Struts2源码阅读(三)_Dispatcher&ConfigurationProvider
首先强调一下struts2的线程程安全,在Struts2中大量采用ThreadLocal线程局部变量的方法来保证线程的安全,像Dispatcher等都是通过ThreadLocal来保存变量值,使得每个线程都有自己独立的实例变量,互不相干.
接下来就从Dispatcher开始看起,先看其构造函数:
//创建Dispatcher,此类是一个Delegate,它是真正完成根据url解析转向,读取对应Action的地方
public Dispatcher(ServletContext servletContext, Map<String, String> initParams) {
this.servletContext = servletContext;
//配置在web.xml中的param参数
this.initParams = initParams;
}
我们再看在FilterDispatcher创建Dispatcher的:
protected Dispatcher createDispatcher(FilterConfig filterConfig) {
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<String, String>();
for (Enumeration e = filterConfig.getInitParameterNames(); e.hasMoreElements();) {
String name = (String) e.nextElement();
String value = filterConfig.getInitParameter(name);
params.put(name, value);
}
return new Dispatcher(filterConfig.getServletContext(), params);
}
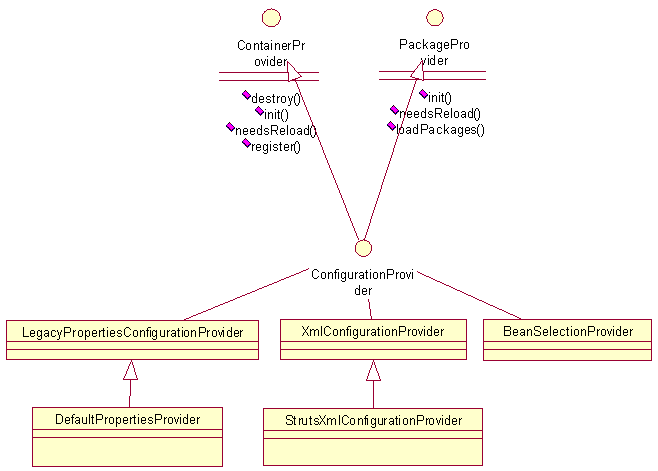
分七步载入各种配置属性,都是通过ConfigurationProvider接口进行的,这个接口提供init(),destroy(),register()等方法.
将各种ConfigurationProvider初始化之后将实例添加到ConfigurationManager的List里面.
最后通过循环调用List里的这些destroy(),register()等方法实现对配置文件的属性进行注册和销毁等功能.
下面将分析这七层功夫是怎样一步步练成的.
XxxProvider类图:
首先是init_DefaultProperties()
创建Dispatcher之后,来看init()方法
init()方法是用来Load用户配置文件,资源文件以及默认的配置文件.
主要分七步走,看下面注释
public void init() {
if (configurationManager == null) {
//设置ConfigurationManager的defaultFrameworkBeanName.
//这里DEFAULT_BEAN_NAME为struts,这是xwork框架的内容,Framework可以是xwork,struts,webwork等
configurationManager = new ConfigurationManager(BeanSelectionProvider.DEFAULT_BEAN_NAME);
}
//读取properties信息,默认的default.properties,
init_DefaultProperties(); // [1]
//读取xml配置文件,默认的struts-default.xml,struts-plugin.xml,struts.xml
init_TraditionalXmlConfigurations(); // [2]
//读取用户自定义的struts.properties
init_LegacyStrutsProperties(); // [3]
//自定义的configProviders
init_CustomConfigurationProviders(); // [5]
//载入FilterDispatcher传进来的initParams
init_FilterInitParameters() ; // [6]
//将配置文件中的bean与具体的类映射
init_AliasStandardObjects() ; // [7]
//构建一个用于依赖注射的Container对象
//在这里面会循环调用上面七个ConfigurationProvider的register方法
//其中的重点就是DefaultConfiguration的#reload()方法
Container container = init_PreloadConfiguration();
container.inject(this);
init_CheckConfigurationReloading(container);
init_CheckWebLogicWorkaround(container);
if (!dispatcherListeners.isEmpty()) {
for (DispatcherListener l : dispatcherListeners) {
l.dispatcherInitialized(this);
}
}
}
分七步载入各种配置属性,都是通过ConfigurationProvider接口进行的,这个接口提供init(),destroy(),register()等方法.
将各种ConfigurationProvider初始化之后将实例添加到ConfigurationManager的List里面.
最后通过循环调用List里的这些destroy(),register()等方法实现对配置文件的属性进行注册和销毁等功能.
下面将分析这七层功夫是怎样一步步练成的.
首先是init_DefaultProperties()
private void init_DefaultProperties() {
configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider(new DefaultPropertiesProvider());
}
//接来看DefaultPropertiesProvider好了,DefaultPropertiesProvider实际上只是实现了register()方法
public void register(ContainerBuilder builder, LocatableProperties props)
throws ConfigurationException {
Settings defaultSettings = null;
try {
defaultSettings = new PropertiesSettings("org/apache/struts2/default");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ConfigurationException("Could not find or error in org/apache/struts2/default.properties", e);
}
loadSettings(props, defaultSettings);
}
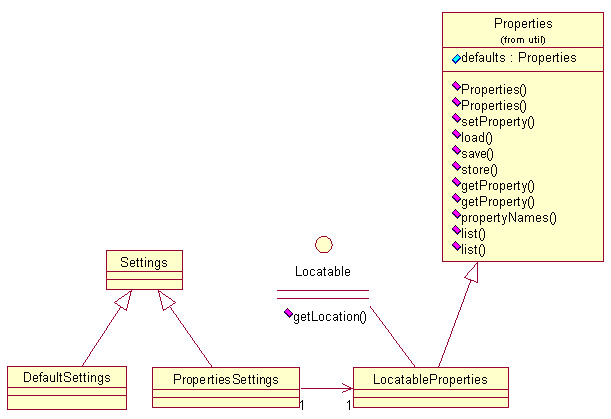
PropertiesSettings类图:
//PropertiesSettings构造方法
//读取org/apache/struts2/default.properties的配置信息,如果项目中需要覆盖,可以在classpath里的struts.properties里覆写
public PropertiesSettings(String name) {
URL settingsUrl = ClassLoaderUtils.getResource(name + ".properties", getClass());
if (settingsUrl == null) {
LOG.debug(name + ".properties missing");
settings = new LocatableProperties();
return;
}
settings = new LocatableProperties(new LocationImpl(null, settingsUrl.toString()));
// Load settings
InputStream in = null;
try {
in = settingsUrl.openStream();
settings.load(in);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new StrutsException("Could not load " + name + ".properties:" + e, e);
} finally {
if(in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch(IOException io) {
LOG.warn("Unable to close input stream", io);
}
}
}
}
//loadSettings主要是将progerty的value和Locale从上面PropertiesSettings中取得并存放到LocatableProperties props
//这个props是register的一个入参.
protected void loadSettings(LocatableProperties props, final Settings settings) {
// We are calling the impl methods to get around the single instance of Settings that is expected
for (Iterator i = settings.listImpl(); i.hasNext(); ) {
String name = (String) i.next();
props.setProperty(name, settings.getImpl(name), settings.getLocationImpl(name));
}
}
ClassLoaderUtils.getResource( resourceName, callingClass ): 查找指定资源
public static URL getResource(String resourceName, Class callingClass) {
URL url = null;
url = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource(resourceName);
if (url == null) {
url = ClassLoaderUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResource(resourceName);
}
if (url == null) {
url = callingClass.getClassLoader().getResource(resourceName);
}
return url;
}
为什么要按照这个顺序?前面的加载为什么可能会失败?
LocatableProperties.load( inputStream ): 将文件内容加载到 LocatableProperties 对象内。
public void load(InputStream in) throws IOException {
Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(in);
PropertiesReader pr = new PropertiesReader(reader);
while (pr.nextProperty()) {
String name = pr.getPropertyName();
String val = pr.getPropertyValue();
int line = pr.getLineNumber();
String desc = convertCommentsToString(pr.getCommentLines());
Location loc = new LocationImpl(desc, location.getURI(), line, 0);
setProperty(name, val, loc);
}
}
LocatableProperties.setProperty( name, value, location ): 如何实现一个属性名称对应一个属性值,而且有对应一个Location
LocatableProperties 内部有一个Map<String,Location> propLocations;
Properties 类本身又类似一个Map,这样通过两个Map 来实现内部存储。
public Object setProperty(String key, String value, Object locationObj) {
Object obj = super.setProperty(key, value);
if (location != null) {
Location loc = LocationUtils.getLocation(locationObj);
propLocations.put(key, loc);
}
return obj;
}
的十大书店
的十大书店
的十大书店
private void init_TraditionalXmlConfigurations() {
//首先读取web.xml中的config初始参数值
//如果没有配置就使用默认的DEFAULT_CONFIGURATION_PATHS:"struts-default.xml,struts-plugin.xml,struts.xml",
//这儿就可以看出为什么默认的配置文件必须取名为这三个名称了
//如果不想使用默认的名称,直接在web.xml中配置config初始参数即可
String configPaths = initParams.get("config");
if (configPaths == null) {
configPaths = DEFAULT_CONFIGURATION_PATHS;
}
String[] files = configPaths.split("//s*[,]//s*");
for (String file : files) {
if (file.endsWith(".xml")) {
if ("xwork.xml".equals(file)) {
//XmlConfigurationProvider负责解析xwork.xml
configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider(new XmlConfigurationProvider(file, false));
} else {
//其它xml都是由StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider来解析
configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider(new StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider(file, false, servletContext));
}
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid configuration file name");
}
}
}
对于其它配置文件只用StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider,此类继承XmlConfigurationProvider,而XmlConfigurationProvider又实现ConfigurationProvider接口。
类XmlConfigurationProvider负责配置文件的读取和解析,
首先通过init()中的loadDocuments(configFileName);利用DomHelper中的
public static Document parse(InputSource inputSource, Map<String, String> dtdMappings) 将configFileName配置文件通过SAX解析方式按照DtdMappings解析成Document对象.
然后通过Provider的register()方法加载"bean"和"constant"属性,再通过loadPackages()加载package及package中的属性
addAction()方法负责读取<action>标签,并将数据保存在ActionConfig中;
addResultTypes()方法负责将<result-type>标签转化为ResultTypeConfig对象;
loadInterceptors()方法负责将<interceptor>标签转化为InterceptorConfi对象;
loadInterceptorStack()方法负责将<interceptor-ref>标签转化为InterceptorStackConfig对象;
loadInterceptorStacks()方法负责将<interceptor-stack>标签转化成InterceptorStackConfig对象。
而上面的方法最终会被addPackage()方法调用,addPackage又会被Provider的loadPackages()调用,将所读取到的数据汇集到PackageConfig对象中。
protected PackageConfig addPackage(Element packageElement) throws ConfigurationException {
PackageConfig.Builder newPackage = buildPackageContext(packageElement);
if (newPackage.isNeedsRefresh()) {
return newPackage.build();
}
// add result types (and default result) to this package
addResultTypes(newPackage, packageElement);
// load the interceptors and interceptor stacks for this package
loadInterceptors(newPackage, packageElement);
// load the default interceptor reference for this package
loadDefaultInterceptorRef(newPackage, packageElement);
// load the default class ref for this package
loadDefaultClassRef(newPackage, packageElement);
// load the global result list for this package
loadGlobalResults(newPackage, packageElement);
// load the global exception handler list for this package
loadGobalExceptionMappings(newPackage, packageElement);
// get actions
NodeList actionList = packageElement.getElementsByTagName("action");
for (int i = 0; i < actionList.getLength(); i++) {
Element actionElement = (Element) actionList.item(i);
addAction(actionElement, newPackage);
}
// load the default action reference for this package
loadDefaultActionRef(newPackage, packageElement);
PackageConfig cfg = newPackage.build();
configuration.addPackageConfig(cfg.getName(), cfg);
return cfg;
}
loadConfigurationFiles解析读取xml中的内容
private List<Document> loadConfigurationFiles(String fileName, Element includeElement) {
...
//通过DomHelper调用SAX进行解析xml
doc = DomHelper.parse(in, dtdMappings);
...
Element rootElement = doc.getDocumentElement();
NodeList children = rootElement.getChildNodes();
int childSize = children.getLength();
for (int i = 0; i < childSize; i++) {
Node childNode = children.item(i);
if (childNode instanceof Element) {
Element child = (Element) childNode;
final String nodeName = child.getNodeName();
if ("include".equals(nodeName)) {
String includeFileName = child.getAttribute("file");
//解析每个action配置是,对于include文件可以使用通配符*来进行配置
//如Struts.xml中可配置成<include file="actions_*.xml"/>
if (includeFileName.indexOf('*') != -1) {
ClassPathFinder wildcardFinder = new ClassPathFinder();
wildcardFinder.setPattern(includeFileName);
Vector<String> wildcardMatches = wildcardFinder.findMatches();
for (String match : wildcardMatches) {
//递归Load子file中的<include/>
docs.addAll(loadConfigurationFiles(match, child));
}
} else {
docs.addAll(loadConfigurationFiles(includeFileName, child));
}
}
}
}
docs.add(doc);
loadedFileUrls.add(url.toString());
...
return docs;
}