基础数据结构之数组与链表(一)
本系列文章将主要介绍两种“基础数据结构”——数组和链表,及其变种。(参考教材:Foundational Data Structures)
数组与链表是两种最基本的数据结构。 在《数据结构与算法》的学习中,我们将遇到多种"Abstract Data Types (ADTs)",包括:stacks, queues, deques, ordered lists, sorted lists, hash and scatter tables, trees, priority queues, sets and graphs等。对于这些ADTs中的任意一个,我们都可以选择使用数组或链表来实现。因此,深入理解数组和链表是学好其他数据结构的基础。
首先,我们来学习一下数组。数组可能是最常用的一种聚集数据的方式,C++语言也提供了对数组内置(built-in)支持,但这种支持也不是没有缺陷,具体如下:
1,没有“数组值”表达式,因此数组不能直接作为函数参数和返回值,也不能直接进行数组间的赋值(需要使用指针转换);
2,数组不自动进行下标越界检查;
3,数组的大小必须在编译期确定,不能延迟到运行时确定;
4,采用指针形式,不能确定数组的size,不能直接区分指针指向的是数组还是一个普通值;
下面我们指针C++普通数组的缺点,我们设计一个自定义的“Dynamic Array”。
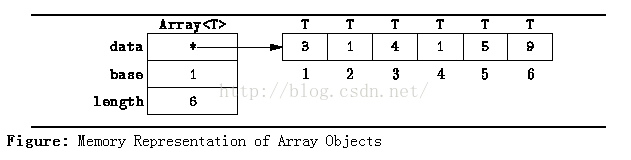
如上图所示,这个“Dynamic Array”设计了两个结构,左边的结构包含了三个field,右边的结构是一个普通数组。具体设计见如下代码:
#ifndef DYNAMIC_ARRAY_H
#define DYNAMIC_ARRAY_H
#include <stdexcept> //std::out_of_range
// Two structures are used. The first is a structure which comprises three fields--data, base and length.
// The member variable data is a pointer to the array data. Variables base and length are used in the array subscript calculation.
// The second structure comprises contiguous memory locations which hold the array elements.
namespace FoundationalDataStructure
{
template <typename T>
class Array
{
public:
Array();
Array(unsigned int, unsigned int = 0);
~Array();
Array(const Array &);
Array & operator=(const Array &);
T const& operator[](unsigned int) const; // called by const Array Object
T & operator[](unsigned int);
T const* Data() const;
unsigned int Base() const;
unsigned int Length() const;
void SetBase(unsigned int);
void SetLength(unsigned int);
protected:
T * data;
unsigned int base;
unsigned int length;
};
template <typename T>
Array<T>::Array()
: data(new T[0]{})
, base(0)
, length(0)
{}
template <typename T>
Array<T>::Array(unsigned int n, unsigned int m)
: data(new T[n]{})
, base(m)
, length(n)
{}
template <typename T>
Array<T>::~Array()
{
delete[] data;
}
template <typename T>
Array<T>::Array(const Array & array)
: data(new T[array.Length()]{})
, base(array.Base())
, length(array.Length())
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < length; ++i)
data[i] = array[i];
}
template <typename T>
Array<T> & Array<T>::operator=(const Array & array)
{
data = new T[array.Length()]{};
base = array.Base();
length = array.Length();
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < length; ++i)
data[i] = array.Data()[i];
return *this;
}
template <typename T>
T const * Array<T>::Data() const
{
return data;
}
template <typename T>
unsigned int Array<T>::Base() const
{
return base;
}
template <typename T>
unsigned int Array<T>::Length() const
{
return length;
}
template <typename T>
T const & Array<T>::operator[](unsigned int position) const
{
unsigned int const offset = position - base;
if (offset >= length)
throw std::out_of_range("invalid position");
return data[offset];
}
template <typename T>
T & Array<T>::operator[](unsigned int position)
{
unsigned int const offset = position - base;
if (offset >= length)
throw std::out_of_range("invalid position");
return data[offset];
}
template <typename T>
void Array<T>::SetBase(unsigned int newBase)
{
base = newBase;
}
template <typename T>
void Array<T>::SetLength(unsigned int newLength)
{
if (length == newLength)
return;
T * const newData = new T[newLength]{};
unsigned int const min =
length < newLength ? length : newLength;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < min; ++i)
newData[i] = data[i];
delete[] data;
data = newData;
length = newLength;
}
} // namespace FoundationalDataStructure
#endif // DYNAMIC_ARRAY_H
PS:原书代码有少许错误,以上代码我进行了调优。经验如下:
1,关于std::out_of_range,它是标准库中的一个类,继承关系:exception <-- logic_error <-- out_of_range,参考std::out_of_range。
2,添加了一个namespace FoundationalDataStructure,防止与标准库冲突。本意是想将模版类的声明和函数实现分离到.h和.cpp文件,才添加namespace,但未成功。
3,对new出来的数组,及时初始化(添加花括符)。
4,模版类代码要全面测试,函数的实现在用到的时候才会报错。
5,可以用智能指针管理heap空间。