Opencv2源码分析系列之——cornerHarris
1. cornerHarris函数分析
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( void )
{
//read image
Mat image = imread("D:\\testpic\\mypic.jpg", 0);
if ( !image.data )
{
cout << "read image error" << endl;
waitKey( 10000 );
return 0;
}
imshow("original", image);
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Detect Harris Corners
cv::Mat cornerStrength;
cv::cornerHarris(image, //单通道待处理图像
cornerStrength, //类型:CV_32FC1
7, // neighborhood size, 就是窗口函数大小 W(x, y);
3, // aperture size for the Sobel(); 因为我们用sobel函数来得到Ix, Iy;
0.06); // Harris parameter 论文里的 K
// threshold the corner strengths
cv::Mat harrisCorners;
double threshold= 0.001;
cv::threshold(cornerStrength,harrisCorners,
threshold,255,cv::THRESH_BINARY);
//show image
imshow("Harris", harrisCorners);
while( char(waitKey(1)) != 'q' )
{
;
}
return 0;
}
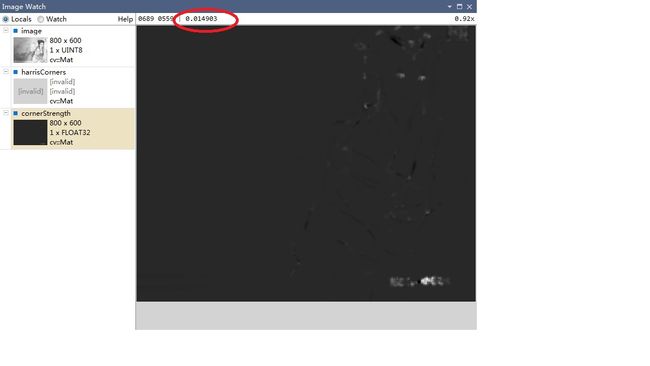
图片最亮的像素点对应的值为0.014903,所以我们选择0.01作为阈值。
2. cornerHarris源码分析
//Harris角点实现函数,截取cornerHarris中的关键代码做了简化....
void myHarris( const Mat& src, Mat& eigenv, int block_size, int aperture_size, double k = 0. )
{
eigenv.create(src.size(), CV_32F);
Mat Dx, Dy;
//sobel operation get Ix, Iy
Sobel(src, Dx, CV_32F, 1, 0, aperture_size);
Sobel(src, Dy, CV_32F, 0, 1, aperture_size);
//get covariance matrix
Size size = src.size();
Mat cov(size, CV_32FC3); //创建一个三通道cov矩阵分别存储[Ix*Ix, Ix*Iy; Iy*Ix, Iy*Iy];
for ( int i = 0; i < size.height; i++ )
{
float* cov_data = cov.ptr<float>(i);
const float* dxdata = Dx.ptr<float>(i);
const float* dydata = Dy.ptr<float>(i);
for ( int j = 0; j < size.width; j++ )
{
float dx = dxdata[j];
float dy = dydata[j];
cov_data[j*3] = dx * dx; //即 Ix*Ix
cov_data[j*3 + 1] = dx * dy; //即 Ix*Iy
cov_data[j*3 + 2] = dy * dy; //即 Iy*Iy
}
}
//方框滤波 W(x,y)卷积 , 也可用高斯核加权...
//W(X,Y)与矩阵cov卷积运算得到 H 矩阵,后面通过H矩阵的特征值决定是否是角点
boxFilter(cov, cov, cov.depth(), Size(block_size, block_size), Point(-1, -1), false);
//cale Harris
size = cov.size();
if ( cov.isContinuous() && eigenv.isContinuous() )
{
size.width *= size.height;
size.height = 1;
//cout << "yes" << endl;
}
//此处计算响应R= det(H) - k*trace(H)*trace(H);
for ( int i = 0; i < size.height; i++ )
{
const float* covPtr = cov.ptr<float>(i);
float* dstPtr = eigenv.ptr<float>(i);
for ( int j = 0; j < size.width; j++ )
{
float a = covPtr[j*3];
float b = covPtr[j*3 + 1];
float c = covPtr[j*3 + 2];
//根据公式 R = det(H) - k* trace(H)*trace(H);
dstPtr[j] = (float)(a*c - b*b - k*(a + c)*(a + c));
}
}
double max, min;
minMaxLoc(eigenv, &min, &max);
//cout << max << endl;
double threshold = 0.1 * max;
cv::threshold(eigenv, eigenv, threshold, 1, CV_THRESH_BINARY); //eigenv的类型是CV_32F,
imshow("eigenv", eigenv);
}
3. goodFeaturesToTrack
从cornerHarris得到角点响应图像即使阈值化也不能得到我们想要的角点,因为可能出现一片连续的区域的角点响应都大于阈值。所以OpenCV中有个goodFeaturesToTrack的函数帮我们选择好的角点:
//mask 在固定区域检测Harris角点
Mat maskArea = Mat(image.size(), CV_8UC1, Scalar(0));
Mat maskROI = maskArea(Rect(300, 50, 150, 200));
maskROI.setTo(255);
imshow("mask", maskArea);
vector<Point2f> points;
Mat cornersImage = image.clone();
goodFeaturesToTrack(image,
points, //存储检测到的角点
100, //你想返回的角点个数,如果检测的角点超过这个数目,从大到小依次返回
0.01, //角点响应阈值 , eg: best corner has the quality measure = 1500, and the
//qualityLevel = 0.01, then all the corners with the quality measure less than 15 are rejected.
20., //两角点之间的最小距离: Minimum possible Euclidean distance between the returned corners
maskArea, //region of interest
5, //w(x, y)
true, //useHarrisDetector
0.06); //cornerHarris中的 K
for ( vector<Point2f>::const_iterator itBegin = points.begin(); itBegin != points.end(); itBegin++ )
{
circle(cornersImage, *itBegin, 5, Scalar(255), 1);
}
imshow("corners", cornersImage);
4. goodFeaturesToTrack源码分析
//GoodFeaturesToTrack关键代码截取
void myGoodFeaturesToTrack( Mat& image, double qualityLevel, double minDistance, int maxCorners )
{
Mat eig;
Mat tmp;
cornerHarris(image, eig, 5, 3, 0.06); //Harris corners;
double maxVal = 0;
minMaxLoc(eig, 0, &maxVal, 0, 0, Mat());
//cout << maxVal << endl << maxVal*255. << endl;
//除去角点响应小于 角点最大响应qualityLevel倍的点
threshold(eig, eig, qualityLevel*maxVal, 0, THRESH_TOZERO); //eig is CV_32F
//normalize(eig, result, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8U); //normalize to show image.
//get corners max in 3*3 if Mat();
//为什么膨胀操作:膨胀的本质是用当前像素周围的最大值替代当前像素值,
//因此,通过膨胀前后比较能取得局部角点响应最大的点。
//第一次是在《OpenCV Programming Cookbook》中看到这种做法,觉得这想法太给力了...
//最后结果存储在tmpCorners中
dilate(eig, tmp, Mat()); //for later operation
vector<const float*> tmpCorners;
Size imageSize = image.size();
{
// HANDLE hSemaphore = CreateSemaphore(NULL, 0, 1, NULL);
// CRITICAL_SECTION g_cs;
//#pragma omp parallel for //【此处并行为什么出错呢???????????????】
for ( int y = 1; y < imageSize.height -1; y++ )
{
float* eig_data = (float*)eig.ptr<float>(y); //角点响应
float* tmp_data = (float*)tmp.ptr<float>(y); // 膨胀之后
//#pragma omp parallel for
for ( int x =1; x < imageSize.width -1; x++ )
{
float val = eig_data[x];
if ( val != 0 && val == tmp_data[x] ) //如果膨胀前后的值不变,说明这个像素点是[3*3]邻域的最大值
{
// #pragma omp atomic //原子操作
// WaitForSingleObject(hSemaphore, NULL);
//EnterCriticalSection(&g_cs);
tmpCorners.push_back(eig_data + x);
//LeaveCriticalSection(&g_cs);
// ReleaseSemaphore(hSemaphore, NULL, NULL);
}
}
}
}
//ShellExecuteEx
//tmpCorners存储角点的地址, 排序操作
sort(tmpCorners, greaterThanPtr<float>());
vector<Point2f> corners;
size_t i, j, total = tmpCorners.size(), ncorners = 0;
if ( minDistance >= 1 ) //如果有角点之间最小距离限制
{
//将图片分为各个grid...每个grid的边长为minDistance
int w = image.cols;
int h = image.rows;
//cvRound :Rounds floating-point number to the nearest integer
const int cell_size = cvRound(minDistance);
const int grid_width = (w + cell_size -1) / cell_size;
const int grid_height = (h + cell_size -1) /cell_size;
//每个grid用一个vector<Point2f> 存储角点
vector<vector<Point2f> > grid(grid_width*grid_height);
minDistance *= minDistance;
for ( i =0; i < total; i++ )
{
//先得到当前点的坐标
int ofs = (int)((const uchar*)tmpCorners[i] - eig.data);
int y = (int)(ofs / eig.step);
int x = (int)((ofs - y*eig.step) / sizeof(float));
bool good = true;
//确定当前点对应哪个grid
int x_cell = x / cell_size;
int y_cell = y / cell_size;
//得到上下,左右[-1,1]范围内grid
int x1 = x_cell - 1;
int y1 = y_cell - 1;
int x2 = x_cell + 1;
int y2 = y_cell + 1;
x1 = max(0, x1);
y1 = max(0, y1);
x2 = min(grid_width-1, x2);
y2 = min(grid_height-1, y2);
//上面说过每个grid用一个vector<Point2f> 存储位于这个区域内的角点
//对当前角点,先得到坐标,然后找到属于哪个grid,并和周围的8(最大是8)个grid中
//的 Point2f 比较距离,如果两点之间的距离小于minDistance则放弃这个角点
//因为我们是按角点响应的降序依次访问的...
for ( int yy = y1; yy <= y2; yy++ )
{
for ( int xx = x1; xx <= x2; xx++ )
{
//m存储对应grid中角点。一个grid中可能有多个角点
vector<Point2f>& m = grid[yy*grid_width + xx];
if ( m.size() )
{
//求当前角点到这个grid内所有角点的距离,若小于当前grid中的某个点,直接跳到break_out,其他
//grid不用再比较,直到周围grid都没有距离小于minstance的值,则将角点push进当前grid中
for ( j =0; j < m.size(); j++ )
{
float dx = x - m[j].x;
float dy = y - m[j].y;
if ( dx*dx + dy*dy < minDistance )
{
good = false;
goto break_out;
}
}
}
}
}
break_out:
if ( good )
{
//将当前角点存入grid中
grid[y_cell*grid_width + x_cell].push_back(Point2f((float)x, (float)y));
circle(image, Point(x, y), 5, Scalar(255), 2);
corners.push_back(Point2f((float)x, (float)y));
++ncorners;
if ( maxCorners > 0 && (int)ncorners == maxCorners )
{
break;
}
}
}
}
else //如果不考虑角点间最小距离限制
{
for ( i = 0; i < total; i++ )
{
//因为eig.step 是Number of bytes each matrix row occupies.
int ofs = (int)((const uchar*)tmpCorners[i] - eig.data);
//通过tmpCorner存储的角点在内存中的地址还原得到图像中的坐标..
int y = (int)(ofs / eig.step);
int x = (int)((ofs - y*eig.step) / sizeof(float));
circle(image, Point(x, y), 5, Scalar(255), 2);
corners.push_back(Point2f((float)x, (float)y));
++ncorners;
if ( maxCorners > 0 && (int)ncorners == maxCorners )
{
break;
}
}
}
imshow("eig", image);
}