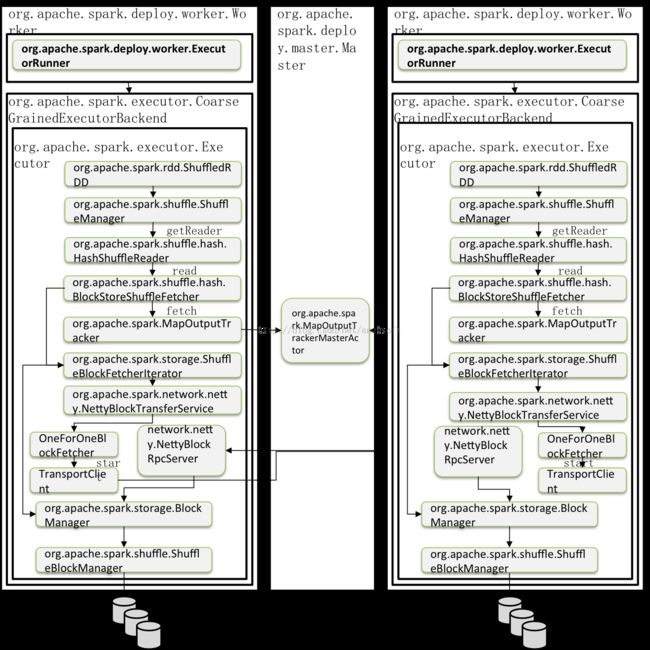
Spark技术内幕:Shuffle Read的整体流程
回忆一下,每个Stage的上边界,要么需要从外部存储读取数据,要么需要读取上一个Stage的输出;而下边界,要么是需要写入本地文件系统(需要Shuffle),以供childStage读取,要么是最后一个Stage,需要输出结果。这里的Stage,在运行时的时候就是可以以pipeline的方式运行的一组Task,除了最后一个Stage对应的是ResultTask,其余的Stage对应的都是ShuffleMap Task。
而除了需要从外部存储读取数据和RDD已经做过cache或者checkpoint的Task,一般Task的开始都是从ShuffledRDD的ShuffleRead开始的。本节将详细讲解Shuffle Read的过程。
先看一下ShuffleRead的整体架构图。
org.apache.spark.rdd.ShuffledRDD#compute 开始,通过调用org.apache.spark.shuffle.ShuffleManager的getReader方法,获取到org.apache.spark.shuffle.ShuffleReader,然后调用其read()方法进行读取。在Spark1.2.0中,不管是Hash BasedShuffle或者是Sort BasedShuffle,内置的Shuffle Reader都是 org.apache.spark.shuffle.hash.HashShuffleReader。核心实现:
- override def read(): Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = {
- val ser =Serializer.getSerializer(dep.serializer)
- // 获取结果
- val iter = BlockStoreShuffleFetcher.fetch(handle.shuffleId,startPartition, context, ser)
- // 处理结果
- val aggregatedIter: Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = if(dep.aggregator.isDefined) {//需要聚合
- if (dep.mapSideCombine) {//需要map side的聚合
- new InterruptibleIterator(context, dep.aggregator.get.combineCombinersByKey(
- iter, context))
- } else {//只需要reducer端的聚合
- new InterruptibleIterator(context,dep.aggregator.get.combineValuesByKey(
- iter, context))
- }
- }else { // 无需聚合操作
- iter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[Product2[K,C]]].map(pair => (pair._1, pair._2))
- }
- // Sort the output if there is a sort ordering defined.
- dep.keyOrdering match {//判断是否需要排序
- case Some(keyOrd: Ordering[K]) => //对于需要排序的情况
- // 使用ExternalSorter进行排序,注意如果spark.shuffle.spill是false,那么数据是
- // 不会spill到硬盘的
- val sorter = new ExternalSorter[K, C, C](ordering = Some(keyOrd),
- serializer= Some(ser))
- sorter.insertAll(aggregatedIter)
- context.taskMetrics.memoryBytesSpilled += sorter.memoryBytesSpilled
- context.taskMetrics.diskBytesSpilled += sorter.diskBytesSpilled
- sorter.iterator
- case None => //无需排序
- aggregatedIter
- }
- }
org.apache.spark.shuffle.hash.BlockStoreShuffleFetcher#fetch会获得数据,它首先会通过
org.apache.spark.MapOutputTracker#getServerStatuses来获得数据的meta信息,这个过程有可能需要向org.apache.spark.MapOutputTrackerMasterActor发送读请求,这个读请求是在org.apache.spark.MapOutputTracker#askTracker发出的。在获得了数据的meta信息后,它会将这些数据存入Seq[(BlockManagerId,Seq[(BlockId, Long)])]中,然后调用org.apache.spark.storage.ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator最终发起请求。ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator根据数据的本地性原则进行数据获取。如果数据在本地,那么会调用org.apache.spark.storage.BlockManager#getBlockData进行本地数据块的读取。而getBlockData对于shuffle类型的数据,会调用ShuffleManager的ShuffleBlockManager的getBlockData。
如果数据在其他的Executor上,那么如果用户使用的spark.shuffle.blockTransferService是netty,那么就会通过org.apache.spark.network.netty.NettyBlockTransferService#fetchBlocks获取;如果使用的是nio,那么就会通过org.apache.spark.network.nio.NioBlockTransferService#fetchBlocks获取。
数据读取策略的划分
org.apache.spark.storage.ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator会通过splitLocalRemoteBlocks划分数据的读取策略:如果在本地有,那么可以直接从BlockManager中获取数据;如果需要从其他的节点上获取,那么需要走网络。由于Shuffle的数据量可能会很大,因此这里的网络读有以下的策略:
1) 每次最多启动5个线程去最多5个节点上读取数据
2) 每次请求的数据大小不会超过spark.reducer.maxMbInFlight(默认值为48MB)/5
这样做的原因有几个:
1) 避免占用目标机器的过多带宽,在千兆网卡为主流的今天,带宽还是比较重要的。如果机器使用的万兆网卡,那么可以通过设置spark.reducer.maxMbInFlight来充分利用带宽。
2) 请求数据可以平行化,这样请求数据的时间可以大大减少。请求数据的总时间就是请求中耗时最长的。这样可以缓解一个节点出现网络拥塞时的影响。
主要的实现:
- private[this] def splitLocalRemoteBlocks():ArrayBuffer[FetchRequest] = {
- val targetRequestSize = math.max(maxBytesInFlight / 5, 1L)
- val remoteRequests = new ArrayBuffer[FetchRequest]
- for ((address, blockInfos) <- blocksByAddress) {
- if (address.executorId == blockManager.blockManagerId.executorId) {
- // Block在本地,需要过滤大小为0的block。
- localBlocks ++= blockInfos.filter(_._2 != 0).map(_._1)
- numBlocksToFetch += localBlocks.size
- } else { //需要远程获取的Block
- val iterator = blockInfos.iterator
- var curRequestSize = 0L
- var curBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, Long)]
- while (iterator.hasNext) {
- //blockId 是org.apache.spark.storage.ShuffleBlockId,
- // 格式:"shuffle_" +shuffleId + "_" + mapId + "_" + reduceId
- val (blockId, size) = iterator.next()
- // Skip empty blocks
- if (size > 0) {
- curBlocks += ((blockId, size))
- remoteBlocks += blockId
- numBlocksToFetch += 1
- curRequestSize += size
- }
- if (curRequestSize >= targetRequestSize) {
- // 当前总的size已经可以批量放入一次request中
- remoteRequests += new FetchRequest(address, curBlocks)
- curBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, Long)]
- curRequestSize = 0
- }
- }
- // 剩余的请求组成一次request
- if (curBlocks.nonEmpty) {
- remoteRequests += new FetchRequest(address, curBlocks)
- }
- }
- }
- remoteRequests
- }
本地读取
fetchLocalBlocks() 负责本地Block的获取。在splitLocalRemoteBlocks中,已经将本地的Block列表存入了localBlocks:private[this] val localBlocks = newArrayBuffer[BlockId]()
具体过程如下:
- val iter = localBlocks.iterator
- while (iter.hasNext) {
- val blockId = iter.next()
- try {
- val buf = blockManager.getBlockData(blockId)
- shuffleMetrics.localBlocksFetched += 1
- buf.retain()
- results.put(new SuccessFetchResult(blockId, 0, buf))
- } catch {
- }
- }
而blockManager.getBlockData(blockId)的实现是:
- override def getBlockData(blockId:BlockId): ManagedBuffer = {
- if (blockId.isShuffle) {
- shuffleManager.shuffleBlockManager.getBlockData(blockId.asInstanceOf[ShuffleBlockId])
- }
以Hash BasedShuffle为例,它的ShuffleBlockManager是org.apache.spark.shuffle.FileShuffleBlockManager。FileShuffleBlockManager有两种情况,一种是File consolidate的,这种的话需要根据Map ID和 Reduce ID首先获得FileGroup的一个文件,然后根据在文件中的offset和size来获取需要的数据;如果是没有File consolidate,那么直接根据Shuffle Block ID直接读取整个文件就可以。
- override def getBlockData(blockId:ShuffleBlockId): ManagedBuffer = {
- if (consolidateShuffleFiles) {
- val shuffleState = shuffleStates(blockId.shuffleId)
- val iter = shuffleState.allFileGroups.iterator
- while(iter.hasNext) {
- // 根据Map ID和Reduce ID获取File Segment的信息
- val segmentOpt = iter.next.getFileSegmentFor(blockId.mapId,blockId.reduceId)
- if (segmentOpt.isDefined) {
- val segment = segmentOpt.get
- // 根据File Segment的信息,从FileGroup中找到相应的File和Block在
- // 文件中的offset和size
- return new FileSegmentManagedBuffer(
- transportConf, segment.file, segment.offset, segment.length)
- }
- }
- throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to find shuffle block:" + blockId)
- }else {
- val file = blockManager.diskBlockManager.getFile(blockId) //直接获取文件句柄
- new FileSegmentManagedBuffer(transportConf, file, 0, file.length)
- }
- }
对于Sort BasedShuffle,它需要通过索引文件来获得数据块在数据文件中的具体位置信息,从而读取这个数据。
具体实现在org.apache.spark.shuffle.IndexShuffleBlockManager#getBlockData中。
- override def getBlockData(blockId: ShuffleBlockId): ManagedBuffer = {
- // 根据ShuffleID和MapID从org.apache.spark.storage.DiskBlockManager 获取索引文件
- val indexFile = getIndexFile(blockId.shuffleId, blockId.mapId)
- val in = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(indexFile))
- try {
- ByteStreams.skipFully(in, blockId.reduceId * 8) //跳到本次Block的数据区
- val offset = in.readLong() //数据文件中的开始位置
- val nextOffset = in.readLong() //数据文件中的结束位置
- new FileSegmentManagedBuffer(
- transportConf,
- getDataFile(blockId.shuffleId, blockId.mapId),
- offset,
- nextOffset - offset)
- }finally {
- in.close()
- }
- }