SGI STL的rb_tree浅析
rb_tree是一种特殊的平衡二叉搜索树,但是其对平衡的要求比avl_tree低,avl_tree要求左右子树的高度差不能大于1,而rb_tree只要求从一个节点至树的尾端的任何路径的黑节点的个数相等
rb_tree必须满足的规则:
1.每个节点不是黑色就是红色;
2.根节点必须为黑色;
3.若节点为红色,则其子节点必须为黑色(红不连);
4.任意节点至树尾端的任何路径的黑色节点的个数必须相等;总结一下,也就是——>一头一脚黑, 黑同红不连
为何要用rb_tree, avl_tree:
rb_tree, avl_tree都可以实现平衡二叉搜索树,它们都比一般的(无法绝对维持平衡的)二叉搜索树复杂,因此其插入和删除节点的平均时间也比较长但是它们可以避免极难处理的高度不平衡情况,因为它们总是维持着某种平衡(即每插入一个节点就会判断树是否平衡,不平衡就调整),所以其元素的访问(搜寻)时间平均来说比较少.
rb_tree的节点设计—->rb_tree节点设计分两层,node_base和node,node_base主要负责红黑树的连接部分 (parent,left,right),而node负责红黑树的数据部分(value_filed节点值)
struct __rb_tree_node_base
{
typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type; //节点颜色
typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr; //父节点指针
//rb树的父节点的成员
color_type color; //颜色
base_ptr parent; //父节点指针
base_ptr left; //左树
base_ptr right; //右树
//最小节点
static base_ptr minimum(base_ptr x)
{
while(x->left != 0){
x = x->left;
}
return x;
}
//最大节点
static base_ptr maximum(base_ptr x)
{
while(x->right != 0){
x = x->right;
}
return x;
}
};
//rb树的节点
template<class Value>
struct __rb_tree_node : public __rb_tree_node_base
{
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value>* link_type; //rb树的节点指针
Value value_filed; //rb树的节点的值
};
rb_tree的迭代器设计—>rb_tree的迭代器也设计为两层,base_iterator和iterator
//rb树的迭代器
struct __rb_tree_base_iterator
{
typedef __rb_tree_node_base::base_ptr base_ptr;
typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
base_ptr node;
//指向下一个节点(++操作)
void increment()
{
if(node->right != 0){ //若当前节点的右树不空,则其直接前驱就在其右树部分
node = node->right; //在node的右树中找出最左的节点就是node的直接前驱
while(node->left != 0){
node = node->left;
}
}else{ //node的右树为空,则进行上溯查找node的父节点,直到找到node的直接前驱
base_ptr y = node->parent;
while(node == y->right){
node = y;
y = y->parent;
}
if(node->right != y){
node = y;
}
}
}
//指向上一个节点(--操作)
void decrement()
{
if(node->color == __rb_tree_red && node->parent->parent == node){ //node为header
node = node->right;
}else if(node->left != 0){ //若node的左树不为空,就在左树中找到最右侧的节点
base_ptr y = node->left;
while(y->right != 0){
y = y->right;
}
node = y;
}else{ //node的左树为空,则上溯,查找node的父节点,找到node的直接前驱
base_ptr y = node->parent;
while(node == y->left){
node = y;
y = y->parent;
}
node = y;
}
}
};
template<class Value, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __rb_tree_iterator : public __rb_tree_base_iterator
{
typedef Value value_type;
typedef Ref reference;
typedef Ptr pointer;
typedef __rb_tree_iterator<Value, Value& , Value*> iterator;
typedef __rb_tree_iterator<Value, const Value&, const Value*> const_iterator;
typedef __rb_tree_iterator<Value, Ref, Ptr> self;
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value>* link_type;
__rb_tree_iterator()
{
}
__rb_tree_iterator(link_type x)
{
node = x;
}
__rb_tree_iterator(const iterator& it)
{
node = it.node;
}
reference operator*()const
{
return link_type(node)->value_filed;
}
pointer operator->()const
{
return &(operator*());
}
self& operator++()
{
increment();
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
increment();
return tmp;
}
self& operator--()
{
decrement();
return *this;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
decrement();
return tmp;
}
};
rb_tree的无论是节点还是迭代器都是以struct定义的原因是: struct的所有成员都是public,所以其所有成员都可被外界自由取用
rb_tree的实现使用了一个技巧,那就是使用了header
rb_tree的数据结构
//rb树
template<class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc = alloc>
class rb_tree{
protected:
typedef void* void_pointer;
typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr; //rb树的父节点指针
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node; //rb树的节点
typedef simple_alloc<rb_tree_node, Alloc> rb_tree_node_allocator; //以节点的大小为配置单位
typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type; //rb树的节点的颜色
public:
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Value value_type;
typedef value_type* pointer;
typedef const value_type* const_pointer;
typedef value_type& reference;
typedef const value_type& const_reference;
typedef rb_tree_node* link_type; //rb树的节点指针
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
protected:
link_type get_node()
{
return rb_tree_node_allocator::allocate();
}
link_type create_node(const value_type& x)
{
link_type tmp = get_node();
construct(&tmp->value_filed, x);
return tmp;
}
link_type clone_node(link_type x)
{
link_type tmp = create_node(x->value_filed);
tmp->color = x->color;
tmp->left = 0;
tmp->right = 0;
return tmp;
}
void destroy_node(link_type p)
{
destroy(&p->value_filed);
put_node(p);
}
protected:
size_type node_count; //rb树的节个数
link_type header; //rb树的头指针,相当于链表的第一个空节点
Compare key_compare;
protected:
link_type& root()const
{
return (link_type&)header->parent;
}
link_type& leftmost()const
{
return (link_type&)header->left;
}
link_type& rightmost()const
{
return (link_type&)header->right;
}
protected:
static link_type& left(link_type x)
{
return (link_type&)(x->left);
}
static link_type& right(link_type x)
{
return (link_type&)(x->right);
}
static link_type& parent(link_type x)
{
return (link_type&)(x->parent);
}
static reference value(link_type x)
{
return x->value_filed;
}
static const Key& key(link_type x)
{
return KeyOfValue()(value(x));
}
static color_type& color(link_type x)
{
return (color_type&)(x->color);
}
static link_type& left(base_ptr x)
{
return (link_type&)(x->left);
}
static link_type& right(base_ptr x)
{
return (link_type&)(x->right);
}
static link_type& parent(base_ptr x)
{
return (link_type&)(x->parent);
}
static reference value(base_ptr x)
{
return ((link_type)x)->value_filed;
}
static const Key& key(base_ptr x)
{
return KeyOfValue()(value(link_type(x)));
}
static color_type& color(base_ptr x)
{
return (color_type&)(link_type(x)->color);
}
static link_type minimum(link_type x)
{
return (link_type) __rb_tree_node_base::minimum(x);
}
static link_type maximum(link_type x)
{
return (link_type) __rb_tree_node_base::maximum(x);
}
public:
typedef __rb_tree_iterator<value_type, reference, pointer> iterator;
typedef __rb_tree_iterator<value_type, const_reference, const_pointer> const_iterator;
private:
void init()
{
header = get_node(); //配置一个节点
color(header) = __rb_tree_red; //将header节点设为红色
root() = 0; //将header的父节点赋空
leftmost() = header; //将header指向最左的节点
rightmost() = header; //将header指向最右的节点
}
public:
rb_tree(const Compare& comp = Compare()) : node_count(0), key_compare(comp)
{
init(); //生成一个空节点header
}
public:
iterator begin()
{
return leftmost();
}
iterator end()
{
return header;
}
public:
pair<iterator, bool> insert_unique(const value_type& x);
protected:
iterator __insert(base_ptr x_, base_ptr y_, const Value& v);
};
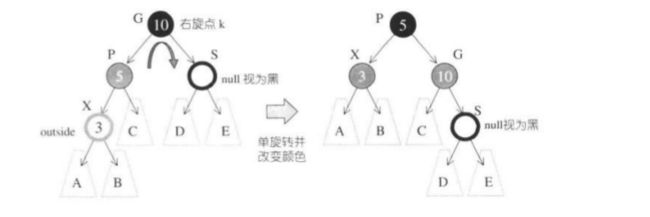
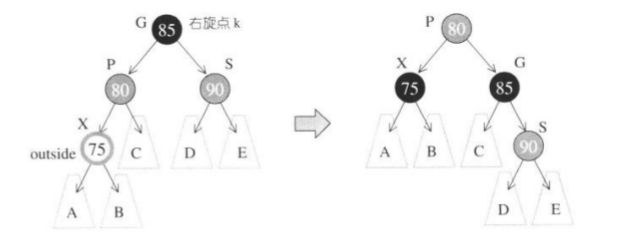
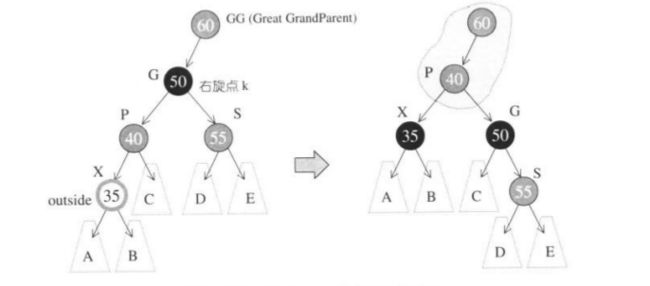
红黑树的插入:根据插入的节点的位置,以及其外围节点(s伯父节点,GG曾祖父节点)的颜色,会出现以下四种状况:
(先作以下假设:假设x为新插入的节点,p为其父节点,G为其祖父节点,S为其伯父节点,GG为其曾祖父节点)
状况一:
S为黑色并且x为外侧插入,此时要先对P, G作一次单旋转,再更改P,G的颜色,就可满足红黑树的规则。
状况二: S为黑色并且x为内侧插入;要先对P,X作一次单旋转,再更改G,X的颜色,最后将所得结果再对G作一次单旋转,就可以满足红黑树的规则。
状况三:S为红色并且X为外侧插入;先对P,G作一次单旋转,再改变X
的颜色,若此时的GG为黑色,则树是平衡的,若不是,则要继续上溯,判断树的平衡性并调整。
状况四:S为红色并且X为内侧插入;先对P,G作一次单选装,改变X的颜色,此时若GG为红色,就要继续往根的方向走,直到不在有父子节点连续为红色的状况。
红黑树的插入操作:
template<class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc>
pair<typename rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::iterator, bool>
rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::insert_unique(const Value& v)
{
link_type y = header;
link_type x = root(); //从根开始
bool comp = true;
//从根开始查找,得到插入节点的位置
while(x != 0){
y = x;
comp = key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v), key(x)); //比较大小,若v小于x则comp为true
x = comp ? left(x) : right(x); //comp为true则x要插入左树,fouze是右树
}
//while结束,y就是要插入节点的父节点,此时y必为叶子节点
iterator j = iterator(y); //迭代器j指向插入节点的父节点
if(comp){ //while结束,若comp为true,则在左侧插入
if(j == begin()){ //若插入点的父节点为最左侧的节点
//x为插入点,y为插入点的父节点,v要插入的值
return pair<iterator, bool>(__insert(x, y, v), true);
}else{ //插入点的父节点不为最左节点
--j; //回溯判断插入的新值是否符合该树的当前节点没有和其值一样的,因Comp用的是判断小于,所以有可能相等
}
}
if(key_compare(key(j.node), KeyOfValue()(v))){ //若j所指的节点的值小于v,则在右侧插入
//x为插入点,y为插入点的父节点,v要插入的值
return pair<iterator, bool>(__insert(x, y, v), true);
}
//此时,说明新值x与树中的健值重复,不进行插入
return pair<iterator, bool>(j, false);
}
template<class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc>
typename rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::iterator
rb_tree<Key, Value, KeyOfValue, Compare, Alloc>::
__insert(base_ptr x_, base_ptr y_, const Value& v)
{
//x_为插入点,y_为插入点的父节点,v要插入的值
link_type x = (link_type) x_;
link_type y = (link_type) y_;
link_type z;
if(y == header || x != 0 ||key_compare(KeyOfValue()(v), key(y))){
z = create_node(v); //配置一个新节点,z就成为要插入的节点
left(y) = z; //若y==header时,leftmost() = z
if(y == header){ //若y为header空节点,则z就为根结点,也为最右节点
root() = z;
rightmost() = z;
}else if(y == leftmost()){ //若y为最左节点,则新插入的节点就变成最左节点
leftmost() = z;
}
}else{
z = create_node(v); //配置一个节点z
right(y) = z; //使z成为插入点x的父节点y的右节点
if(y == rightmost()){ //若y为最右节点,则z就是新的最右节点
rightmost() = z;
}
}
//调整z的父节点和z的左右节点
parent(z) = y;
left(z) = 0;
right(z) = 0;
__rb_tree_rebalance(z, header->parent); //调整z节点一直上溯到根结点的平衡
++node_count; //节点数增加
return iterator(z); //返回一个迭代器,指向新增节点
}插入节点所需的调整平衡的函数
//x为新插入节点,root为根结点
inline void __rb_tree_rebalance(__rb_tree_node_base* x, __rb_tree_node_base*& root)
{
x->color = __rb_tree_red; //新插入节点的颜色为红色
while(x != root && x->parent->color == __rb_tree_red){ //父节点为红色,就不平衡需要调整
//整体左侧插入
if(x->parent == x->parent->parent->left){ //父节点为祖父节点的左节点
__rb_tree_node_base* y = x->parent->parent->right; //y为x的叔伯节点
if(y && y->color == __rb_tree_red){ //伯父节点存在,并且伯父节点为红色
x->parent->color = __rb_tree_black; //将x的父节点变黑色
y->color = __rb_tree_black; //将x的伯父节点变为黑色
x->parent->parent->color = __rb_tree_red; //将x的祖父节点变为红色,此时要上溯查看其曾祖父节点的颜色,若为红则不平衡要调整
x = x->parent->parent; //继续上溯查找不平衡并调整平衡
}else{ //没有伯父节点或伯父节点为黑色(没有时默认黑色)
if(x == x->parent->right){ //内侧插入
x = x->parent;
//先进行左旋
__rb_tree_rotate_left(x, root);
}
//或是左侧插入,直接进行右旋即可
x->parent->color = __rb_tree_black;
x->parent->parent->color = __rb_tree_red;
//再进行右旋
__rb_tree_rotate_right(x->parent->parent, root);
}
}
//整体右侧插入
else{
__rb_tree_node_base* y = x->parent->parent->left; //y为x的伯父节点
if(y && y->color == __rb_tree_red){ //伯父节点存在并为红色,插入节点又为红色,所以黑色节点不平衡
x->parent->color == __rb_tree_black; //改变父节点的颜色
y->color = __rb_tree_black; //改变伯父节点的颜色
x->parent->parent->color = __rb_tree_red; //改变祖父节点的颜色为红色,则其曾祖父节点可能为红色,要上溯进行查看调整
x = x->parent->parent; //继续上溯查找不平衡点并调整
}else{ //伯父节点不存在或伯父节点为黑色
if(x == x->parent->left){ //内侧插入
x = x->parent;
//先进行右旋
__rb_tree_rotate_right(x, root);
}
//或是右侧插入,直接进行左旋
x->parent->color = __rb_tree_black; //改变父节点和祖父节点的颜色
x->parent->parent->color = __rb_tree_red;
//再进行左旋
__rb_tree_rotate_left(x->parent->parent, root);
}
}
}
//将根结点的颜色置为黑色
root->color = __rb_tree_black;
}
//左旋
inline void __rb_tree_rotate_left(__rb_tree_node_base* x, __rb_tree_node_base*& root)
{
__rb_tree_node_base* y = x->right; //y为旋转点x的右节点
x->right = y->left; //左旋要将x的右节点的左树挂接到y的右树部分
if(y->left != 0){
y->left->parent = x; //改变y的左树的父节点指向
}
y->parent = x->parent; //改变y的父节点
//对x和y作旋转
if(x == root){ //若新插入的节点为根结点,则让x的右节点y作根结点
root = y;
}else if(x == x->parent->left){ //若x是其父节点的左节点,则让x的右节点y作其父节点的左节点
x->parent->left = y;
}else{ //x是其父节点的右节点,则让x的右节点作其父节点的右节点
x->parent->right = y;
}
//更改指向
y->left = x;
x->parent = y;
}
//右旋
inline void __rb_tree_rotate_right(__rb_tree_node_base* x, __rb_tree_node_base*& root)
{
__rb_tree_node_base* y = x->left; //y为x的左节点
x->left = y->right; //将x旋转下来,y旋转上去,将y的右节点给予x的左节点
if(y->right != 0){ //若y的右节点不空,更改其父节点指向
y->right->parent = x;
}
y->parent = x->parent; //更改y的父节点
//对x和y进行旋转
if(x == root){
root = y;
}else if(x == x->parent->right){
x->parent->right = y;
}else{
x->parent->left = y;
}
y->right = x;
x->parent = y;
}