C++STL学习(5)容器map和multimap
注:博客内容均来自于对《C++标准库》侯捷,华中科技大学出版社一书的笔记。转载请注明出处。
所有例程在Red Hat Linux 3.2.2-5版本上编译运行,g++的版本是 g++ (GCC) 3.2.2 20030222。
1、map和multimap
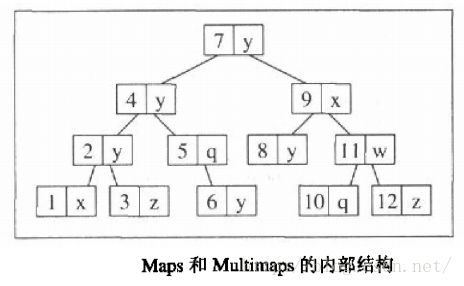
map、multimap同set、multiset非常相似,他们里面的元素也都是“有序的”。也会根据规定的排序准则排序。不同的是map和multimap的元素都是键/值对的形式。除此之外他们并无其他的本质区别。
排序规则都是基于键的,所以说不会出现按照值排序的情况!!!这只是说仅仅在使用map的时候。非要按照值排序的时候可以借助vector来实现。这类的实现很多,比如:点我转到
set和multiset参见博客:
C++STL学习(4)容器set和multiset
2、map和mutimap的操作
2.1 构造和析构
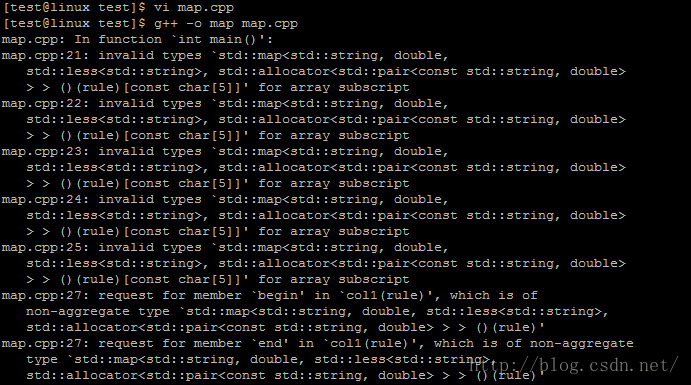
上述红框内标记给出会出错,例子如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
typedef map<string,double> StringDoubleMap;
class rule
{
public:
bool operator ()(const string& a, const string& b)
{
return a[0] < b[0];
}
};
int main()
{
StringDoubleMap col1(rule);
col1["ABCD"] = 173.20;
col1["BCDA"] = 231.23;
col1["CDAB"] = 531.54;
col1["DCFE"] = 6331.76;
col1["EDSa"] = 3142.91;
StringDoubleMap::iterator pos;
for(pos = col1.begin();pos != col1.end();++pos)
{
cout<< "Name: " << pos->first << "\t"
<< "Value: " << pos->second << endl;
}
return 0;
}出错信息:
根据错误来看,很可能是因为这个版本的STL中并没有重载红框内的构造函数。
编译器的版本:
当这样使用的时候,程序就回正常的运行。
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
typedef map<string,double> StringDoubleMap;
class rule
{
public:
bool operator ()(const string& a, const string& b)
{
return a[0] < b[0];
}
};
int main()
{
map<string,double,rule> col1;
col1["ABCD"] = 173.20;
col1["BCDA"] = 231.23;
col1["CDAB"] = 531.54;
col1["DCFE"] = 6331.76;
col1["EDSa"] = 3142.91;
StringDoubleMap::iterator pos;
for(pos = col1.begin();pos != col1.end();++pos)
{
cout<< "Name: " << pos->first << "\t"
<< "Value: " << pos->second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
2.2 其他操作
其他的操作同set/multiset大致上相同,并无很大区别。
需要注意的是:
1>运用value_type
std::map<std::string,float> col1;
col1.insert(std::map<std::string,float>::value_type("otto",22.3));
2>运用pair<>
std::map<std::string,float> col1;
col1.insert(std::pair<std::string,float>("otto",22.3));
col1.insert(const std::pair<std::string,float>("otto",22.3));
3>运用make_pair()
std::map<std::string,float> col1;
col1.insert(std::make_pair("otto",13.2));
example:
//multimap当做字典来使用
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//类型重定义
typedef multimap<string, string> StrStrMMap;
StrStrMMap dict;
//插入数值
//使用value_type()插入数值
dict.insert(StrStrMMap::value_type("techer","lao shi"));
//使用pair()插入数值
dict.insert(pair<string,string>("smart","zhi neng de"));
//使用make_pair()插入数值
dict.insert(make_pair("day","tian"));
dict.insert(make_pair("strange","qi guai de"));
dict.insert(make_pair("car","qi che"));
dict.insert(make_pair("smart","cong ming de"));
dict.insert(make_pair("get","hu oqu"));
dict.insert(make_pair("image","tu xiang"));
dict.insert(make_pair("compound","hua he wu"));
dict.insert(make_pair("sponge","hai mian"));
//输出容器内所有元素
StrStrMMap::iterator pos;
cout.setf(ios::left, ios::adjustfield); //调整输出格式
cout << ' ' << setw(10) << "english "
<< "Chinese " << endl;
cout << setfill('-') << setw(20) << " "
<< setfill(' ') << endl;
for(pos = dict.begin(); pos != dict.end(); ++pos)
{
cout << ' ' << setw(10) << pos->first
<< pos->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//查找"smart"并输出所有含义
string word("smart");
cout << word << ": " << endl;
for(pos = dict.lower_bound(word);
pos != dict.upper_bound(word); ++pos)
{
cout<< " " << pos->second << endl;
}
word = "raffiniert";
cout << word << ": " << endl;
for(pos = dict.lower_bound(word);
pos != dict.upper_bound(word); ++pos)
{
cout<< " " << pos->second << endl;
}
cout<<endl;
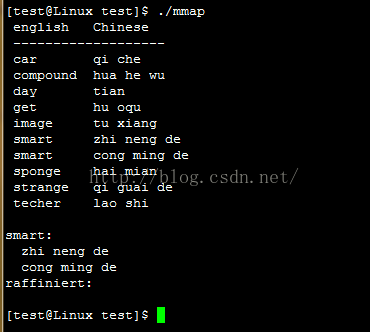
}输出结果:
example2:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
template <class K, class V>
class value_equals
{
private:
V value;
public:
value_equals(const V& v) : value(v)
{
}
bool operator() (pair<const K, V> elem)
{
return elem.second == value;
}
};
int main()
{
typedef map<float, float> FloatFloatMap;
FloatFloatMap col1;
col1[1] = 7;
col1[2] = 4;
col1[3] = 2;
col1[4] = 3;
col1[5] = 6;
col1[6] = 1;
col1[7] = 3;
//查找键值为3.0的节点
FloatFloatMap::iterator pos;
pos = col1.find(3.0);
if(pos != col1.end())
{
cout << pos->first << ":"
<< pos->second << endl;
}
//查找值为3的节点
pos = find_if(col1.begin(), col1.end(),
value_equals<float,float>(3.0));
if(pos != col1.end())
{
cout << pos->first << ":"
<< pos->second << endl;
}
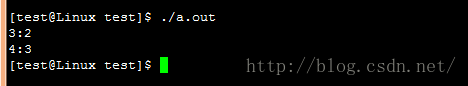
}运行结果:
4、综合实例
关注一下几点
1> 如何使用仿函数(重点)
2> 如何在执行期间定义排序准则(上篇博客中也有相关的例子)
3> “在不关注大小写”的情况下对字符串进行排序
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class RuntimeStringCmp
{
public:
enum cmp_mode {normal, nocase};
private:
const cmp_mode mode;
static bool nocase_compare(char c1, char c2)
{
return toupper(c1) < toupper(c2);
}
public:
RuntimeStringCmp(cmp_mode m = normal) : mode(m)
{
}
bool operator() (const string& s1, const string& s2) const
{
if(mode == normal)
{
return s1 < s2;
}
else
{
return lexicographical_compare(s1.begin(), s1.end(),
s2.begin(), s2.end(),
nocase_compare);
}
}
};
typedef map<string, string, RuntimeStringCmp> StrStrMap;
void FillAndPrint(StrStrMap& col1)
{
col1["Deutschland"] = "Germany";
col1["deutsch"] = "German";
col1["Haken"] = "snag";
col1["arbeiten"] = "work";
col1["hund"] = "dog";
col1["gehen"] = "go";
col1["Jnternehmen"] = "enterprise";
col1["unternehmen"] = "undertake";
col1["gehen"] = "walk";
col1["Bestatter"] = "undertaker";
StrStrMap::iterator pos;
cout.setf(ios::left, ios::adjustfield);
for(pos = col1.begin(); pos != col1.end(); ++pos)
{
cout << setw(15) << pos->first << " "
<< pos->second <<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
StrStrMap col1;
FillAndPrint(col1);
RuntimeStringCmp ignorecase(RuntimeStringCmp::nocase);
StrStrMap col2(ignorecase);
FillAndPrint(col2);
return 0;
}
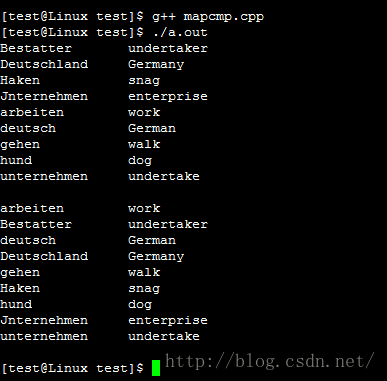
运行结果:
注:博客内容均来自于对《C++标准库》侯捷,华中科技大学出版社一书的笔记。转载请注明出处。
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class RuntimeStringCmp
{
public:
enum cmp_mode {normal, nocase};
private:
const cmp_mode mode;
static bool nocase_compare(char c1, char c2)
{
return toupper(c1) < toupper(c2);
}
public:
RuntimeStringCmp(cmp_mode m = normal) : mode(m)
{
}
bool operator() (const string& s1, const string& s2) const
{
if(mode == normal)
{
return s1 < s2;
}
else
{
return lexicographical_compare(s1.begin(), s1.end(),
s2.begin(), s2.end(),
nocase_compare);
}
}
};
typedef map<string, string, RuntimeStringCmp> StrStrMap;
void FillAndPrint(StrStrMap& col1)
{
col1["Deutschland"] = "Germany";
col1["deutsch"] = "German";
col1["Haken"] = "snag";
col1["arbeiten"] = "work";
col1["hund"] = "dog";
col1["gehen"] = "go";
col1["Jnternehmen"] = "enterprise";
col1["unternehmen"] = "undertake";
col1["gehen"] = "walk";
col1["Bestatter"] = "undertaker";
StrStrMap::iterator pos;
cout.setf(ios::left, ios::adjustfield);
for(pos = col1.begin(); pos != col1.end(); ++pos)
{
cout << setw(15) << pos->first << " "
<< pos->second <<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
StrStrMap col1;
FillAndPrint(col1);
RuntimeStringCmp ignorecase(RuntimeStringCmp::nocase);
StrStrMap col2(ignorecase);
FillAndPrint(col2);
return 0;
}
运行结果: