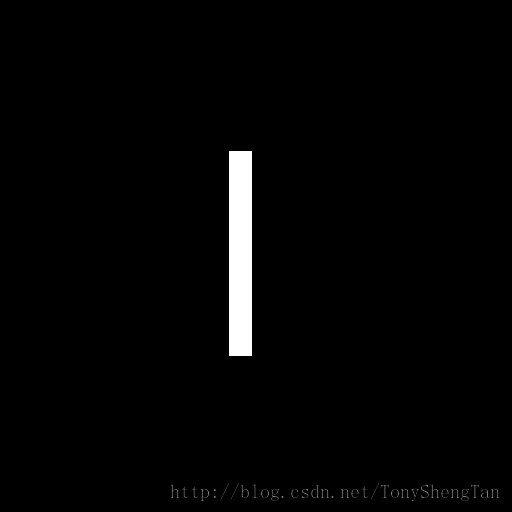图像傅里叶变换(快速傅里叶变换FFT)
学习DIP第7天,图像傅里叶变换
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/tonyshengtan,欢迎大家转载,发现博客被某些论坛转载后,图像无法正常显示,无法正常表达本人观点,对此表示很不满意。。。。。。。。
习惯性,开篇废话
今天公司的网不知怎么了,死活打不开CSDN,公司有100多架客机,也有极限速度60kb/s的网速,还有3K的工资。
图像FFT
上篇已经介绍了关于2D FFT的相关知识,这篇只介绍在图像中的应用,对于一幅图像,做二维FFT后,即可得到其傅里叶变换,傅里叶变换后是二维复数矩阵,因为二维数组,如果是实数,是可以通过变换到0~255通过灰度图像显示出来,而变换结果是复数,所以我们通过显示其幅度,即复数的模,来显示傅里叶谱(幅度谱),不废话,上图:
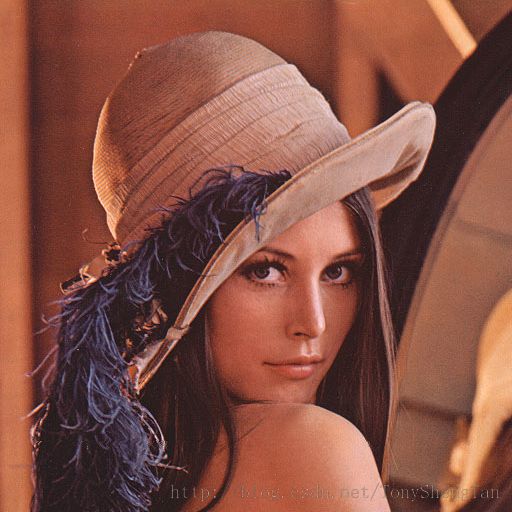
原图
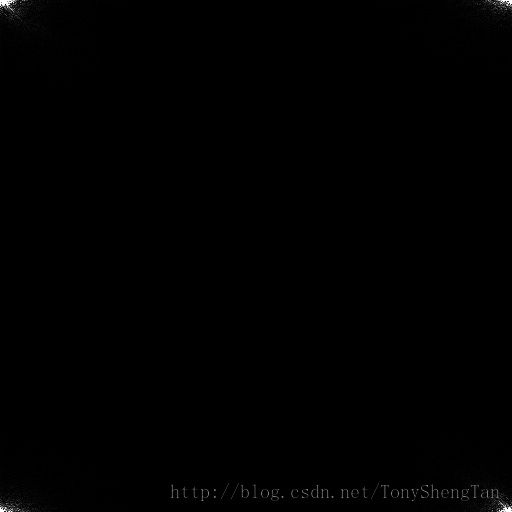
FFT结果
可以看出,原图为大名鼎鼎的Lenna图,下面的为FFT后的幅度谱,其主要数值分布在四个顶点附近,图像中的位置坐标表示为(u,v),四个顶点分别表示(0,0),(0,max(v)),(max(u),0),(max(u),max(v)),至于为啥是这四个点,我也没研究明白,但是(0,0)附近是可以解释为低频分量较多,但是我们平时看到matlab的图是在图像中心的,这一步需要经过一个简单的变换,只要将原图中(坐标为表示x,y)x+y为偶数时,f(x,y)变成是其相反数,即-f(x,y),我们称之为Shift;之后可以得到:
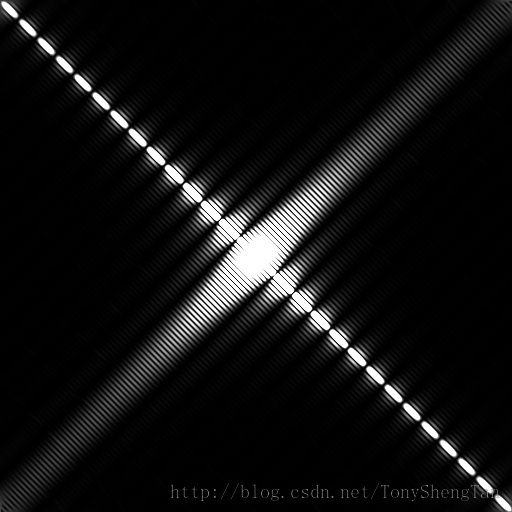
中心化后的幅度谱
此图中图像聚集在图像中心,与Matlab中结果类似,但Matlab中显示的更多,具体原因不清楚,但我感觉是Matlab
对最大值做了处理,因为最大值和最小值之间相差太大,所以拉伸后在变换到0~255,有些结果小于1,无法显示。
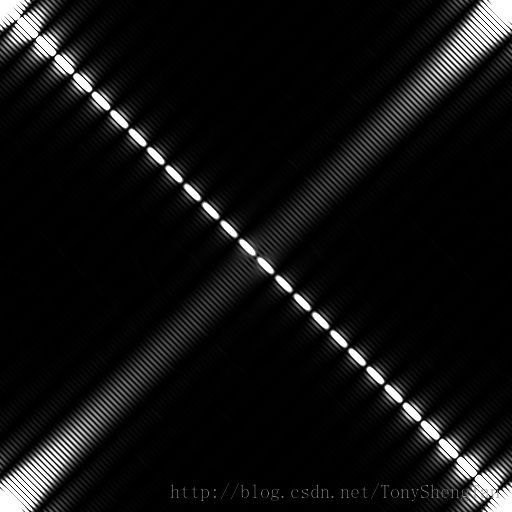
中心局部放大
经过傅里叶逆变换后,再把图像Shift回来,即可得到原图,下面再描述一些变换结果:
原图
频谱
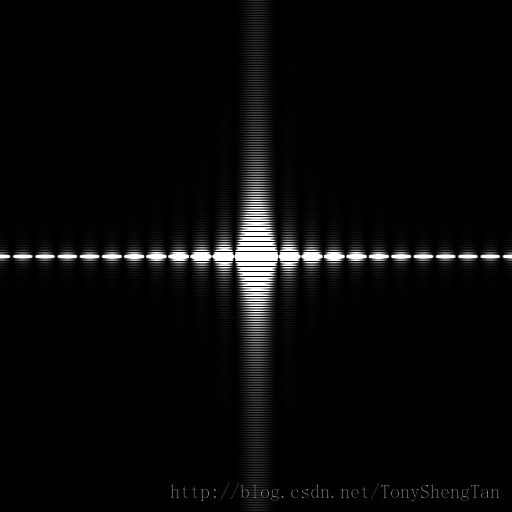
原图
频谱
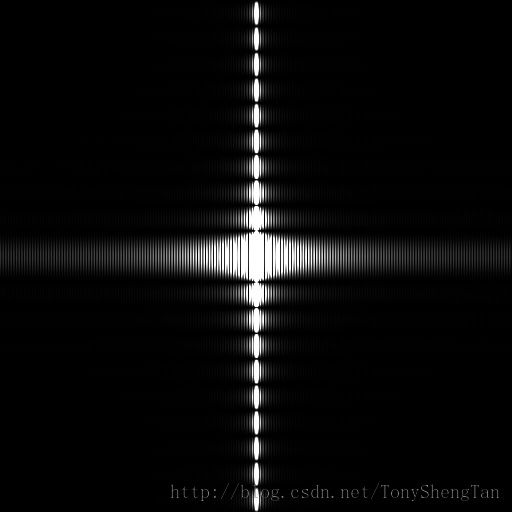
原图
频谱
未中心化的频谱
#include "Image_FFT.h"
/*
中心化,根据傅里叶性质的平移性质
*/
void FFT_Shift(double * src,int size_w,int size_h){
for(int j=0;j<size_h;j++)
for(int i=0;i<size_w;i++){
if((i+j)%2)
src[j*size_w+i]=-src[j*size_w+i];
}
}
/*
图像快速傅里叶变换,图像大小为2的N次幂
*/
void ImageFFT(IplImage * src,Complex * dst){
//FFT_Shift(src, src);
if(src->depth!=IPL_DEPTH_8U)
exit(0);
int width=src->width;
int height=src->height;
double *image_data=(double*)malloc(sizeof(double)*width*height);
for(int j=0;j<height;j++)
for(int i=0;i<width;i++){
image_data[j*width+i]=GETPIX(src, j, i);
}
FFT_Shift(image_data,width, height);//图像中心化
FFT2D(image_data, dst, width, height);
free(image_data);
}
/*
将幅度值伸缩到0到255,用于频谱显示
*/
void Nomalsize(double *src,double *dst,int size_w,int size_h){
double max=0.0,min=DBL_MAX;
for(int i=0;i<size_w*size_h;i++){
max=src[i]>max?src[i]:max;
min=src[i]<min?src[i]:min;
}
double step=255.0/(max-min);
//printf("%d",test);
//printf("max:%lf min:%lf\n",max,min);
for(int i=0;i<size_w*size_h;i++){
dst[i]=(src[i]-min)*step;
dst[i]*=45.9*log((double)(1+dst[i]));
}
}
/*
获得频谱
*/
void getAmplitudespectrum(Complex * src,int size_w,int size_h,IplImage *dst){
double *despe=(double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*size_w*size_h);
if(despe==NULL)
exit(0);
double real=0.0;
double imagin=0.0;
for(int j=0;j<size_h;j++)
for(int i=0;i<size_w;i++){
real=src[j*size_w+i].real;
imagin=src[j*size_w+i].imagin;
despe[j*size_w+i]=sqrt(real*real+imagin*imagin);
}
Nomalsize(despe, despe, size_w, size_h);
for(int j=0;j<size_h;j++)
for(int i=0;i<size_w;i++){
cvSetReal2D(dst, j, i, despe[j*size_w+i]);
}
free(despe);
}
/*
图像傅里叶反变换
*/
void ImageIFFT(Complex *src,IplImage *dst,int size_w,int size_h){
Complex *temp_c=(Complex*)malloc(sizeof(Complex)*size_w*size_h);
if(temp_c==NULL)
exit(0);
for(int i=0;i<size_w*size_h;i++)
Copy_Complex(&src[i],&temp_c[i]);
Complex *temp=(Complex*)malloc(sizeof(Complex)*size_w*size_h);
if(temp==NULL)
exit(0);
double *temp_d=(double *)malloc(sizeof(double)*size_w*size_h);
if(temp_d==NULL)
exit(0);
IFFT2D(temp_c,temp,size_w,size_h);
for(int j=0;j<size_h;j++)
for(int i=0;i<size_w;i++){
temp_d[j*size_w+i]=temp[j*size_w+i].real;
}
FFT_Shift(temp_d, size_w, size_h);
for(int j=0;j<size_h;j++)
for(int i=0;i<size_w;i++){
cvSetReal2D(dst, j, i, temp_d[j*size_w+i]);
}
free(temp);
free(temp_c);
free(temp_d);
}
下一篇继续研究傅里叶变换的应用;