android 4.4 电池电量管理底层分析(C\C++层)
参考文献:http://blog.csdn.net/wlwl0071986/article/details/38778897
简介:
Linux电池驱动用于和PMIC交互、负责监听电池产生的相关事件,例如低电报警、电量发生变化、高温报警、USB插拔等等。
Android电池服务,用来监听内核上报的电池事件,并将最新的电池数据上报给系统,系统收到新数据后会去更新电池显示状态、剩余电量等信息。如果收到过温报警和低电报警,系统会自动触发关机流程,保护电池和机器不受到危害。
Android电池服务的启动和运行流程:
Android电源管理底层用的是Linux powersupply框架,从Android 4.4开始,Google专门提供了一个healthd来监控电源状态。它的路径在:system/core/healthd文件夹下,编译出来的文件为/sbin/healthd。

电池系统从底层向Framework层上报数据的流程:

这里我把文章框架按语言分成 C/C++ 层与Java层。(这篇介绍C/C++ 层, Java 层请看另外一篇博客http://blog.csdn.net/daweibalang717/article/details/40615453),
关于C/C++ 层与驱动交互的代码我不全部贴出,只给出路径,大家可以自己查找阅读,这里值讲述关键函数。
一、关系图:
二、Healthd
包含两个文件:\system\core\healthd\healthd.h ,\system\core\healthd\healthd.cpp
简要说明:
health.h 是个头文件,只要声明函数与变量,不做过多介绍。我们说下healthd.cpp ,
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int ch;
klog_set_level(KLOG_LEVEL);
while ((ch = getopt(argc, argv, "n")) != -1) {
switch (ch) {
case 'n':
nosvcmgr = true;
break;
case '?':
default:
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "Unrecognized healthd option: %c\n", ch);
}
}
healthd_board_init(&healthd_config);
wakealarm_init();
uevent_init();
binder_init();
gBatteryMonitor = new BatteryMonitor();
gBatteryMonitor->init(&healthd_config, nosvcmgr);
healthd_mainloop();
return 0;
}
这是main函数,跟Java中的main是一样的,作为程序的入口。这里做一些初始化工作,获得BatteryMonitor的指针对象。我们索要关注的是healthd_mainloop()的调用,仅凭函数名就能知道会进入一个无限循环,这样也就能达到监控电源状态的目的了。下面我们看一下这个函数:
static void healthd_mainloop(void) {
struct epoll_event ev;
int epollfd;
int maxevents = 0;
epollfd = epoll_create(MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS);
if (epollfd == -1) {
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG,
"healthd_mainloop: epoll_create failed; errno=%d\n",
errno);
return;
}
if (uevent_fd >= 0) {
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ev.data.ptr = (void *)uevent_event;
if (epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, uevent_fd, &ev) == -1)
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG,
"healthd_mainloop: epoll_ctl for uevent_fd failed; errno=%d\n",
errno);
else
maxevents++;
}
if (wakealarm_fd >= 0) {
ev.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLWAKEUP;
ev.data.ptr = (void *)wakealarm_event;
if (epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, wakealarm_fd, &ev) == -1)
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG,
"healthd_mainloop: epoll_ctl for wakealarm_fd failed; errno=%d\n",
errno);
else
maxevents++;
}
if (binder_fd >= 0) {
ev.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLWAKEUP;
ev.data.ptr= (void *)binder_event;
if (epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, binder_fd, &ev) == -1)
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG,
"healthd_mainloop: epoll_ctl for binder_fd failed; errno=%d\n",
errno);
else
maxevents++;
}
while (1) {
struct epoll_event events[maxevents];
int nevents;
IPCThreadState::self()->flushCommands();
nevents = epoll_wait(epollfd, events, maxevents, awake_poll_interval);
if (nevents == -1) {
if (errno == EINTR)
continue;
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "healthd_mainloop: epoll_wait failed\n");
break;
}
for (int n = 0; n < nevents; ++n) {
if (events[n].data.ptr)
(*(void (*)())events[n].data.ptr)();
}
if (!nevents)
periodic_chores();
}
return;
}
我们来看一下这个函数都干了哪些事情呢?首先,代码:epollfd = epoll_create(MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS);创建一个 epoll 实例,并要求内核分配一个可以保存 size 个描述符的空间( 关于epoll,Linux中的字符 设备驱动中有一个函数是poll,Linux 2.5.44版本后被epoll取代,请参考:http://baike.baidu.com/view/1385104.htm?fr=aladdin ), 然后把函数赋值 ev.data.ptr = (void *)uevent_event; 在while(1) 的 调用 nevents = epoll_wait(epollfd, events, maxevents, awake_poll_interval); 等待EPOLL事件的发生,相当于监听。当收到监听后,就是在
for (int n = 0; n < nevents; ++n) {
if (events[n].data.ptr)
(*(void (*)())events[n].data.ptr)();
}
for循环中调用 事件赋值 ev.data.ptr = (void *)uevent_event; 所赋值的函数, 其实相当于Java中的回调接口。我们这里值关注 uevent_event 函数。因为这个是跟电池属性相关的。 uevent_event 函数如下:
static void uevent_event(void) {
char msg[UEVENT_MSG_LEN+2];
char *cp;
int n;
n = uevent_kernel_multicast_recv(uevent_fd, msg, UEVENT_MSG_LEN);
if (n <= 0)
return;
if (n >= UEVENT_MSG_LEN) /* overflow -- discard */
return;
msg[n] = '\0';
msg[n+1] = '\0';
cp = msg;
while (*cp) {
if (!strcmp(cp, "SUBSYSTEM=" POWER_SUPPLY_SUBSYSTEM)) {
battery_update();
break;
}
/* advance to after the next \0 */
while (*cp++)
;
}
}
它会读取socket中的字符串,然后判断事件来源是否是由kernel的power_supply发出的,代码if (!strcmp(cp, "SUBSYSTEM=" POWER_SUPPLY_SUBSYSTEM)) ,如果是,那就调用battery_update()更新电源状态。下面来看看battery_update()是如何更新电源状态的:
static void battery_update(void) {
// Fast wake interval when on charger (watch for overheat);
// slow wake interval when on battery (watch for drained battery).
int new_wake_interval = gBatteryMonitor->update() ?
healthd_config.periodic_chores_interval_fast :
healthd_config.periodic_chores_interval_slow;
if (new_wake_interval != wakealarm_wake_interval)
wakealarm_set_interval(new_wake_interval);
// During awake periods poll at fast rate. If wake alarm is set at fast
// rate then just use the alarm; if wake alarm is set at slow rate then
// poll at fast rate while awake and let alarm wake up at slow rate when
// asleep.
if (healthd_config.periodic_chores_interval_fast == -1)
awake_poll_interval = -1;
else
awake_poll_interval =
new_wake_interval == healthd_config.periodic_chores_interval_fast ?
-1 : healthd_config.periodic_chores_interval_fast * 1000;
}主要就是这一句:gBatteryMonitor->update() ,
gBatteryMonitor 是在mian 函数中初始化的BatteryMonitor的指针对象。 看关系图,这里就由Healthd 跳到
BatteryMonitor了。
下面,我们看一下BatteryMonitor。
三、BatteryMonitor
包含两个文件:\system\core\healthd\BatteryMonitor.h ,\system\core\healthd\BatteryMonitor.cpp
简要说明:
BatteryMonitor.h 是个头文件,只要声明函数与变量,不做过多介绍。我们说下BatteryMonitor.cpp ,
上面说到,battery_update() 中会调用gBatteryMonitor->update() ,那BatteryMonitor.cpp 中的 update()都做了什么了?代码如下:
bool BatteryMonitor::update(void) {
struct BatteryProperties props;
bool logthis;
props.chargerAcOnline = false;
props.chargerUsbOnline = false;
props.chargerWirelessOnline = false;
props.batteryStatus = BATTERY_STATUS_UNKNOWN;
props.batteryHealth = BATTERY_HEALTH_UNKNOWN;
props.batteryCurrentNow = INT_MIN;
props.batteryChargeCounter = INT_MIN;
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath.isEmpty())
props.batteryPresent = getBooleanField(mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath);
else
props.batteryPresent = true;
props.batteryLevel = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityPath);
props.batteryVoltage = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath) / 1000;
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath.isEmpty())
props.batteryCurrentNow = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath);
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeCounterPath.isEmpty())
props.batteryChargeCounter = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeCounterPath);
props.batteryTemperature = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath);
const int SIZE = 128;
char buf[SIZE];
String8 btech;
if (readFromFile(mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath, buf, SIZE) > 0)
props.batteryStatus = getBatteryStatus(buf);
if (readFromFile(mHealthdConfig->batteryHealthPath, buf, SIZE) > 0)
props.batteryHealth = getBatteryHealth(buf);
if (readFromFile(mHealthdConfig->batteryTechnologyPath, buf, SIZE) > 0)
props.batteryTechnology = String8(buf);
unsigned int i;
for (i = 0; i < mChargerNames.size(); i++) {
String8 path;
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/online", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
mChargerNames[i].string());
if (readFromFile(path, buf, SIZE) > 0) {
if (buf[0] != '0') {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/type", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
mChargerNames[i].string());
switch(readPowerSupplyType(path)) {
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_AC:
props.chargerAcOnline = true;
break;
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_USB:
props.chargerUsbOnline = true;
break;
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_WIRELESS:
props.chargerWirelessOnline = true;
break;
default:
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "%s: Unknown power supply type\n",
mChargerNames[i].string());
}
}
}
}
logthis = !healthd_board_battery_update(&props);
if (logthis) {
char dmesgline[256];
snprintf(dmesgline, sizeof(dmesgline),
"battery l=%d v=%d t=%s%d.%d h=%d st=%d",
props.batteryLevel, props.batteryVoltage,
props.batteryTemperature < 0 ? "-" : "",
abs(props.batteryTemperature / 10),
abs(props.batteryTemperature % 10), props.batteryHealth,
props.batteryStatus);
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath.isEmpty()) {
char b[20];
snprintf(b, sizeof(b), " c=%d", props.batteryCurrentNow / 1000);
strlcat(dmesgline, b, sizeof(dmesgline));
}
KLOG_INFO(LOG_TAG, "%s chg=%s%s%s\n", dmesgline,
props.chargerAcOnline ? "a" : "",
props.chargerUsbOnline ? "u" : "",
props.chargerWirelessOnline ? "w" : "");
}
if (mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar != NULL)
mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar->notifyListeners(props);
return props.chargerAcOnline | props.chargerUsbOnline |
props.chargerWirelessOnline;
}这个函数首先定义了BatteryProperties props; 这个属性集(为了减少介绍的复杂度,大家可以简单的认为只是一个包含各种属性的类),然后给这个属性集 props 里面的属性赋值。然后在最后会在最后判断有无注册监听 ,如果有的话,调用注册的监听,把属性传入监听:
if (mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar != NULL)
mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar->notifyListeners(props);调用的就是上面的东西。 到目前为止,我们知道了health 里面有个无线循环,监控驱动事件,然后调用BatteryProperties中的update方法。 然后update会读取各种属性值,然后调用注册的监听。如下图
那么问题来了------->挖掘机技术哪家强?哈哈,开个玩笑。下面我们就要分两个分支来讲述:
(1)这些属性是从哪里来的。
(2)属性变化后调用的监听是谁注册的。
首先,(1)这些属性是从哪里来的。
我们先看一下 上面的 healthd.cpp 的main 函数初始化 BatteryMonitor 时,调用了
gBatteryMonitor = new BatteryMonitor();
gBatteryMonitor->init(&healthd_config, nosvcmgr); 这个init 初始化的时候都干了些什么呢
void BatteryMonitor::init(struct healthd_config *hc, bool nosvcmgr) {
String8 path;
mHealthdConfig = hc;
DIR* dir = opendir(POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH);
if (dir == NULL) {
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "Could not open %s\n", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH);
} else {
struct dirent* entry;
while ((entry = readdir(dir))) {
const char* name = entry->d_name;
if (!strcmp(name, ".") || !strcmp(name, ".."))
continue;
char buf[20];
// Look for "type" file in each subdirectory
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/type", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
switch(readPowerSupplyType(path)) {
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_AC:
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_USB:
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_WIRELESS:
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/online", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path.string(), R_OK) == 0)
mChargerNames.add(String8(name));
break;
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_BATTERY:
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/status", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath = path;
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryHealthPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/health", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryHealthPath = path;
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/present", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath = path;
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/capacity", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityPath = path;
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/voltage_now",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) {
mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath = path;
} else {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/batt_vol",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath = path;
}
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/current_now",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath = path;
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeCounterPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/charge_counter",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeCounterPath = path;
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/temp", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,
name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) {
mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath = path;
} else {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/batt_temp",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath = path;
}
}
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryTechnologyPath.isEmpty()) {
path.clear();
path.appendFormat("%s/%s/technology",
POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
mHealthdConfig->batteryTechnologyPath = path;
}
break;
case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_UNKNOWN:
break;
}
}
closedir(dir);
}
if (!mChargerNames.size())
KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "No charger supplies found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryStatusPath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryHealthPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryHealthPath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryPresentPath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryCapacityPath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryVoltagePath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryTemperaturePath not found\n");
if (mHealthdConfig->batteryTechnologyPath.isEmpty())
KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryTechnologyPath not found\n");
if (nosvcmgr == false) {
mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar = new BatteryPropertiesRegistrar(this);
mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar->publish();
}
}
在init()里会调用opendir(POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH);
opendir()函数的作用是:打开目录句柄,将返回一组目录流(一组目录字符串),说白了就是目录下的文件名。
#define POWER_SUPPLY_SUBSYSTEM "power_supply" #define POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH "/sys/class/" POWER_SUPPLY_SUBSYSTEM其实 opendir 打开的就是 sys/class/power_supply ,并返回这个路径下的所有文件。文件如下:

比如ac (充电器就叫AC)目录下面都有什么呢:
然后我们看init()代码里面,其实就是把各种路径读取出来,然后把路径赋值。 我们知道了init()干了什么,然后回归到主题:update() 中的属性从哪里来的。
我们只举一个例子。在update()中如何读取的当前电量级别(其他属性获取都是类似的)。在 update()函数中,获取当前电量等级代码如下:
if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath.isEmpty())
props.batteryCurrentNow = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath);会用getIntField() 去读取当前电量值。而且传入的参数是我们init()时获取的文件路径。 从路径下读取的值是什么呢,大家看下截图就明白了。如下:
看到没,其实就是读取文件里面的值。 100 是我当前手机的电量,我的手机是满电状态。
到此,我们第一个问题:
BatteryMonitor 中 update 方面里面如何获取的属性已经解决。就是根据路径,读取文件获得的。
下面来看第二个问题:
(2)属性变化后调用谁注册的监听。
在BatteryMonitor.cpp中的init()函数末尾 有这么一句:
if (nosvcmgr == false) {
mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar = new BatteryPropertiesRegistrar(this);
mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar->publish();
}
而在在BatteryMonitor.cpp中的update()函数末尾 有这么一句:
if (mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar != NULL)
mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar->notifyListeners(props);
由上面两个函数中的调用,我们很容易推测出 注册监听跟 BatteryPropertiesRegistrar有关。
我们来分析下 BatteryPropertiesRegistrar 有什么。
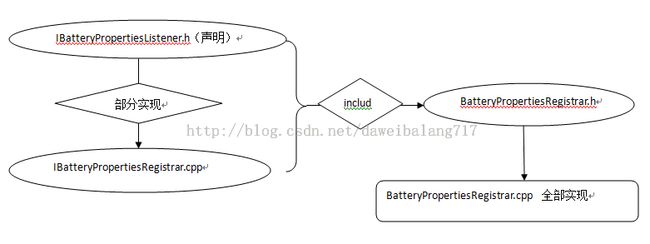
BatteryPropertiesRegistrar:
此类的相关文件有4个,具体路径:
\frameworks\native\include\batteryservice\IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.h
\frameworks\native\services\batteryservice\IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.cpp
\system\core\healthd\BatteryPropertiesRegistrar.cpp
\system\core\healthd\BatteryPropertiesRegistrar.h
\frameworks\native\include\batteryservice\IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.h文件内容:
#ifndef ANDROID_IBATTERYPROPERTIESREGISTRAR_H
#define ANDROID_IBATTERYPROPERTIESREGISTRAR_H
#include <binder/IInterface.h>
#include <batteryservice/IBatteryPropertiesListener.h>
namespace android {
// must be kept in sync with interface defined in IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.aidl
enum {
REGISTER_LISTENER = IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION,
UNREGISTER_LISTENER,
};
class IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar : public IInterface {
public:
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(BatteryPropertiesRegistrar);
virtual void registerListener(const sp<IBatteryPropertiesListener>& listener) = 0;
virtual void unregisterListener(const sp<IBatteryPropertiesListener>& listener) = 0;
};
class BnBatteryPropertiesRegistrar : public BnInterface<IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar> {
public:
virtual status_t onTransact(uint32_t code, const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags = 0);
};
}; // namespace android
#endif // ANDROID_IBATTERYPROPERTIESREGISTRAR_H
咦,我们可以看到IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar 继承于 IInterface ,还有一个类BnBatteryPropertiesRegistrar 继承于BnInterface。 而且还调用了
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(BatteryPropertiesRegistrar);这个宏定义接口。如果你有看过我上篇 Binder 初解( http://blog.csdn.net/daweibalang717/article/details/41382603 )的话,你可以很轻易的看出这里是Binder的写法。而且明显是个 native service。 对于这四个文件的关系。你读完 Binder 初解后,就一目了然了。
\frameworks\native\services\batteryservice\IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.cpp的内容
#define LOG_TAG "IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar"
//#define LOG_NDEBUG 0
#include <utils/Log.h>
#include <batteryservice/IBatteryPropertiesListener.h>
#include <batteryservice/IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <binder/Parcel.h>
namespace android {
class BpBatteryPropertiesRegistrar : public BpInterface<IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar> {
public:
BpBatteryPropertiesRegistrar(const sp<IBinder>& impl)
: BpInterface<IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar>(impl) {}
void registerListener(const sp<IBatteryPropertiesListener>& listener) {
Parcel data;
data.writeInterfaceToken(IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar::getInterfaceDescriptor());
data.writeStrongBinder(listener->asBinder());
remote()->transact(REGISTER_LISTENER, data, NULL);
}
void unregisterListener(const sp<IBatteryPropertiesListener>& listener) {
Parcel data;
data.writeInterfaceToken(IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar::getInterfaceDescriptor());
data.writeStrongBinder(listener->asBinder());
remote()->transact(UNREGISTER_LISTENER, data, NULL);
}
};
IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(BatteryPropertiesRegistrar, "android.os.IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar");
status_t BnBatteryPropertiesRegistrar::onTransact(uint32_t code,
const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply,
uint32_t flags)
{
switch(code) {
case REGISTER_LISTENER: {
CHECK_INTERFACE(IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar, data, reply);
sp<IBatteryPropertiesListener> listener =
interface_cast<IBatteryPropertiesListener>(data.readStrongBinder());
//这个方法并不是上面 BpBatteryPropertiesRegistrar中的registerListener(),他们就不是一个类。这个方法还未实现
registerListener(listener);
return OK;
}
case UNREGISTER_LISTENER: {
CHECK_INTERFACE(IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar, data, reply);
sp<IBatteryPropertiesListener> listener =
interface_cast<IBatteryPropertiesListener>(data.readStrongBinder());
//这个方法并不是上面 BpBatteryPropertiesRegistrar中的unregisterListener(),他们就不是一个类。这个方法还未实现
unregisterListener(listener);
return OK;
}
}
return BBinder::onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
};
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
}; // namespace android
我们看到 这里是服务端与代理端的实现。 但是服务端 onTransact( )中调用的 registerListener(listener); 与unregisterListener(listener); 是没有实现的。这两个方法是在
\system\core\healthd\BatteryPropertiesRegistrar.cpp 中实现的。
\system\core\healthd\BatteryPropertiesRegistrar.h 中的内容:
#ifndef HEALTHD_BATTERYPROPERTIES_REGISTRAR_H
#define HEALTHD_BATTERYPROPERTIES_REGISTRAR_H
#include "BatteryMonitor.h"
#include <binder/IBinder.h>
#include <utils/Mutex.h>
#include <utils/Vector.h>
#include <batteryservice/BatteryService.h>
#include <batteryservice/IBatteryPropertiesListener.h>
#include <batteryservice/IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.h>
namespace android {
class BatteryMonitor;
class BatteryPropertiesRegistrar : public BnBatteryPropertiesRegistrar,
public IBinder::DeathRecipient {
public:
BatteryPropertiesRegistrar(BatteryMonitor* monitor);
void publish();
void notifyListeners(struct BatteryProperties props);
private:
BatteryMonitor* mBatteryMonitor;
Mutex mRegistrationLock;
Vector<sp<IBatteryPropertiesListener> > mListeners;
void registerListener(const sp<IBatteryPropertiesListener>& listener);
void unregisterListener(const sp<IBatteryPropertiesListener>& listener);
void binderDied(const wp<IBinder>& who);
};
}; // namespace android
#endif // HEALTHD_BATTERYPROPERTIES_REGISTRAR_H
这个类是对\frameworks\native\include\batteryservice\IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.h 中的 BnBatteryPropertiesRegistrar的扩展,并继承于public IBinder::DeathRecipient
然后是\system\core\healthd\BatteryPropertiesRegistrar.cpp 的内容:
#include "BatteryPropertiesRegistrar.h"
#include <batteryservice/BatteryService.h>
#include <batteryservice/IBatteryPropertiesListener.h>
#include <batteryservice/IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.h>
#include <binder/IServiceManager.h>
#include <utils/Errors.h>
#include <utils/Mutex.h>
#include <utils/String16.h>
namespace android {
BatteryPropertiesRegistrar::BatteryPropertiesRegistrar(BatteryMonitor* monitor) {
mBatteryMonitor = monitor;
}
void BatteryPropertiesRegistrar::publish() {
defaultServiceManager()->addService(String16("batterypropreg"), this);
}
void BatteryPropertiesRegistrar::notifyListeners(struct BatteryProperties props) {
Mutex::Autolock _l(mRegistrationLock);
for (size_t i = 0; i < mListeners.size(); i++) {
mListeners[i]->batteryPropertiesChanged(props);
}
}
void BatteryPropertiesRegistrar::registerListener(const sp<IBatteryPropertiesListener>& listener) {
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(mRegistrationLock);
// check whether this is a duplicate
for (size_t i = 0; i < mListeners.size(); i++) {
if (mListeners[i]->asBinder() == listener->asBinder()) {
return;
}
}
mListeners.add(listener);
listener->asBinder()->linkToDeath(this);
}
mBatteryMonitor->update();
}
void BatteryPropertiesRegistrar::unregisterListener(const sp<IBatteryPropertiesListener>& listener) {
Mutex::Autolock _l(mRegistrationLock);
for (size_t i = 0; i < mListeners.size(); i++) {
if (mListeners[i]->asBinder() == listener->asBinder()) {
mListeners[i]->asBinder()->unlinkToDeath(this);
mListeners.removeAt(i);
break;
}
}
}
void BatteryPropertiesRegistrar::binderDied(const wp<IBinder>& who) {
Mutex::Autolock _l(mRegistrationLock);
for (size_t i = 0; i < mListeners.size(); i++) {
if (mListeners[i]->asBinder() == who) {
mListeners.removeAt(i);
break;
}
}
}
} // namespace android
这个类是对 \system\core\healthd\BatteryPropertiesRegistrar.h 的实现。 真正 调用registerListener(listener); 与unregisterListener(listener); 的地方。
这个BatteryPropertiesRegistrar:其实就是注册监听的类,而且监听的接口叫IBatteryPropertiesListener。
IBatteryPropertiesListener :
文件路径:
\frameworks\native\include\batteryservice\IBatteryPropertiesListener.h
\frameworks\native\services\batteryservice\IBatteryPropertiesListener.cpp
文件内容:
IBatteryPropertiesListener.h
#ifndef ANDROID_IBATTERYPROPERTIESLISTENER_H
#define ANDROID_IBATTERYPROPERTIESLISTENER_H
#include <binder/IBinder.h>
#include <binder/IInterface.h>
#include <batteryservice/BatteryService.h>
namespace android {
// must be kept in sync with interface defined in IBatteryPropertiesListener.aidl
enum {
TRANSACT_BATTERYPROPERTIESCHANGED = IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION,
};
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
class IBatteryPropertiesListener : public IInterface {
public:
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(BatteryPropertiesListener);
virtual void batteryPropertiesChanged(struct BatteryProperties props) = 0;
};
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
}; // namespace android
#endif
咦,这个依然用的是Binder 机制。这里进行代理与服务端的声明。
IBatteryPropertiesListener.cpp:
#include <stdint.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <batteryservice/IBatteryPropertiesListener.h>
#include <binder/Parcel.h>
namespace android {
class BpBatteryPropertiesListener : public BpInterface<IBatteryPropertiesListener>
{
public:
BpBatteryPropertiesListener(const sp<IBinder>& impl)
: BpInterface<IBatteryPropertiesListener>(impl)
{
}
void batteryPropertiesChanged(struct BatteryProperties props)
{
Parcel data, reply;
data.writeInterfaceToken(IBatteryPropertiesListener::getInterfaceDescriptor());
data.writeInt32(1);
props.writeToParcel(&data);
status_t err = remote()->transact(TRANSACT_BATTERYPROPERTIESCHANGED, data, &reply, IBinder::FLAG_ONEWAY);
}
};
IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(BatteryPropertiesListener, "android.os.IBatteryPropertiesListener");
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
}; // namespace android
这里进行代理的实现。 但是并没有对服务端进行实现。这个应该是在BatteryService.java 中的:
private final class BatteryListener extends IBatteryPropertiesListener.Stub {
public void batteryPropertiesChanged(BatteryProperties props) {
BatteryService.this.update(props);
}
中进行实现的。
到这里我们对于第二个问题:属性变化后调用谁注册的监听。 还没有解决, 只是了解下注册类与注册接口。那么真正注册在那呢? 是在\frameworks\base\services\java\com\android\server\BatteryService.java中:
这个BatteryService 继承于Binder 类,在他的构造函数中,是这么注册的:
mBatteryPropertiesListener = new BatteryListener();
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("batterypropreg");
mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar = IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.Stub.asInterface(b);
try {
mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.registerListener(mBatteryPropertiesListener);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// Should never happen.
}
大家不禁要问了。这里是Java 代码呀,怎么掉的C++的呢,这就是Binder机制了。 而且上面所述的 IBatteryPropertiesListener 、IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar 在Java层都有对应的aidl 文件。目录:
\frameworks\base\core\java\android\os\IBatteryPropertiesListener.aidl
package android.os;
import android.os.BatteryProperties;
/**
* {@hide}
*/
oneway interface IBatteryPropertiesListener {
void batteryPropertiesChanged(in BatteryProperties props);
}
\frameworks\base\core\java\android\os\IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.aidl
package android.os;
import android.os.IBatteryPropertiesListener;
/**
* {@hide}
*/
interface IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar {
void registerListener(IBatteryPropertiesListener listener);
void unregisterListener(IBatteryPropertiesListener listener);
}
当编译的时候会自动生成 IBatteryPropertiesListener.java 与 IBatteryPropertiesRegistrar.java 文件。这个我就不多赘述了。
好吧,我们总结下第二个问题:
1、在BatteryService.java 实现回调函数中的接口,并注册到BatteryPropertiesRegistrar 中。
2、Healthd 中监控PMU 驱动,事件变更,调用BatteryMonitor中的update()函数中回调BatteryPropertiesRegistrar注册的接口,调用的就是BatteryService.java 实现的接口
到此,我们电池电量管理底层分析(C\C++层) 的分析已经完成。 如果你要了解 BatteryService.java 中被回调后执行了哪些事情,请观看我的博客 :
android 4.4 电池电量显示分析(低电量提醒与电池图标)Java 层 (http://blog.csdn.net/daweibalang717/article/details/40615453)