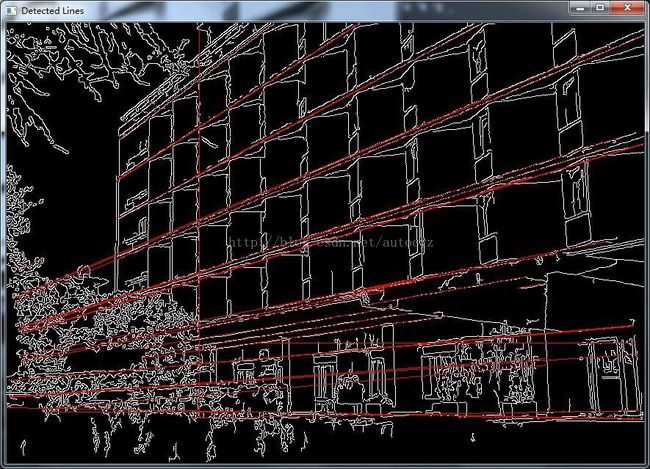
【opencv2】直线hough变换
在opencv2中,直线Hough变换有以下两种形式:
标准霍夫线变换(HoughLines)
原理在这里的博客已经说了。此函数能给我们提供一组参数对(θ,rθ) 的集合来表示检测到的直线
统计概率霍夫线变换(HoughLinesP )
这是执行起来效率更高的霍夫线变换. 它输出检测到的直线的端点(x0,y0,xn,xn)
先看程序,后面会讲一下每个函数的用法:
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
string imageName = "1.jpg";
Mat src, dst, color_dst;
src = imread("1.jpg", 0); //读取图像,以灰度的方式
Canny(src, dst, 50, 200, 3);//使用canny算子进行边缘检测
cvtColor(dst, color_dst, CV_GRAY2BGR);//将单通道的灰度图转化为3通到的图,用于后面用彩色画笔画线
#if 0 //标准Hough变换
vector<Vec2f> lines;
HoughLines( dst, lines, 1, CV_PI/180, 100 );
for( size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++ )
{
float rho = lines[i][0];
float theta = lines[i][1];
double a = cos(theta), b = sin(theta);
double x0 = a*rho, y0 = b*rho;
Point pt1(cvRound(x0 + 1000*(-b)),
cvRound(y0 + 1000*(a)));
Point pt2(cvRound(x0 - 1000*(-b)),
cvRound(y0 - 1000*(a)));
line( color_dst, pt1, pt2, Scalar(0,0,255), 3, 8 );
}
#else //统计概率Hough变换
vector<Vec4i> lines;
HoughLinesP(dst, lines, 1, CV_PI / 180, 200, 30, 10);
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++)
{
line(color_dst, Point(lines[i][0], lines[i][1]),
Point(lines[i][2], lines[i][3]), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, 8);
}
#endif
namedWindow( "Source", 1 );
imshow( "Source", src );
namedWindow( "Detected Lines", 1 );
imshow("Detected Lines", color_dst);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
这是opencv手册中给出的参数解释,有些特殊符号打不出来,可以参见这里:
标准hough变换函数:
void HoughLines(InputArray image, OutputArray lines, double rho, double theta, int threshold, double srn=0, double stn=0 )
· image – 8-bit, single-channel binary source image. The image may be modified by the function.
· lines – Output vector of lines. Each line is represented by a two-element vector(ρ,θ)
ρis the distance from the coordinate origin (topleft corner of the image). θis the line rotation angle in radians (0,pi).
· rho – Distance resolution of the accumulator in pixels.
· theta – Angle resolution of the accumulator in radians.
· threshold – Accumulator threshold parameter. Only those lines are returned that get enough votes .
· srn – For the multi-scale Hough transform, it is a divisor for the distance resolution rho . The coarse accumulator distance resolution is rho and the accurate accumulator resolution is rho/srn . If both srn=0 and stn=0 , the classical Hough transform is used. Otherwise, both these parameters should be positive.
· stn – For the multi-scale Hough transform, it is a divisor for the distance resolution theta.
下面是我的翻译和理解:
dst: 边缘检测的输出图像. 它应该是个灰度图 (但事实上是个二值化图)
lines: 储存着检测到的直线的参数对(ρ,θ)的容器
rho : 参数极径 ρ 以像素值为单位的分辨率. 程序里使用的是 1 像素.
theta: 参数极角 θ 以弧度为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1度 (即CV_PI/180)
threshold: 确认一条直线的累加器的最小累加值。即认为累加器累加的次数超过threshold后,其参数对应的线才为直线。
srn和stn一组额外的参数,用于多尺度hough变换。当这两个参数都为0时才执行标准hough算法。
统计概率hough变换函数:
void HoughLinesP(InputArray image, OutputArray lines, double rho, double theta, int threshold, double minLineLength=0, double maxLineGap=0 )
前面的几个参数都与标准hough含义一致,只有最后两个不一样。
这里是opencv手册给出的解释:
minLineLength – Minimum line length. Line segments shorter than that are rejected.
maxLineGap – Maximum allowed gap between points on the same line to link them.
下面是我的翻译和理解:
minLinLength:直线的最小长度。即当检测出的直线长度大于minLinLength,才认为这是一条直线。
maxLineGap: 能够允许一条直线所存在缺口(中断)点数的最大值。即假若直线从中间某处断开,那么所允许的缺口的最大长度。
下面给出原图:
具体效果要看参数的选择。