DexClassLoader4.4.2动态加载分析(磁盘加载分析)
转自:http://bbs.pediy.com/showthread.php?t=199230
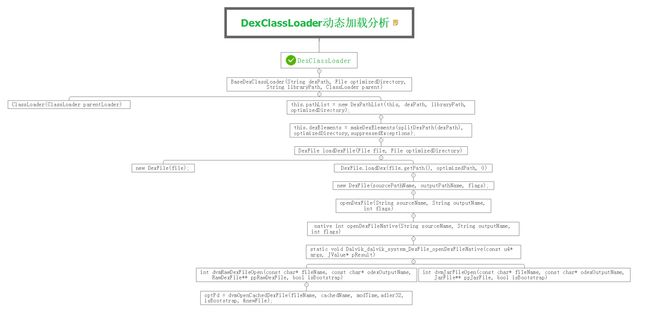
研究Android源码的过程是一个艰辛的过程,但又是一个历练的过程,今天就来跟大家一起分享一下Android4.4.2版本中的DexClassLoader的实现源码!
下面就是DexClassLoader这个动态加载器的java源码,地址是:
http://androidxref.com/4.4.2_r1/xref/libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system/DexClassLoader.java
我们开始正式分析源代码:
看到下面的代码,我们一定注意到了非常多的注释,这里想告诉大家的是当你看源码时,特别不要忘记看这每一个注释,
因为这是最原生态的,最能够解释清楚你为什么要用,怎么用这些功能的关键点,好了,废话说多了,回到正题吧!
package dalvik.system;
import java.io.File;
下面这段注释说明了3点:
1.这个类加载器加载的文件是.jar或者.apk文件,并且这个.jar或.apk中是包含classes.dex这个入口文件的,
主要是用来执行那些没有被安装的一些可执行文件的;
2.这个类加载器需要一个属于应用的私有的,可以的目录作为它自己的缓存优化目录,其实这个目录也就作为下面
这个构造函数的第二个参数,至于怎么实现,注释中也已经给出了答案;
3.不要把上面第二点中提到的这个缓存目录设为外部存储,因为外部存储容易收到代码注入的攻击
/**
* A class loader that loads classes from {@code .jar} and {@code .apk} files
* containing a {@code classes.dex} entry. This can be used to execute code not
* installed as part of an application.
*
* <p>This class loader requires an application-private, writable directory to
* cache optimized classes. Use {@code Context.getDir(String, int)} to create
* such a directory: <pre> {@code
* File dexOutputDir = context.getDir("dex", 0);
* }</pre>
*
* <p><strong>Do not cache optimized classes on external storage.</strong>
* External storage does not provide access controls necessary to protect your
* application from code injection attacks.
*/
public class DexClassLoader extends BaseDexClassLoader {
下面这段注释详细地说明了这个构造函数中各个参数地意义,不作阐述了,希望大家能够认真阅读,思考;
/**
* Creates a {@code DexClassLoader} that finds interpreted and native
* code. Interpreted classes are found in a set of DEX files contained
* in Jar or APK files.
*
* <p>The path lists are separated using the character specified by the
* {@code path.separator} system property, which defaults to {@code :}.
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param optimizedDirectory directory where optimized dex files
* should be written; must not be {@code null}
* @param libraryPath the list of directories containing native
* libraries, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}; may be
* {@code null}
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public DexClassLoader(String dexPath, String optimizedDirectory,
String libraryPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, new File(optimizedDirectory), libraryPath, parent);
}
}
好了,让我们进入最有含金量地部分吧,当你想要一个可执行文件地时候,你就会调用这个类加载器对象来帮你完成任务,
首先你就会通过java中最常用地创建对象地方式来new这个DexClassLoader吧,那么这时候就会先去执行父类BaseDexClassLoader的构造函数:
super(dexPath, new File(optimizedDirectory), libraryPath, parent);
父类BaseDexClassLoader的构造函数如下:
/**
* Constructs an instance.
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param optimizedDirectory directory where optimized dex files
* should be written; may be {@code null}
* @param libraryPath the list of directories containing native
* libraries, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}; may be
* {@code null}
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public BaseDexClassLoader(String dexPath, File optimizedDirectory,
String libraryPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(parent);
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexPath, libraryPath, optimizedDirectory);
}
然后当执行这个构造函数地时候又会先去执行BaseDexClassLoader地父类ClassLoader的构造函数,
父类ClassLoader的构造函数如下:
/**
* Constructs a new instance of this class with the specified class loader
* as its parent.
*
* @param parentLoader
* The {@code ClassLoader} to use as the new class loader's
* parent.
*/
protected ClassLoader(ClassLoader parentLoader) {
this(parentLoader, false);
}
/*
* constructor for the BootClassLoader which needs parent to be null.
*/
ClassLoader(ClassLoader parentLoader, boolean nullAllowed) {
if (parentLoader == null && !nullAllowed) {
throw new NullPointerException("parentLoader == null && !nullAllowed");
}
parent = parentLoader;
}
最终把传进来的一个父类加载器对象parentLoader赋给了partent对象,partent对象是ClassLoader类中的一个私有变量,后续就会有用,暂时可以不用想那么多
现在返回到上一个BaseDexClassLoader类中的构造函数继续执行下一条语句,
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexPath, libraryPath, optimizedDirectory);
pathList是这个类的私有成员,类型为:DexPathList, 然后new了一新的DexPathList的对象,看下面代码:
/**
* Constructs an instance.
*
* @param definingContext the context in which any as-yet unresolved
* classes should be defined
* @param dexPath list of dex/resource path elements, separated by
* {@code File.pathSeparator}
* @param libraryPath list of native library directory path elements,
* separated by {@code File.pathSeparator}
* @param optimizedDirectory directory where optimized {@code .dex} files
* should be found and written to, or {@code null} to use the default
* system directory for same
*/
public DexPathList(ClassLoader definingContext, String dexPath,
String libraryPath, File optimizedDirectory) {
if (definingContext == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("definingContext == null");
}
if (dexPath == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("dexPath == null");
}
if (optimizedDirectory != null) {
if (!optimizedDirectory.exists()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"optimizedDirectory doesn't exist: "
+ optimizedDirectory);
}
if (!(optimizedDirectory.canRead()
&& optimizedDirectory.canWrite())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"optimizedDirectory not readable/writable: "
+ optimizedDirectory);
}
}
this.definingContext = definingContext;
ArrayList<IOException> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<IOException>();
this.dexElements = makeDexElements(splitDexPath(dexPath), optimizedDirectory,
suppressedExceptions);
if (suppressedExceptions.size() > 0) {
this.dexElementsSuppressedExceptions =
suppressedExceptions.toArray(new IOException[suppressedExceptions.size()]);
} else {
dexElementsSuppressedExceptions = null;
}
this.nativeLibraryDirectories = splitLibraryPath(libraryPath);
}
上面的代码中做了一系列的检测与判断,然后来分析这一句代码:
this.dexElements = makeDexElements(splitDexPath(dexPath), optimizedDirectory,suppressedExceptions);
dexElements对象的类型为:Element[ ],Element是一个接口类,我们再来看makeDexElements这个函数,代码如下:
/**
* Makes an array of dex/resource path elements, one per element of
* the given array.
*/
private static Element[] makeDexElements(ArrayList<File> files, File optimizedDirectory,
ArrayList<IOException> suppressedExceptions) {
ArrayList<Element> elements = new ArrayList<Element>();
/*
* Open all files and load the (direct or contained) dex files
* up front.
*/
for (File file : files) {
File zip = null;
DexFile dex = null;
String name = file.getName();
这里开始判断文件名的后缀,是dex还是apk,jar,zip
if (name.endsWith(DEX_SUFFIX)) {
如果文件是一个单独的dex文件,而不是附属于一个压缩文件中,那么就执行if中的功能
// Raw dex file (not inside a zip/jar).
try {
dex = loadDexFile(file, optimizedDirectory);
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.logE("Unable to load dex file: " + file, ex);
}
}
如果文件是以apk或者jar或者zip为后缀,就执行else if中的功能
else if (name.endsWith(APK_SUFFIX) || name.endsWith(JAR_SUFFIX)
|| name.endsWith(ZIP_SUFFIX)) {
zip = file;
try {
dex = loadDexFile(file, optimizedDirectory);
} catch (IOException suppressed) {
/*
* IOException might get thrown "legitimately" by the DexFile constructor if the
* zip file turns out to be resource-only (that is, no classes.dex file in it).
* Let dex == null and hang on to the exception to add to the tea-leaves for
* when findClass returns null.
*/
suppressedExceptions.add(suppressed);
}
} else if (file.isDirectory()) {
// We support directories for looking up resources.
// This is only useful for running libcore tests.
elements.add(new Element(file, true, null, null));
} else {
System.logW("Unknown file type for: " + file);
}
if ((zip != null) || (dex != null)) {
elements.add(new Element(file, false, zip, dex));
}
}
return elements.toArray(new Element[elements.size()]);
}
通过上面的这个函数的功能描述,可以知道要么加载的是一个dex文件,要么是一个压缩格式的文件,最终都要执行loadDexFile这个函数,
下面是loadDexFile的源码:
/**
* Constructs a {@code DexFile} instance, as appropriate depending
* on whether {@code optimizedDirectory} is {@code null}.
*/
private static DexFile loadDexFile(File file, File optimizedDirectory)
throws IOException {
if (optimizedDirectory == null) {
return new DexFile(file);
} else {
String optimizedPath = optimizedPathFor(file, optimizedDirectory);
return DexFile.loadDex(file.getPath(), optimizedPath, 0);
}
}
显然这里是以optimizedDirectory是否为空来分两条路径执行加载Dex的功能,这里假设optimizedDirectory是不为空的,所以执行else分支
中的内容,所以我们接下来看loadDex的内容:
/**
* Open a DEX file, specifying the file in which the optimized DEX
* data should be written. If the optimized form exists and appears
* to be current, it will be used; if not, the VM will attempt to
* regenerate it.
*
* This is intended for use by applications that wish to download
* and execute DEX files outside the usual application installation
* mechanism. This function should not be called directly by an
* application; instead, use a class loader such as
* dalvik.system.DexClassLoader.
*
* @param sourcePathName
* Jar or APK file with "classes.dex". (May expand this to include
* "raw DEX" in the future.)
* @param outputPathName
* File that will hold the optimized form of the DEX data.
* @param flags
* Enable optional features. (Currently none defined.)
* @return
* A new or previously-opened DexFile.
* @throws IOException
* If unable to open the source or output file.
*/
static public DexFile loadDex(String sourcePathName, String outputPathName,
int flags) throws IOException {
/*
* TODO: we may want to cache previously-opened DexFile objects.
* The cache would be synchronized with close(). This would help
* us avoid mapping the same DEX more than once when an app
* decided to open it multiple times. In practice this may not
* be a real issue.
*/
return new DexFile(sourcePathName, outputPathName, flags);
}
这里直接返回一个DexFile的对象,下面来看这个类的构造函数DexFile(sourcePathName, outputPathName, flags)
代码如下:
/**
* Opens a DEX file from a given filename, using a specified file
* to hold the optimized data.
*
* @param sourceName
* Jar or APK file with "classes.dex".
* @param outputName
* File that will hold the optimized form of the DEX data.
* @param flags
* Enable optional features.
*/
private DexFile(String sourceName, String outputName, int flags) throws IOException {
if (outputName != null) {
try {
String parent = new File(outputName).getParent();
if (Libcore.os.getuid() != Libcore.os.stat(parent).st_uid) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Optimized data directory " + parent
+ " is not owned by the current user. Shared storage cannot protect"
+ " your application from code injection attacks.");
}
} catch (ErrnoException ignored) {
// assume we'll fail with a more contextual error later
}
}
mCookie = openDexFile(sourceName, outputName, flags);
mFileName = sourceName;
guard.open("close");
//System.out.println("DEX FILE cookie is " + mCookie);
}
这里主要集中于对openDexFile这个函数的分析上,注意返回值保存在了mCookie中,是一个整形的值,文件名称保存在了mFileName中,
openDexFile的源代码如下:
/*
* Open a DEX file. The value returned is a magic VM cookie. On
* failure, an IOException is thrown.
*/
private static int openDexFile(String sourceName, String outputName,
int flags) throws IOException {
return openDexFileNative(new File(sourceName).getCanonicalPath(),
(outputName == null) ? null : new File(outputName).getCanonicalPath(),
flags);
}
native private static int openDexFileNative(String sourceName, String outputName,
int flags) throws IOException;
显然这里会调用一个Native函数openDexFileNative来做dex地加载,接下来,我们将会重点分析Native层地函数地实现,
openDexFileNative的源码如下:(路径为:http://androidxref.com/4.4.2_r1/xref/dalvik/vm/native/dalvik_system_DexFile.cpp)
* private static int openDexFileNative(String sourceName, String outputName,
* int flags) throws IOException
*
* Open a DEX file, returning a pointer to our internal data structure.
*
* "sourceName" should point to the "source" jar or DEX file.
*
* If "outputName" is NULL, the DEX code will automatically find the
* "optimized" version in the cache directory, creating it if necessary.
* If it's non-NULL, the specified file will be used instead.
*
* TODO: at present we will happily open the same file more than once.
* To optimize this away we could search for existing entries in the hash
* table and refCount them. Requires atomic ops or adding "synchronized"
* to the non-native code that calls here.
*
* TODO: should be using "long" for a pointer.
*/
这个函数中有两个参数,args参数是u4类型的,也就是无符号的整形,而pResult是JValue类型,它是一个Union结构体类型,读者可自行查看
static void Dalvik_dalvik_system_DexFile_openDexFileNative(const u4* args,
JValue* pResult)
{
args[0]和args[1]就是java层传过来的两个参数,sourceName和outputName,这里转化成了StringObject对象,
StringObject* sourceNameObj = (StringObject*) args[0];
StringObject* outputNameObj = (StringObject*) args[1];
DexOrJar,JarFile,RawDexFile这几个数据结构读者可以自行查看,这里不作过多解释
DexOrJar* pDexOrJar = NULL;
JarFile* pJarFile;
RawDexFile* pRawDexFile;
char* sourceName;
char* outputName;
if (sourceNameObj == NULL) {
dvmThrowNullPointerException("sourceName == null");
RETURN_VOID();
}
sourceName = dvmCreateCstrFromString(sourceNameObj);
if (outputNameObj != NULL)
outputName = dvmCreateCstrFromString(outputNameObj);
else
outputName = NULL;
/*
* We have to deal with the possibility that somebody might try to
* open one of our bootstrap class DEX files. The set of dependencies
* will be different, and hence the results of optimization might be
* different, which means we'd actually need to have two versions of
* the optimized DEX: one that only knows about part of the boot class
* path, and one that knows about everything in it. The latter might
* optimize field/method accesses based on a class that appeared later
* in the class path.
*
* We can't let the user-defined class loader open it and start using
* the classes, since the optimized form of the code skips some of
* the method and field resolution that we would ordinarily do, and
* we'd have the wrong semantics.
*
* We have to reject attempts to manually open a DEX file from the boot
* class path. The easiest way to do this is by filename, which works
* out because variations in name (e.g. "/system/framework/./ext.jar")
* result in us hitting a different dalvik-cache entry. It's also fine
* if the caller specifies their own output file.
*/
dvmClassPathcontains这个函数是判断要加载的Dex文件是否是系统中的某个Dex
这里的gDvm是DvmGlobals的一个全局对象,虚拟机的很多状态属性等都会存储在这个数据结构中,读者可自行查看这个数据结构
if (dvmClassPathContains(gDvm.bootClassPath, sourceName)) {
ALOGW("Refusing to reopen boot DEX '%s'", sourceName);
dvmThrowIOException(
"Re-opening BOOTCLASSPATH DEX files is not allowed");
free(sourceName);
free(outputName);
RETURN_VOID();
}
/*
* Try to open it directly as a DEX if the name ends with ".dex".
* If that fails (or isn't tried in the first place), try it as a
* Zip with a "classes.dex" inside.
*/
hasDexExtension函数用来判断这个文件的后缀是否是dex或者其他压缩格式,如果是dex并且dvmRawDexFileOpen函数的返回值是0,那么就执行if分支中的代码
if (hasDexExtension(sourceName)
&& dvmRawDexFileOpen(sourceName, outputName, &pRawDexFile, false) == 0) {
ALOGV("Opening DEX file '%s' (DEX)", sourceName);
pDexOrJar = (DexOrJar*) malloc(sizeof(DexOrJar));
pDexOrJar->isDex = true;
pDexOrJar->pRawDexFile = pRawDexFile;
pDexOrJar->pDexMemory = NULL;
}
如果if中的任何一个条件不满足或都不满足,再来判断else if中的条件,如果dvmJarFileOpen返回0,则执行else if中的代码
else if (dvmJarFileOpen(sourceName, outputName, &pJarFile, false) == 0) {
ALOGV("Opening DEX file '%s' (Jar)", sourceName);
pDexOrJar = (DexOrJar*) malloc(sizeof(DexOrJar));
pDexOrJar->isDex = false;
pDexOrJar->pJarFile = pJarFile;
pDexOrJar->pDexMemory = NULL;
}
否则就抛出异常
else {
ALOGV("Unable to open DEX file '%s'", sourceName);
dvmThrowIOException("unable to open DEX file");
}
if (pDexOrJar != NULL) {
pDexOrJar->fileName = sourceName;
把pDexOrJar这个结构体中的内容加到gDvm中的userDexFile结构的hash表中,以便dalvik以后的查找
addToDexFileTable(pDexOrJar);
} else {
free(sourceName);
}
free(outputName);
RETURN_PTR(pDexOrJar);
}
那么上述代码中其实主要分两种情况来分析,主要是取决去sourceName这个的格式,是dex还是jar,好了,着重来分析dvmRawDexFileOpen和dvmJarFileOpen这两个函数,
先来看dvmRawDexFileOpen的代码(这种情况是针对dex文件的)
/* See documentation comment in header. */
int dvmRawDexFileOpen(const char* fileName, const char* odexOutputName,
RawDexFile** ppRawDexFile, bool isBootstrap)
{
/*
* TODO: This duplicates a lot of code from dvmJarFileOpen() in
* JarFile.c. This should be refactored.
*/
DvmDex* pDvmDex = NULL;
char* cachedName = NULL;
int result = -1;
int dexFd = -1;
int optFd = -1;
u4 modTime = 0;
u4 adler32 = 0;
size_t fileSize = 0;
bool newFile = false;
bool locked = false;
打开dex文件,返回一个文件描述符dexFd
dexFd = open(fileName, O_RDONLY);
if (dexFd < 0) goto bail;
/* If we fork/exec into dexopt, don't let it inherit the open fd. */
dvmSetCloseOnExec(dexFd);
判断dex文件的前8个字节的值是否正确,并把第八个字节往后的四个字节的值赋给了adler
if (verifyMagicAndGetAdler32(dexFd, &adler32) < 0) {
ALOGE("Error with header for %s", fileName);
goto bail;
}
得到dex文件的修改时间和大小,分别保存在变量modTime和filesize中
if (getModTimeAndSize(dexFd, &modTime, &fileSize) < 0) {
ALOGE("Error with stat for %s", fileName);
goto bail;
}
/*
* See if the cached file matches. If so, optFd will become a reference
* to the cached file and will have been seeked to just past the "opt"
* header.
*/
odexOutputName代表优化dex后的输出目录,如果为空,则系统生成一个符合规范的目录,如果不为空,就用odexOutputName作为目录
if (odexOutputName == NULL) {
cachedName = dexOptGenerateCacheFileName(fileName, NULL);
if (cachedName == NULL)
goto bail;
} else {
cachedName = strdup(odexOutputName);
}
ALOGV("dvmRawDexFileOpen: Checking cache for %s (%s)",
fileName, cachedName);
dvmOpenCachedDexFile这个函数主要用来验证缓存目录到正确性,然后将DexOptHeader的结构写入了fd文件中
optFd = dvmOpenCachedDexFile(fileName, cachedName, modTime,
adler32, isBootstrap, &newFile, /*createIfMissing=*/true);
if (optFd < 0) {
ALOGI("Unable to open or create cache for %s (%s)",
fileName, cachedName);
goto bail;
}
locked = true;
/*
* If optFd points to a new file (because there was no cached
* version, or the cached version was stale), generate the
* optimized DEX. The file descriptor returned is still locked,
* and is positioned just past the optimization header.
*/
newFile这里的值为true
if (newFile) {
u8 startWhen, copyWhen, endWhen;
bool result;
off_t dexOffset;
dexOffest为文件的当前写入位置
dexOffset = lseek(optFd, 0, SEEK_CUR);
result = (dexOffset > 0);
if (result) {
startWhen = dvmGetRelativeTimeUsec();
将dex文件中的内容写入文件的当前位置,也就是从dexOffset的偏移处开始写
result = copyFileToFile(optFd, dexFd, fileSize) == 0;
copyWhen = dvmGetRelativeTimeUsec();
}
这里result的值为true
if (result) {
对dex文件进行优化
result = dvmOptimizeDexFile(optFd, dexOffset, fileSize,
fileName, modTime, adler32, isBootstrap);
}
这里result为true
if (!result) {
ALOGE("Unable to extract+optimize DEX from '%s'", fileName);
goto bail;
}
endWhen = dvmGetRelativeTimeUsec();
ALOGD("DEX prep '%s': copy in %dms, rewrite %dms",
fileName,
(int) (copyWhen - startWhen) / 1000,
(int) (endWhen - copyWhen) / 1000);
}
/*
* Map the cached version. This immediately rewinds the fd, so it
* doesn't have to be seeked anywhere in particular.
*/
dvmDexFileOpenFromFd这个函数最主要在这里干了两件事情
1.将优化后得dex文件(也就是odex文件)通过mmap映射到内存中,并通过mprotect修改它的映射内存为只读权限
2.将映射为只读的这块dex数据中的内容全部提取到DexFile这个数据结构中去
if (dvmDexFileOpenFromFd(optFd, &pDvmDex) != 0) {
ALOGI("Unable to map cached %s", fileName);
goto bail;
}
if (locked) {
/* unlock the fd */
if (!dvmUnlockCachedDexFile(optFd)) {
/* uh oh -- this process needs to exit or we'll wedge the system */
ALOGE("Unable to unlock DEX file");
goto bail;
}
locked = false;
}
ALOGV("Successfully opened '%s'", fileName);
*ppRawDexFile = (RawDexFile*) calloc(1, sizeof(RawDexFile));
(*ppRawDexFile)->cacheFileName = cachedName;
(*ppRawDexFile)->pDvmDex = pDvmDex;
cachedName = NULL; // don't free it below
result = 0;
bail:
free(cachedName);
if (dexFd >= 0) {
close(dexFd);
}
if (optFd >= 0) {
if (locked)
(void) dvmUnlockCachedDexFile(optFd);
close(optFd);
}
return result;
}
再来看dvmJarFileOpen的代码(这是针对压缩文件的情况,其实是跟上面的情况类似的,读者可自行查看)
/*
* Open a Jar file. It's okay if it's just a Zip archive without all of
* the Jar trimmings, but we do insist on finding "classes.dex" inside
* or an appropriately-named ".odex" file alongside.
*
* If "isBootstrap" is not set, the optimizer/verifier regards this DEX as
* being part of a different class loader.
*/
int dvmJarFileOpen(const char* fileName, const char* odexOutputName,
JarFile** ppJarFile, bool isBootstrap)
{
/*
* TODO: This function has been duplicated and modified to become
* dvmRawDexFileOpen() in RawDexFile.c. This should be refactored.
*/
ZipArchive archive;
DvmDex* pDvmDex = NULL;
char* cachedName = NULL;
bool archiveOpen = false;
bool locked = false;
int fd = -1;
int result = -1;
/* Even if we're not going to look at the archive, we need to
* open it so we can stuff it into ppJarFile.
*/
验证并解析压缩文件的数据结构
if (dexZipOpenArchive(fileName, &archive) != 0)
goto bail;
archiveOpen = true;
/* If we fork/exec into dexopt, don't let it inherit the archive's fd.
*/
dvmSetCloseOnExec(dexZipGetArchiveFd(&archive));
/* First, look for a ".odex" alongside the jar file. It will
* have the same name/path except for the extension.
*/
fd = openAlternateSuffix(fileName, "odex", O_RDONLY, &cachedName);
if (fd >= 0) {
ALOGV("Using alternate file (odex) for %s ...", fileName);
if (!dvmCheckOptHeaderAndDependencies(fd, false, 0, 0, true, true)) {
ALOGE("%s odex has stale dependencies", fileName);
free(cachedName);
cachedName = NULL;
close(fd);
fd = -1;
goto tryArchive;
} else {
ALOGV("%s odex has good dependencies", fileName);
//TODO: make sure that the .odex actually corresponds
// to the classes.dex inside the archive (if present).
// For typical use there will be no classes.dex.
}
} else {
ZipEntry entry;
tryArchive:
/*
* Pre-created .odex absent or stale. Look inside the jar for a
* "classes.dex".
*/
entry = dexZipFindEntry(&archive, kDexInJarName);
if (entry != NULL) {
bool newFile = false;
/*
* We've found the one we want. See if there's an up-to-date copy
* in the cache.
*
* On return, "fd" will be seeked just past the "opt" header.
*
* If a stale .odex file is present and classes.dex exists in
* the archive, this will *not* return an fd pointing to the
* .odex file; the fd will point into dalvik-cache like any
* other jar.
*/
if (odexOutputName == NULL) {
cachedName = dexOptGenerateCacheFileName(fileName,
kDexInJarName);
if (cachedName == NULL)
goto bail;
} else {
cachedName = strdup(odexOutputName);
}
ALOGV("dvmJarFileOpen: Checking cache for %s (%s)",
fileName, cachedName);
fd = dvmOpenCachedDexFile(fileName, cachedName,
dexGetZipEntryModTime(&archive, entry),
dexGetZipEntryCrc32(&archive, entry),
isBootstrap, &newFile, /*createIfMissing=*/true);
if (fd < 0) {
ALOGI("Unable to open or create cache for %s (%s)",
fileName, cachedName);
goto bail;
}
locked = true;
/*
* If fd points to a new file (because there was no cached version,
* or the cached version was stale), generate the optimized DEX.
* The file descriptor returned is still locked, and is positioned
* just past the optimization header.
*/
if (newFile) {
u8 startWhen, extractWhen, endWhen;
bool result;
off_t dexOffset;
dexOffset = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR);
result = (dexOffset > 0);
if (result) {
startWhen = dvmGetRelativeTimeUsec();
result = dexZipExtractEntryToFile(&archive, entry, fd) == 0;
extractWhen = dvmGetRelativeTimeUsec();
}
if (result) {
result = dvmOptimizeDexFile(fd, dexOffset,
dexGetZipEntryUncompLen(&archive, entry),
fileName,
dexGetZipEntryModTime(&archive, entry),
dexGetZipEntryCrc32(&archive, entry),
isBootstrap);
}
if (!result) {
ALOGE("Unable to extract+optimize DEX from '%s'",
fileName);
goto bail;
}
endWhen = dvmGetRelativeTimeUsec();
ALOGD("DEX prep '%s': unzip in %dms, rewrite %dms",
fileName,
(int) (extractWhen - startWhen) / 1000,
(int) (endWhen - extractWhen) / 1000);
}
} else {
ALOGI("Zip is good, but no %s inside, and no valid .odex "
"file in the same directory", kDexInJarName);
goto bail;
}
}
/*
* Map the cached version. This immediately rewinds the fd, so it
* doesn't have to be seeked anywhere in particular.
*/
if (dvmDexFileOpenFromFd(fd, &pDvmDex) != 0) {
ALOGI("Unable to map %s in %s", kDexInJarName, fileName);
goto bail;
}
if (locked) {
/* unlock the fd */
if (!dvmUnlockCachedDexFile(fd)) {
/* uh oh -- this process needs to exit or we'll wedge the system */
ALOGE("Unable to unlock DEX file");
goto bail;
}
locked = false;
}
ALOGV("Successfully opened '%s' in '%s'", kDexInJarName, fileName);
*ppJarFile = (JarFile*) calloc(1, sizeof(JarFile));
(*ppJarFile)->archive = archive;
(*ppJarFile)->cacheFileName = cachedName;
(*ppJarFile)->pDvmDex = pDvmDex;
cachedName = NULL; // don't free it below
result = 0;
bail:
/* clean up, closing the open file */
if (archiveOpen && result != 0)
dexZipCloseArchive(&archive);
free(cachedName);
if (fd >= 0) {
if (locked)
(void) dvmUnlockCachedDexFile(fd);
close(fd);
}
return result;
}