Android学习之常见的布局方式
第一种:线性布局
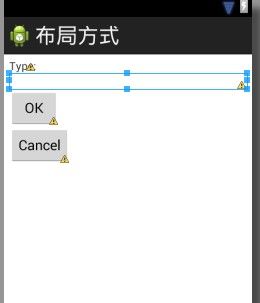
这种布局相对是比较简单的,要么竖向排列,要么横向排列
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="10px">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Type:"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_entry"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ffffff"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/ok"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/et_entry"
android:text="OK"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/cancel"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Cancel"/>
</LinearLayout>效果如下:
第二种:相对布局
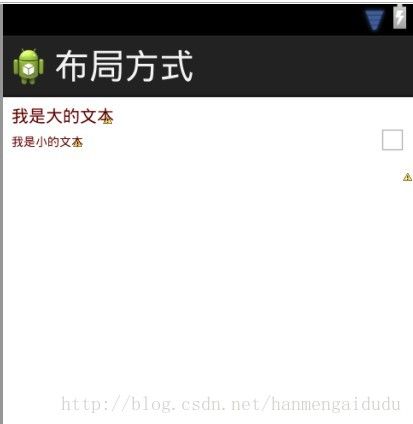
相对布局:即相对于一个参照物的位置,那么必须先有参照物,才能确定接下来的控件的位置,例如先有A,然后B相对于A,在A的右边、下边或者什么位置。当然android中也可以相对于父窗体。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100px"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10px" /*距离父窗体的左边10个像素*/
android:layout_marginTop="10px" /*距离父窗体的顶部10个像素*/
android:textColor="#660000" /*控件上显示文本的颜色RGB*/
android:textSize="20px" /*控件上显示文本的字体大小*/
android:text="我是大的文本" />
<TextView
android:layout_below="@id/tv_title" /*当前控件位于tv_title这个控件的下方*/
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10px"
android:layout_marginTop="10px"
android:textColor="#660000"
android:textSize="14px"
android:text="我是小的文本" />
<CheckBox
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true" /*当前控件与父窗体的右边对齐*/
android:layout_centerVertical="true" /*当前控件在父窗体的竖直中心位置*/
/>
</RelativeLayout>
这个布局如下图所示:
第三种:表格布局
表格布局:比如几行几列的格式,例如excel的样子
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#000000"
android:stretchColumns="1" >
<TableRow >
<TextView
android:text="姓名"
android:padding="10dip"
android:textColor="#ffffff"/>
<EditText
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:background="#ffffff"
/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow >
<TextView
android:text="密码"
android:padding="10dip"
android:textColor="#ffffff"/>
<EditText
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:background="#ffffff"
android:password="true"
/>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>效果如下:
第四种:帧布局
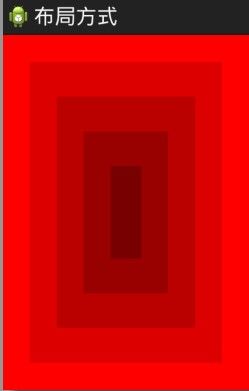
帧布局:其实比较简单的理解就是,一个图片叠加到一个图片的上面,就是图片的叠加
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#ff0000" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="250dp"
android:layout_height="390dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#dd0000" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="180dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#bb0000" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="110dp"
android:layout_height="210dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#990000" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="40dp"
android:layout_height="120dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#770000" />
</FrameLayout>效果如下:
好了,击中常见的布局方式就介绍完了,这些也是自己在看代码的过程中摸索出来的,希望对自己,对别人会有所帮助