2014-11-8Android学习------onLayout()方法和Layout()方法--------动画Animation学习篇
onLayout方法是ViewGroup中子View的布局方法,用于放置子View的位置。
放置子View很简单,只需在重写onLayout方法,然后获取子View的实例,调用子View的layout方法实现布局。
在实际开发中,一般要配合onMeasure测量方法一起使用。(不是必要的)
@Override
protected
abstract
void
onLayout(
boolean
changed,
int
l,
int
t,
int
r,
int
b);
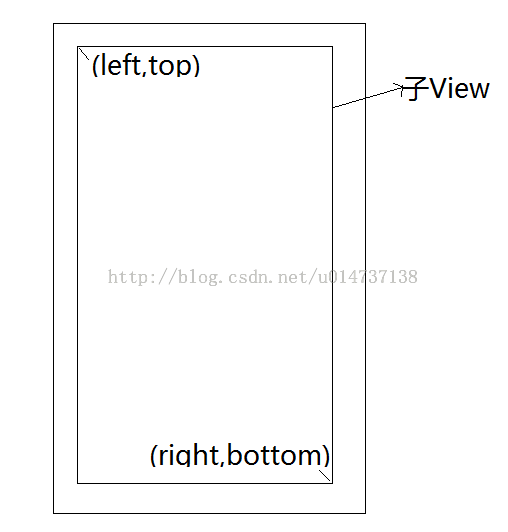
View的放置都是根据一个矩形空间放置的,onLayout传下来的l,t,r,b分别是放置父控件的矩形可用空间(除去margin和padding的空间)的左上角的left、top以及右下角right、bottom值。
看图:
layout方法:
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b);
平常开发所用到RelativeLayout、LinearLayout、FrameLayout...这些都是继承ViewGroup的布局。这些布局的实现都是通过都实现ViewGroup的onLayout方法,只是实现方法不一样而已。
下面是一个自定义ViewGroup的Demo,用onLayout和layout实现子View的水平放置,间隔是20px
public
class
MyViewGroup
extends
ViewGroup {
// 子View的水平间隔
private
final
static
int
padding =
20
;
public
MyViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super
(context, attrs);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
protected
void
onLayout(
boolean
changed,
int
l,
int
t,
int
r,
int
b) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 动态获取子View实例
for
(
int
i =
0
, size = getChildCount(); i < size; i++) {
View view = getChildAt(i);
// 放置子View,宽高都是100
view.layout(l, t, l +
100
, t +
100
);
l +=
100
+ padding;
}
}
}
activity的布局文件xml
<relativelayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:padding="10dp">
<com.example.layout.myviewgroup android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="100dp" android:background="#0000ff">
<view android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#ff0000">
<view android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#00ff00">
</view></view></com.example.layout.myviewgroup>
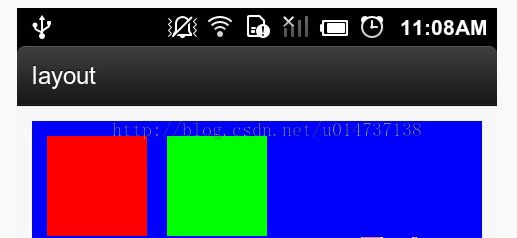
</relativelayout>效果:
上图MyViewGroup是蓝色,两个子View分别为红色和绿色。
在自定义View中,onLayout配合onMeasure方法一起使用,可以实现自定义View的复杂布局。自定义View首先调用onMeasure进行测量,然后调用onLayout方法,动态获取子View和子View的测量大小,然后进行layout布局。
原文地址: http://www.2cto.com/kf/201404/291740.html