(4.1.30)XML解析之DOM、SAX
dom
/* * Copyright (C) 2009 Teleca Poland Sp. z o.o. <[email protected]> * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */
package com.android.yunshi.util;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.StringReader;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.xml.sax.InputSource;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
//xml的转换解析器
/** * @author Lukasz Wisniewski */
public class XMLUtil {
/** * singleton */
private static DocumentBuilderFactory documentBuilderFactory = null;
/** * DocumentBuilderFactory instance (lazy initialization) * * @return */
private static DocumentBuilderFactory getDocumentBuilderFactory(){
if(documentBuilderFactory == null){
documentBuilderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
}
return documentBuilderFactory;
}
/** * DocumentBuilder instance * * @return */
private static DocumentBuilder getDocumentBuilder(){
try {
return getDocumentBuilderFactory().newDocumentBuilder();
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
return null;
}
}
/** * Converts String containing XML code to Document * * @param xmlString * @return <code>Document</code> interface */
public static Document stringToDocument(String xmlString){//字符串到xml的解析
if(xmlString == null)
return null;
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = getDocumentBuilder();
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(new StringReader(xmlString));
try {
return documentBuilder.parse(inputSource);
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
package com.android.yunshi.fun;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import com.android.yunshi.util.XMLUtil;
//解析运势字符串,并封装为实体类
public class YunshiFunctions {
private static Document document = null;
private static Element root = null;
public static Map<String, String> ResolveResultString(String xmlString,
String rootstring) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Map<String, String> entity = new HashMap();
NodeList nodes;
int size;
document = XMLUtil.stringToDocument(xmlString);
if (document == null) {
return null;
}
root = document.getDocumentElement();
nodes = root.getElementsByTagName(rootstring);
Element TableName = (Element) nodes.item(0);
nodes = TableName.getChildNodes();
size = nodes.getLength();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node node = (Node) nodes.item(i);
NodeList nodes2 = node.getChildNodes();
int size2 = nodes2.getLength();
for (int j = 0; j < size2; j++) {
Node node2 = (Node) nodes2.item(j);
if (node2.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element childNode = (Element) node2;
entity.put(childNode.getNodeName(),
childNode.getTextContent());
}
}
}
return entity;
}
public static String ResolveResultStringToString(String xmlString,
String rootstring) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String entity;
NodeList nodes;
int size;
document = XMLUtil.stringToDocument(xmlString);
if (document == null) {
return null;
}
root = document.getDocumentElement();
nodes = root.getChildNodes();
entity = nodes.item(0).getTextContent();
return entity;
}
public static List<Map<String, String>> ResolveResultStringToList(
String xmlString, String rootstring) {
List<Map<String, String>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
NodeList nodes;
int size;
document = XMLUtil.stringToDocument(xmlString);
if (document == null) {
return null;
}
root = document.getDocumentElement();
nodes = root.getElementsByTagName(rootstring);
Element TableName = (Element) nodes.item(0);
nodes = TableName.getChildNodes();
size = nodes.getLength();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node node = (Node) nodes.item(i);
NodeList nodes2 = node.getChildNodes();
int size2 = nodes2.getLength();
Map<String, String> entity = new HashMap();
for (int j = 0; j < size2; j++) {
Node node2 = (Node) nodes2.item(j);
if (node2.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element childNode = (Element) node2;
entity.put(childNode.getNodeName(),
childNode.getTextContent());
}
}
list.add(entity);
}
return list;
}
}
SAX
JAVA 解析 XML 通常有两种方式,DOM 和 SAX。即java中的JDK已经内置了SAX和DOM解析的相关包,因此这里不用导入第三方的jar包。 SAX的全称是Simple APIs for XML,也即XML简单应用程序接口。与DOM不同,SAX提供的访问模式是一种顺序模式,这是一种快速读写XML数据的方式。当使用SAX分析器XML文档进行分析时,会触发一系列事件,并激活相应的事件处理函数,应用程序通过这些事件处理函数实现对XML文档的访问,因而SAX接口也被称作事件驱动接口。
下面是sax解析xml 的示例:
1、要解析的person.xml文件
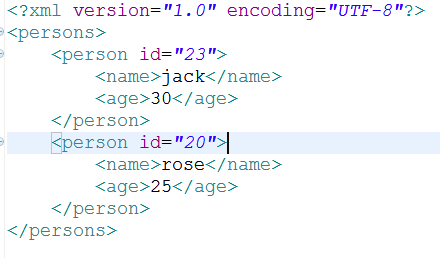
2、获取服务器端xml文件输入流的工具类HttpUtil.java
public class HttpUtil
{
public static InputStream getXML(String path)
{
InputStream in = null;
try
{
URL url = new URL(path);
if (url != null)
{
HttpURLConnection httpConn = (HttpURLConnection) url
.openConnection();
httpConn.setConnectTimeout(3000);
httpConn.setDoInput(true);
httpConn.setRequestMethod("GET");
int code = httpConn.getResponseCode();
if (code == 200)
{
in = httpConn.getInputStream();
}
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return in;
}
}3.处理XML文件的核心类,该类一定要继承DefaultHandler 并覆盖相应的方法
package com.sax.handler;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.jar.Attributes.Name;
import org.xml.sax.Attributes;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler;
public class MyHandler extends DefaultHandler {
private HashMap map = null;// 存储单个解析的完整对象
private List> list = null;// 存储所有的解析对象
private String currentTag = null;// 正在解析的元素的标签
private String currentValue = null;// 解析当前元素的值
private String nodeName = null;// 解析当前的节点名称
public MyHandler(String nodeName) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
this.nodeName = nodeName;
}
public List> getList() {
return list;
}
@Override
public void startDocument() throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 当读到第一个开始标签的时候,会触发这个方法
list = new ArrayList>();
}
@Override
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String qName,
Attributes attributes) throws SAXException {
// 当遇到文档的开头的时候,调用这个方法
if (qName.equals(nodeName)) {
map = new HashMap();
}
if (attributes != null && map != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < attributes.getLength(); i++) {
map.put(attributes.getQName(i), attributes.getValue(i));
}
}
currentTag = qName;
}
@Override
public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length)
throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 这个方法是用来处理xml文件所读取到的内容
if (currentTag != null && map != null) {
currentValue = new String(ch, start, length);
if (currentValue != null && !currentValue.trim().equals("")
&& !currentValue.trim().equals("\n")) {
map.put(currentTag, currentValue);
}
}
currentTag = null;// 把当前的节点的对应的值和标签设置为空
currentValue = null;
}
@Override
public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String qName)
throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 遇到结束标记的时候,会调用这个方法
if (qName.equals(nodeName)) {
list.add(map);
map = null;
}
super.endElement(uri, localName, qName);
}
}4、SAX解析的业务逻辑层
public class SaxService
{
public SaxService()
{
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public static List> readXML(InputStream in,
String nodeName)
{
try
{//获取SAx的实例工厂,并获取解析实例
SAXParserFactory spf = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
SAXParser parser = spf.newSAXParser();
MyHandler handler = new MyHandler(nodeName);
parser.parse(in, handler);// 开始解析XML文件
in.close();
return handler.getList();
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (SAXException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IOException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}5、测试类
public class TestSax
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//要访问的xml文件的服务器地址
String url = "http://localhost:8081/jspchat/person.xml";
//获取服务器端xml文件的输入流
InputStream in = HttpUtil.getXML(url);
//调用业务逻辑层访问xml文件中元素为person的的节点
List> list = SaxService.readXML(in, "person");
for (HashMap map : list)
{
System.out.println(map.toString());
}
}
}