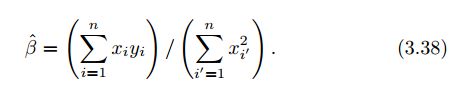ISLR第三章线性回归应用练习题答案(下)
ISLR;R语言; 机器学习 ;线性回归
一些专业词汇只知道英语的,中文可能不标准,请轻喷
12.没有截距的简单线性回归
a)观察3.38式可发现
set.seed(1)
x=rnorm(100)
y=2*x
lm.fit=lm(y~x+0)
lm.fit2=lm(x~y+0)
summary(lm.fit)
输出结果:
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x + 0)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-3.776e-16 -3.378e-17 2.680e-18 6.113e-17 5.105e-16
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
x 2.000e+00 1.296e-17 1.543e+17 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 1.167e-16 on 99 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 1, Adjusted R-squared: 1
F-statistic: 2.382e+34 on 1 and 99 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
线性回归2:
summary(lm.fit2)
输出结果:
Call:
lm(formula = x ~ y + 0)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-1.888e-16 -1.689e-17 1.339e-18 3.057e-17 2.552e-16
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
y 5.00e-01 3.24e-18 1.543e+17 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 5.833e-17 on 99 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 1, Adjusted R-squared: 1
F-statistic: 2.382e+34 on 1 and 99 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
实验发现回归参数不同
c)
sample()函数能够从指定的特定对象集合中随机取样,通过指定某类对象的向量x,然后从中取样size。
例如,从整数1到10中取样,并从中不放回地抽取4个数字使用sample(1:10, 4)
,得到3、4、5、7。如果再做一遍得到的是3、9、8、5。因为选择不放回取样,所以不会得到重复的数字。
> set.seed(1)
> x=rnorm(100)
> y=sample(x,100)
> sum(x^2)
[1] 81.05509
> sum(y^2)
[1] 81.05509
> lm.fit=lm(y~x+0)
> lm.fit2=lm(x~y+0)
> summary(lm.fit)
输出结果:
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x + 0)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.2315 -0.5124 0.1027 0.6877 2.3926
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
x 0.02148 0.10048 0.214 0.831
Residual standard error: 0.9046 on 99 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.0004614, Adjusted R-squared: -0.009635
F-statistic: 0.0457 on 1 and 99 DF, p-value: 0.8312
线性回归2:
Call:
lm(formula = x ~ y + 0)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.2400 -0.5154 0.1213 0.6788 2.3959
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
y 0.02148 0.10048 0.214 0.831
Residual standard error: 0.9046 on 99 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.0004614, Adjusted R-squared: -0.009635
F-statistic: 0.0457 on 1 and 99 DF, p-value: 0.8312
实验发现当x^2之和与y^2之和相等时,线性回归参数相等。
13.
a)
> set.seed(1)
> x=rnorm(100)
b)
> eps=rnorm(100,0,sqrt(0.25))
c)
> y=-1+0.5*x+eps
y向量长度为100;β0=-1;β1=0.5
d)
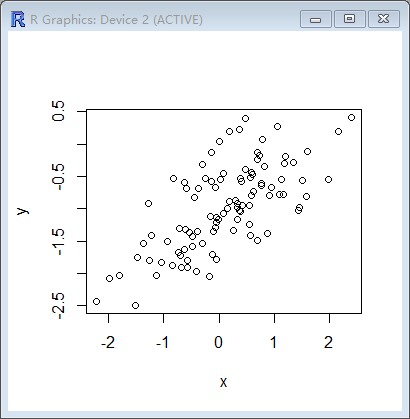
> plot(x,y)
> lm.fit=lm(y~x)
> summary(lm.fit)
输出结果
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-0.93842 -0.30688 -0.06975 0.26970 1.17309
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -1.01885 0.04849 -21.010 < 2e-16 ***
x 0.49947 0.05386 9.273 4.58e-15 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 0.4814 on 98 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.4674, Adjusted R-squared: 0.4619
F-statistic: 85.99 on 1 and 98 DF, p-value: 4.583e-15
β ˆ0=-1.01885,β ˆ1=0.49947与β0=-1;β1=0.5相近,p值接近于零说明具有显著统计关系。
f)
> plot(x,y)
> abline(lm.fit,lwd=3,col="red")
> abline(-1,0.5,lwd=3,col="green")
> legend(-1,legend=c("model fit", "pop regression"),col=2:3,lwd=3)
> lm.fit2=lm(y~x+I(x^2))
> summary(lm.fit2)
输出结果:
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x + I(x^2))
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-0.98252 -0.31270 -0.06441 0.29014 1.13500
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -0.97164 0.05883 -16.517 < 2e-16 ***
x 0.50858 0.05399 9.420 2.4e-15 ***
I(x^2) -0.05946 0.04238 -1.403 0.164
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 0.479 on 97 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.4779, Adjusted R-squared: 0.4672
F-statistic: 44.4 on 2 and 97 DF, p-value: 2.038e-14
R^2和RSE只有微弱的增加,x^2的t值为0.164说明y与x^2无显著统计关系
h)
> set.seed(1)
> esp1=rnorm(100,0,sqrt(0.125))
> y1=-1+0.5*x + esp1
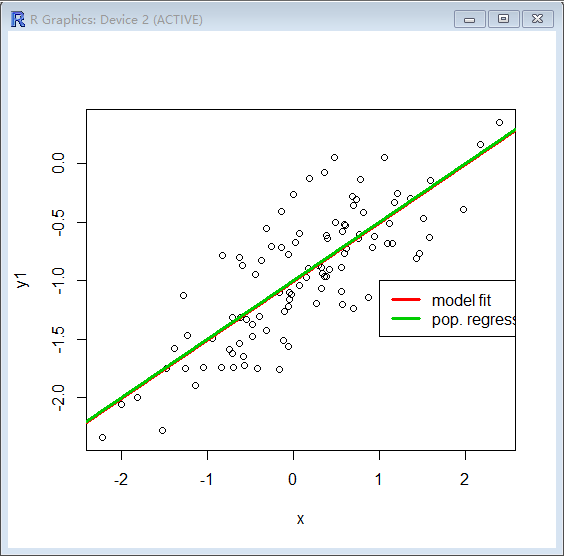
> plot(x,y1)
> lm.fit1=lm(y1~x)
> summary(lm.fit1)
输出结果:
Call:
lm(formula = y1 ~ x)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-0.66356 -0.21700 -0.04932 0.19071 0.82950
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -1.01333 0.03429 -29.55 <2e-16 ***
x 0.49963 0.03809 13.12 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 0.3404 on 98 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.6371, Adjusted R-squared: 0.6334
F-statistic: 172.1 on 1 and 98 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
画图:
> abline(lm.fit1,lwd=3,col=2)
> abline(-1,0.5,lwd=3,col=3)
> legend(-1,legend=c("model fit","pop. regression"),col=2:3,lwd=3)
> esp2=rnorm(100,0,sqrt(0.5))
> y2=-1+0.5*x + esp2
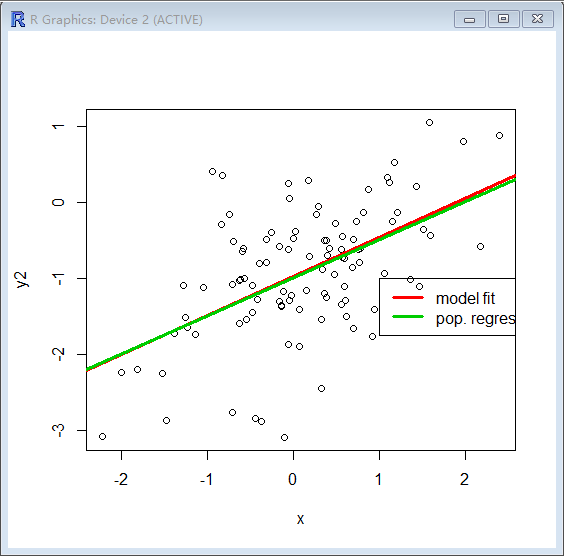
> plot(x,y2)
> lm.fit2=lm(y2~x)
> summary(lm.fit2)
输出结果:
Call:
lm(formula = y2 ~ x)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.06059 -0.34104 -0.03205 0.45908 1.86787
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -0.98065 0.07404 -13.245 < 2e-16 ***
x 0.51497 0.08224 6.262 1.01e-08 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 0.7349 on 98 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.2858, Adjusted R-squared: 0.2785
F-statistic: 39.21 on 1 and 98 DF, p-value: 1.01e-08
画图:
abline(lm.fit2,lwd=3,col=2)
abline(-1,0.5,lwd=3,col=3)
legend(-1,legend=c(“model fit”,”pop. regression”),col=2:3,lwd=3)
> confint(lm.fit)
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) -1.1150804 -0.9226122
x 0.3925794 0.6063602
> confint(lm.fit1)
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) -1.0813741 -0.9452786
x 0.4240422 0.5752080
> confint(lm.fit2)
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) -1.1275711 -0.8337236
x 0.3517741 0.6781604
噪声越大,置信区间相对越大。
14.
a)
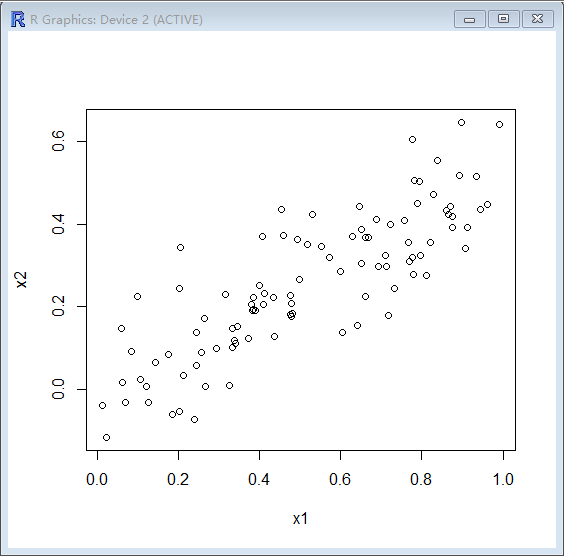
> cor(x1,x2)
[1] 0.8351212
> plot(x1,x2)
> lm.fit=lm(y~x1+x2)
> summary(lm.fit)
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x1 + x2)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.8311 -0.7273 -0.0537 0.6338 2.3359
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 2.1305 0.2319 9.188 7.61e-15 ***
x1 1.4396 0.7212 1.996 0.0487 *
x2 1.0097 1.1337 0.891 0.3754
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 1.056 on 97 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.2088, Adjusted R-squared: 0.1925
F-statistic: 12.8 on 2 and 97 DF, p-value: 1.164e-05
β ˆ0=2.1305;β ˆ1=1.4396;β ˆ2=1.0097
β0=2;β1=2;β2=0.3;
由于t值过大,我们并不能拒绝β2 = 0的假设
d)
> lm.fit1=lm(y~x1)
> summary(lm.fit1)
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x1)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.89495 -0.66874 -0.07785 0.59221 2.45560
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 2.1124 0.2307 9.155 8.27e-15 ***
x1 1.9759 0.3963 4.986 2.66e-06 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 1.055 on 98 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.2024, Adjusted R-squared: 0.1942
F-statistic: 24.86 on 1 and 98 DF, p-value: 2.661e-06
由于p值接近于0可以拒绝H*0 : β*1 = 0假设
e)
> lm.fit2=lm(y~x2)
> summary(lm.fit2)
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x2)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.62687 -0.75156 -0.03598 0.72383 2.44890
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 2.3899 0.1949 12.26 < 2e-16 ***
x2 2.8996 0.6330 4.58 1.37e-05 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 1.072 on 98 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.1763, Adjusted R-squared: 0.1679
F-statistic: 20.98 on 1 and 98 DF, p-value: 1.366e-05
由于p值接近于0可以拒绝H*0 : β*1 = 0假设
f)
因为x1与x2共线的,所以当x1与x2一起做线性回归时很难区分他们的影响,当他们分别做线性回归就很清晰了。
g)
> x1=c(x1,0.1)
> x1=c(x1,0.1)
> x2=c(x2,0.8)
> y=c(y,6)
> lm.fit1 = lm(y~x1+x2)
> summary(lm.fit1)
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x1 + x2)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.73348 -0.69318 -0.05263 0.66385 2.30619
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 2.2267 0.2314 9.624 7.91e-16 ***
x1 0.5394 0.5922 0.911 0.36458
x2 2.5146 0.8977 2.801 0.00614 **
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 1.075 on 98 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.2188, Adjusted R-squared: 0.2029
F-statistic: 13.72 on 2 and 98 DF, p-value: 5.564e-06
> lm.fit2 = lm(y~x1)
> summary(lm.fit2)
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x1)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.8897 -0.6556 -0.0909 0.5682 3.5665
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 2.2569 0.2390 9.445 1.78e-15 ***
x1 1.7657 0.4124 4.282 4.29e-05 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 1.111 on 99 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.1562, Adjusted R-squared: 0.1477
F-statistic: 18.33 on 1 and 99 DF, p-value: 4.295e-05
> lm.fit3 = lm(y~x2)
> summary(lm.fit3)
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x2)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.64729 -0.71021 -0.06899 0.72699 2.38074
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 2.3451 0.1912 12.264 < 2e-16 ***
x2 3.1190 0.6040 5.164 1.25e-06 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 1.074 on 99 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.2122, Adjusted R-squared: 0.2042
F-statistic: 26.66 on 1 and 99 DF, p-value: 1.253e-06
新的数据导致y1中不能拒绝β1=0假设。
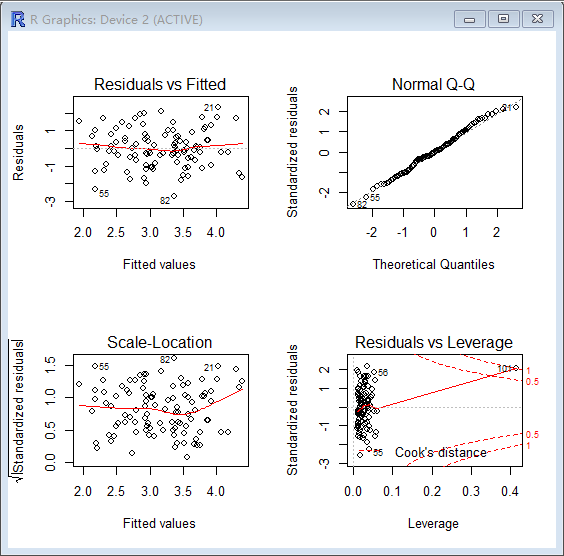
> par(mfrow=c(2,2))
> plot(lm.fit1)
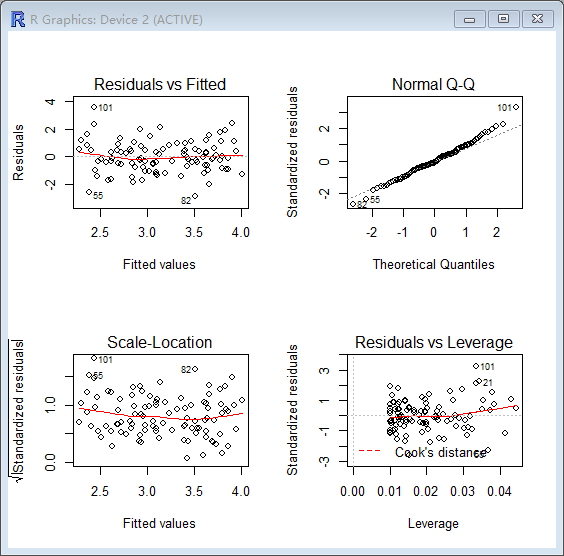
> par(mfrow=c(2,2))
> plot(lm.fit2)
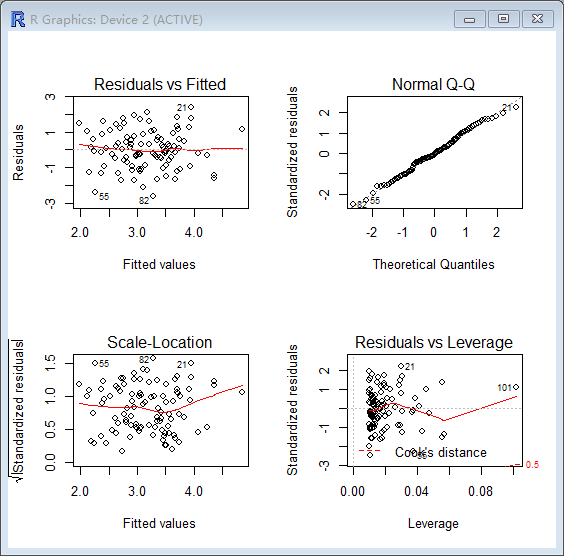
> par(mfrow=c(2,2))
> plot(lm.fit3)
> plot(predict(lm.fit1), rstudent(lm.fit1))
> plot(predict(lm.fit2), rstudent(lm.fit2))
> plot(predict(lm.fit3), rstudent(lm.fit3))