHED进行缩放,并支持水平翻转和旋
//转
decodedBitmap = considerExactScaleAndOrientatiton(decodedBitmap, decodingInfo, imageInfo.exif.rotation,
imageInfo.exif.flipHorizontal);
}
return decodedBitmap;
}ImageAware接口
接下来我们看看ImageAware接口和其实现:
/* ImageAware.java */
public interface ImageAware {
//获取View的宽度
int getWidth();
//获取View的高度
int getHeight();
//获取View的ScaleType
ViewScaleType getScaleType();
//获取View
View getWrappedView();
//标识是否被GC回收
boolean isCollected();
//View的标识id
int getId();
//设置Drawable
boolean setImageDrawable(Drawable drawable);
//设置Bitmap
boolean setImageBitmap(Bitmap bitmap);
}
而ImageAware基类ViewAware中则是保存了View的弱引用。
ViewAware子类ImageViewAware范围缩小到了ImageView。
ImageAware另一实现类NonViewAware的功能是只加载图片,没有显示功能,如果要获取这个图片,可以通过ImageLoadingListener#onLoadingComplete(String imageUri, View view, Bitmap loadedImage)获取到。
再来看看几个任务类:
Task任务
DisplayBitmapTask
用于显示图片的任务。
/* DisplayBitmapTask.java */
@Override
public void run() {
if (imageAware.isCollected()) {
//如果ImageView被GC回收,通知回调cancel
listener.onLoadingCancelled(imageUri, imageAware.getWrappedView());
} else if (isViewWasReused()) {
//如果图片发生错位,通知回调cancel
listener.onLoadingCancelled(imageUri, imageAware.getWrappedView());
} else {
//在imageAware中显示bitmap
displayer.display(bitmap, imageAware, loadedFrom);
//移除ImageLoaderEngine的HashMap中imageAware
//对应的key
engine.cancelDisplayTaskFor(imageAware);
//通知回调complete
listener.onLoadingComplete(imageUri, imageAware.getWrappedView(), bitmap);
}
}
ProcessAndDisplayImageTask
先对Bitmap加工,再去显示
/* ProcessAndDisplayImageTask.java */
@Override
public void run() {
//对Bitmap做加工
BitmapProcessor processor = imageLoadingInfo.options.getPostProcessor();
Bitmap processedBitmap = processor.process(bitmap);
//构造显示Bitmap的任务
DisplayBitmapTask displayBitmapTask = new DisplayBitmapTask(processedBitmap, imageLoadingInfo, engine, LoadedFrom.MEMORY_CACHE);
//在UI线程显示
LoadAndDisplayImageTask.runTask(displayBitmapTask, imageLoadingInfo.options.isSyncLoading(), handler, engine);
}
LoadAndDisplayImageTask
先去加载图片,然后显示。这个任务比前面两个要复杂得多,代码如下:
/* LoadAndDisplayImageTask.java */
@Override
public void run() {
//如果需要暂停执行任务,则阻塞等待
if (waitIfPaused()) return;
//如果有设置延时,则sleep等待
if (delayIfNeed()) return;
ReentrantLock loadFromUriLock = imageLoadingInfo.loadFromUriLock;
loadFromUriLock.lock();
Bitmap bmp;
try {
//如果ImageView被GC回收或被重用,都会抛出
//TaskCancelledException异常
checkTaskNotActual();
//取出内存中的Bitmap
bmp = configuration.memoryCache.get(memoryCacheKey);
if (bmp == null || bmp.isRecycled()) {
//如果内存中找不到或已经被回收,则去加载Bitmap
bmp = tryLoadBitmap();
if (bmp == null) return;
//如果ImageView被GC回收或被重用或当前任务被中断,
//都会抛出TaskCancelledException异常
checkTaskNotActual();
checkTaskInterrupted();
//保存前加工图片
if (options.shouldPreProcess()) {
bmp = options.getPreProcessor().process(bmp);
}
//将Bitmap放入内存
if (bmp != null && options.isCacheInMemory())
configuration.memoryCache.put(memoryCacheKey, bmp);
}
} else {
loadedFrom = LoadedFrom.MEMORY_CACHE;
}
//保存后加工图片
if (bmp != null && options.shouldPostProcess()) {
bmp = options.getPostProcessor().process(bmp);
}
checkTaskNotActual();
checkTaskInterrupted();
} catch (TaskCancelledException e) {
//异步通知ImageLoadingListener任务cancel
fireCancelEvent();
return;
} finally {
loadFromUriLock.unlock();
}
//在UI线程中显示
DisplayBitmapTask displayBitmapTask = new DisplayBitmapTask(bmp, imageLoadingInfo, engine, loadedFrom);
runTask(displayBitmapTask, syncLoading, handler, engine);
}
我们在看看内存中没有Bitmap的话是怎么加载的:
/* LoadAndDisplayImageTask.java */
private Bitmap tryLoadBitmap() throws TaskCancelledException {
Bitmap bitmap = null;
try {
//先去磁盘加载
File imageFile = configuration.diskCache.get(uri);
if (imageFile != null && imageFile.exists() && imageFile.length() > 0) {
loadedFrom = LoadedFrom.DISC_CACHE;
checkTaskNotActual();
//如果磁盘存在,加载磁盘的图片
bitmap = decodeImage(Scheme.FILE.wrap(imageFile.getAbsolutePath()));
}
//如果磁盘照片不存在,或尺寸有误,则去网络加载
if (bitmap == null || bitmap.getWidth() <= 0 || bitmap.getHeight() <= 0) {
loadedFrom = LoadedFrom.NETWORK;
String imageUriForDecoding = uri;
//如果设置缓存到磁盘,则下载并缓存到磁盘
if (options.isCacheOnDisk() && tryCacheImageOnDisk()) {
imageFile = configuration.diskCache.get(uri);
if (imageFile != null) {
imageUriForDecoding = Scheme.FILE.wrap(imageFile.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
checkTaskNotActual();
//将磁盘图片装入到内存
bitmap = decodeImage(imageUriForDecoding);
if (bitmap == null || bitmap.getWidth() <= 0 || bitmap.getHeight() <= 0) {
fireFailEvent(FailType.DECODING_ERROR, null);
}
}
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
fireFailEvent(FailType.NETWORK_DENIED, null);
} catch (TaskCancelledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (IOException e) {
L.e(e);
fireFailEvent(FailType.IO_ERROR, e);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
L.e(e);
fireFailEvent(FailType.OUT_OF_MEMORY, e);
} catch (Throwable e) {
L.e(e);
fireFailEvent(FailType.UNKNOWN, e);
}
return bitmap;
}加载图片顺序
我们看到加载图片的顺序:先去磁盘加载,磁盘没有的情况下去读取网络数据,然后缓存到磁盘,再将磁盘的图片装入到内存中。
看完了LoadAndDisplayImageTask,我们再来看ImageLoaderEngine就比较简单了。除前面介绍的3个线程池外,
还有以下几个成员比较重要:
cacheKeysForImageAwares是在HashMap中缓存了每个View对应的key;
uriLocks则是在WeakHashMap中缓存了每个Uri的原子锁,在每次加载图片过程中对该Uri加锁;
pauseLock则是在滑动时禁止执行加载显示任务的锁。
显示图片方法
说了这么多,其实我们经常用到的加载图片是通过ImageLoader提供的方法加载图片的,ImageLoader中加载图片的实际上有3个方法,最后都调用到了displayImage()方法上:
loadImageSync()
同步方式加载图片
/* ImageLoader.java */
public Bitmap loadImageSync(String uri, ImageSize targetImageSize, DisplayImageOptions options) {
if (options == null) {
options = configuration.defaultDisplayImageOptions;
}
//isSyncLoading设为true
options = new DisplayImageOptions.Builder().cloneFrom(options).syncLoading(true).build();
SyncImageLoadingListener listener = new SyncImageLoadingListener();
//这里调用了loadImage(),图片加载完后会通过
//SyncImageLoadingListener#onLoadingComplete()
//设置到loadedImage。
loadImage(uri, targetImageSize, options, listener);
return listener.getLoadedBitmap();
}loadImage()
- 异步方式加载图片
/* ImageLoader.java */
public void loadImage(String uri, ImageSize targetImageSize, DisplayImageOptions options,
ImageLoadingListener listener, ImageLoadingProgressListener progressListener) {
//如果没传图片的宽和高,则为屏幕的宽和高
if (targetImageSize == null) {
targetImageSize = configuration.getMaxImageSize();
}
//如果没设置显示配置,则使用默认显示配置
if (options == null) {
options = configuration.defaultDisplayImageOptions;
}
//NonViewAware中并没有ImageView的引用,View的
//ScaleType为CROP
NonViewAware imageAware = new NonViewAware(uri, targetImageSize, ViewScaleType.CROP);
//通过listener返回Bitmap
displayImage(uri, imageAware, options, listener, progressListener);
}下面这个方法是我们平时使用到最多的,也是图片加载中最关键同时也是最复杂的方法。
displayImage()
先加载再缓存后加工并显示图片
/* ImageLoader.java */
public void displayImage(String uri, ImageAware imageAware, DisplayImageOptions options,
ImageSize targetSize, ImageLoadingListener listener, ImageLoadingProgressListener progressListener) {
//如果uri为空
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(uri)) {
//移除HashMap中ImageView对应的key
engine.cancelDisplayTaskFor(imageAware);
//通知listener开始加载
listener.onLoadingStarted(uri, imageAware.getWrappedView());
//如果配置默认图,则加载默认图
if (options.shouldShowImageForEmptyUri()) {
imageAware.setImageDrawable(options.getImageForEmptyUri(configuration.resources));
} else {
imageAware.setImageDrawable(null);
}
//通知listener加载完成
listener.onLoadingComplete(uri, imageAware.getWrappedView(), null);
return;
}
//如果uri不为空
if (targetSize == null) {
//先获取imageAware的尺寸,如果无效,则获取配置类
//的图片最大缓存尺寸,如果还无效,则为屏幕尺寸
targetSize = ImageSizeUtils.defineTargetSizeForView(imageAware, configuration.getMaxImageSize());
}
//内存中key的格式为[imageUri]_[width]x[height]
String memoryCacheKey = MemoryCacheUtils.generateKey(uri, targetSize);
//将key存放到HashMap中,HashMap存放的是已经加入到任
//务队列,但是还没显示的任务
engine.prepareDisplayTaskFor(imageAware, memoryCacheKey);
//通知listener开始加载
listener.onLoadingStarted(uri, imageAware.getWrappedView());
Bitmap bmp = configuration.memoryCache.get(memoryCacheKey);
//从内存中取出Bitmap
if (bmp != null && !bmp.isRecycled()) {
//从内存取出后处理Bitmap
if (options.shouldPostProcess()) {
ImageLoadingInfo imageLoadingInfo = new ImageLoadingInfo(uri, imageAware, targetSize, memoryCacheKey,
options, listener, progressListener, engine.getLockForUri(uri));
//先加工,在显示图片
ProcessAndDisplayImageTask displayTask = new ProcessAndDisplayImageTask(engine, bmp, imageLoadingInfo,
defineHandler(options));
if (options.isSyncLoading()) {
//如果在主线程,直接执行
displayTask.run();
} else {
//异步时加载到ImageLoaderEngine执行
engine.submit(displayTask);
}
} else {
//从内存取出后不处理,直接显示
options.getDisplayer().display(bmp, imageAware, LoadedFrom.MEMORY_CACHE);
//通知listener加载完成
listener.onLoadingComplete(uri, imageAware.getWrappedView(), bmp);
}
} else { //内存中没有Bitmap
//如果配置了加载中的默认图
if (options.shouldShowImageOnLoading()) {
imageAware.setImageDrawable(options.getImageOnLoading(configuration.resources));
} else if (options.isResetViewBeforeLoading()) {
//如果配置了resetViewBeforeLoading()方法
imageAware.setImageDrawable(null);
}
ImageLoadingInfo imageLoadingInfo = new ImageLoadingInfo(uri, imageAware, targetSize, memoryCacheKey,
options, listener, progressListener, engine.getLockForUri(uri));
//加载,并显示图片
LoadAndDisplayImageTask displayTask = new LoadAndDisplayImageTask(engine, imageLoadingInfo,
defineHandler(options));
if (options.isSyncLoading()) {
//主线程中直接执行
displayTask.run();
} else {
//异步时加载到ImageLoaderEngine执行
engine.submit(displayTask);
}
}
}
对框架的思考
看完了加载显示图片的整个流程,认真思考的童鞋一定会有一个大大的疑问:这个框架是怎么解决图片错位问题的呢?
要搞清楚这个问题,首先要先看看两个key的存取:
- ImageLoaderEngine的HashMap中的ImageAware实例对应的key
- DisplayBitmapTask的memoryCacheKey。
后者是在构建ImageLoadingInfo实例时传值进去的,即两者都是在ImageLoader#displayImage()时存入的,显示成功后,HashMap中的key则会移除掉。
然后我们分析一下错位时的场景:假设ListView的第一个Item的Uri为uri1,对应的key为key1,我们首先将ImageAware的id和key1的键值对放入HashMap中,然后去执行LoadAndDisplayImageTask任务,此时我们滑动屏幕,第10个Item重用了第一个的ImageAware,而HashMap中的此id对应的key变成key10,而这个时候key1所对应的任务加载成功,显示时传的key还是之前的key1(因为是加载任务前就传进来的),而在显示任务DisplayBitmapTask中就使用isViewWasReused()方法判断了是否错位,代码如下:
/* DisplayBitmapTask.java */
private boolean isViewWasReused() {
String currentCacheKey = engine.getLoadingUriForView(imageAware);
return !memoryCacheKey.equals(currentCacheKey);
}上面的场景中我们看到,从engine的HashMap中取到的key已经变成了key10,而memoryCacheKey中还是key1,说明发生了错位。
而一旦发生了错位的情况,任务也是直接被cancel掉的。
还有一个问题:上面的3个任务,哪些是在UI线程中,哪些又是在非UI线程中呢?首先我们先来看一个方法:
/* ImageLoader.java */
private static Handler defineHandler(DisplayImageOptions options) { Handler handler = options.getHandler();
if (options.isSyncLoading()) {
handler = null;
} else if (handler == null && Looper.myLooper() == Looper.getMainLooper()) { //实际会走到这里 handler = new Handler();
}
return handler;
}如果是同步的话直接执行不需要handler;
如果options未配置handler且在UI线程,默认实例化一个Handler。
默认情况下,图片加载都是异步的,所以Process*Task和Load*Task都是被加入到Engine的线程池中去执行的,自然是在非UI线程。
而显示任务则是通过以下方法添加的:
/* LoadAndDisplayImageTask.java */
static void runTask(Runnable r, boolean sync, Handler handler, ImageLoaderEngine engine) {
if (sync) {
r.run();
} else if (handler == null) {
engine.fireCallback(r);
} else {
//显示的Task会走到这里
handler.post(r);
}
}
由于是异步,并且handler不为空(通过上面的defineHandler()方法传入实例),所以最后会调用到handler.post(r),将任务加入到UI线程的消息队列中,所以DisplayBitmapTask是在UI线程中。
最后一个问题,为了优化滚动时的卡顿,是怎么在滚动时停止加载任务的呢?
我们看看waitIfPaused()中是怎么实现等待的:
/* LoadAndDisplayImageTask.java */
private boolean waitIfPaused() {
AtomicBoolean pause = engine.getPause();
if (pause.get()) {
synchronized (engine.getPauseLock()) {
if (pause.get()) {
try {
engine.getPauseLock().wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
return isTaskNotActual();
}
当新添加任务时,如果发现原子pause被置为true,则一直会阻塞在这里等待释放锁,这个过程中如果任务被中断,则直接退出任务。滑动停止后原子pause被置为false并锁释放后,如果ImageView已经被GC回收或发生错位,则也退出任务,否则继续执行任务。
来看看滚动列表时是怎么停止加载任务的:
/* PauseOnScrollListener.java */
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view, int scrollState) {
switch (scrollState) {
case OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_IDLE:
imageLoader.resume();
break;
case OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_TOUCH_SCROLL:
if (pauseOnScroll) {
imageLoader.pause();
}
break;
case OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_FLING:
if (pauseOnFling) {
imageLoader.pause();
}
break;
}
if (externalListener != null) {
externalListener.onScrollStateChanged(view, scrollState);
}
}处于滚动状态时,暂停新加的任务,但是不会暂停已经开始的任务;
停止滚动后,加载暂停的任务。
/* ImageLoaderEngine.java */
void pause() {
paused.set(true);
}
void resume() {
paused.set(false);
synchronized (pauseLock) {
pauseLock.notifyAll();
}
}
我们看到暂停是将原子paused置为true,恢复则是将其置为false,并释放锁。
图片显示流程总结
分析完了,我们总结下图片加载的整体流程:
如果uri为空则加载默认图,返回;
如果Bitmap在内存中,则直接执行ProcessAndDisplayImageTask任务加工图片,再显示出来;
如果Bitmap不在内存中,执行LoadAndDisplayImageTask任务去下载缓存图片,最后显示出来。
框架部分的思路已然明了,而图片处理中对内存和磁盘的缓存也是一个重头戏,下一篇博客我们就来说说ImageLoader中缓存部分的原理,敬请期待~~~