c# 多线程入门demo
在上一篇博客《java—简单理解线程》中,就简单介绍在java中的多线程应用,以及通过demo来区别不用多线程和使用多线程的时间区别,通过上篇博客中的两张对比图显然能看出他们之间的区别,但是具体的方法运行时间少了多少呢?这篇博客中我们将引入,并分别用thread和task两种方式来实现多线程。
一 线程Thread的使用
(1)不通过委托,直接在线程里实现方法体
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool a =false;
bool b = false;
bool c = false;
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();//测量运行时间
watch.Start();//开始计时
//线程1
Thread threadTest1 = new Thread(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("线程1结束消耗时间:{0}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
a = true;//如果执行则返回true
});
//线程2
Thread threadTest2 = new Thread(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("线程2结束消耗时间:{0}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
b = true;//如果执行则返回true
});
//线程3
Thread threadTest3 = new Thread(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("线程3结束消耗时间:{0}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
c = true;//如果执行则返回true
});
threadTest1.Start();
threadTest2.Start();
threadTest3.Start();
threadTest2.Join();//等待其它线程执行结束
threadTest1.Join();
threadTest3.Join();
if (a == true && b == true && c == true)//当三个子线程全部执行完毕,则执行
{
Console.WriteLine("监控结束消耗时间:{0}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
Console.Read();
}
}
}
} 执行结果:
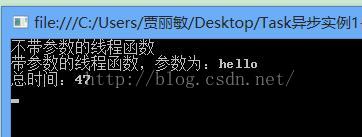
(2)通过委托传递,可以带参,也可以不带参
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();//测量运行时间
watch.Start();//开始计时
//通过委托传递,将testMethod方法委托给线程执行
Thread t1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(TestMethod));
Thread t2 = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(TestMethod));
t1.Start();
t2.Start("hello");
t1.Join();
t2.Join();
Console.WriteLine("总时间:{0}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
Console.Read();
}
public static void TestMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("不带参数的线程函数");
}
public static void TestMethod(object data)
{
string datastr = data as string;
Console.WriteLine("带参数的线程函数,参数为:{0}", datastr);
}
}
}<strong>
</strong> 执行结果:
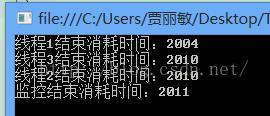
二:使用task类实现多线程
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool a =false;
bool b = false;
bool c = false;
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();//测量运行时间
watch.Start();//开始计时
var Task1 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("线程1结束消耗时间:{0}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
a = true;
});
var Task2 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("线程2结束消耗时间:{0}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
b = true;
});
var Task3 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(2000);
Console.WriteLine("线程3结束消耗时间:{0}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
c = true;
});
Task.WaitAll(Task1, Task2, Task3);
if (a == true && b == true && c == true)
{
Console.WriteLine("监控结束消耗时间:{0}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds);
Console.Read();
}
else
{
//Thread.Sleep(1);
Console.Read();
}
}
}
} 执行结果:
这三个demo只是对于刚刚接触多线程的一个实践,简单易理解。