关于聚类
1 聚类的类型
聚类可以通过人工神经网络来实现,也可以通过专门的聚类算法实现,例如参考资料[3]介绍了较为常见的k-means、层次聚类、SOM以及FCM四种聚类算法,其中SOM属于神经网络方法。本文重点介绍层次聚类算法。
参考资料[3]提到,根据层次分解的顺序是自底向上的还是自上向下的,层次聚类算法又可分为凝聚的层次聚类算法和分裂的层次聚类算法,本文主要介绍前者。
2 凝聚层次聚类算法
参考资料[9]解析了凝聚层次聚类的含义:所谓凝聚的,指的是该算法初始时,将每个点作为一个簇,每一步合并两个最接近的簇。例如:依次取当前最近的点对,如果这个点对当前不在一个簇中,则将这两个点所在的两个簇合并。另外即使到最后,对于噪音点或是离群点也往往还是各占一簇的,除非过度合并。对于这里的"最接近",有下面三种定义:
(1)单链(MIN):定义簇的邻近度为不同两个簇的两个最近的点之间的距离。
(2)全链(MAX):定义簇的邻近度为不同两个簇的两个最远的点之间的距离。
(3)组平均:定义簇的邻近度为取自两个不同簇的所有点对邻近度的平均值。
参考资料[3]对凝聚型层次聚类的策略也作了类似的介绍:先将每个对象作为一个簇,然后合并这些原子簇为越来越大的簇,直到所有对象都在一个簇中,或者某个终结条件被满足。绝大多数层次聚类属于凝聚型层次聚类,它们只是在簇间相似度的定义上有所不同。四种广泛采用的簇间距离度量方法如下:
参考资料[3]给出采用最小距离的凝聚层次聚类算法流程:
(1) 将每个对象看作一类,计算两两之间的最小距离;
(2) 将距离最小的两个类合并成一个新类;
(3) 重新计算新类与所有类之间的距离;
(4) 重复(2)、(3),直到所有类最后合并成一类。
3 凝聚层次聚类的matlab实现
参考资料[8]介绍了matlab中实现凝聚层次聚类的两种方法:a)一次聚类;b)分步聚类。本文重点介绍后者。
3.1 使用pdist计算变量之间的距离
关于pdist,matlab帮助文档的解析如下:
pdist Pairwise distance between pairs of objects Syntax D = pdist(X) D = pdist(X,distance) D = pdist(X) computes the Euclidean distance between pairs of objects in m-by-n data matrix X. Rows of X correspond to observations, and columns correspond to variables. D is a row vector of length m(m–1)/2,corresponding to pairs of observations in X.根据上述的解析可知,pdist主要的作用是计算X矩阵中行与行之间的距离。
3.2 用linkage函数来产生聚类树
matlab帮助文档中对linkage的解析如下:
linkage Agglomerative hierarchical cluster tree Syntax Z = linkage(X) Z = linkage(X,method) Description Z = linkage(X) returns a matrix Z that encodes a tree of hierarchical clusters of the rows of the real matrix X. Z = linkage(X,method) creates the tree using the specified method, where method describes how to measure the distance between clusters.
实例
clear
clc
X = [1
2
3];
Y = pdist(X, 'euclidean');
Z = linkage(Y, 'average');
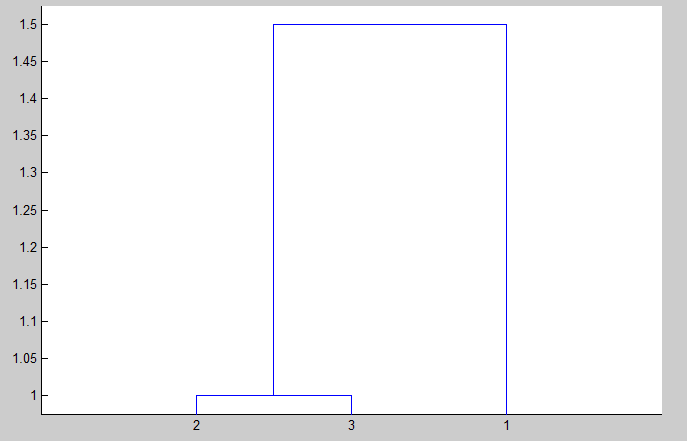
dendrogram(Z); 运算结果如下
Y = [1 2 1]
Z = [2 3 1
1 4 1.5]
解析:Y的三个值分别为X(1)vsX(2),X(1)vsX(3)以及X(2:)vsX(3)。
Z的第1行表示X(2)与X(3)的距离为1,聚为一类,新一类命名为4;
Z的第2行表示X(1)与新产生的类4的距离为1.5,聚为一类(其距离其实是X(1)vsX(2)的距离1和X(1)vsX(3)的距离2的平均值)。
dendrogram将层次聚类树画为如下图:
3.3 用 cluster进行聚类,返回聚类列
matlab帮助文档中关于cluster的说明如下
cluster Construct agglomerative clusters from linkages Syntax T = cluster(Z,'cutoff',c) T = cluster(Z,'cutoff',c,'depth',d) T = cluster(Z,'cutoff',c,'criterion',criterion) T = cluster(Z,'maxclust',n) Description T = cluster(Z,'cutoff',c) constructs clusters from the agglomerative hierarchical cluster tree, Z, as generated by the linkage function. Z is a matrix of size (m – 1)-by-3, where m is the number of observations in the original data. c is a threshold for cutting Z into clusters. Clusters are formed when a node and all of its subnodes have inconsistent value less than c. All leaves at or below the node are grouped into a cluster. t is a vector of size m containing the cluster assignments of each observation.If c is a vector, T is a matrix of cluster assignments with one column per cutoff value.T = cluster(Z,'cutoff',c,'depth',d) evaluates inconsistent values by looking to a depth d below each node. The default depth is 2. T = cluster(Z,'cutoff',c,'criterion',criterion) uses the specified criterion for forming clusters, where criterion is one of the strings 'inconsistent' (default) or 'distance'.The 'distance' criterion uses the distance between the two subnodes merged at a node to measure node height. All leaves at or below a node with height less than c are grouped into a cluster. T = cluster(Z,'maxclust',n) constructs a maximum of n clusters using the 'distance' criterion. cluster finds the smallest height at which a horizontal cut through the tree leaves n or fewer clusters.If n is a vector, T is a matrix of cluster assignments with one column per maximum value.
实例
在上面的实例的基础上,利用cluster对Z进行构建
T = cluster(Z, 2);上面的命令意思为:将Z进行归类,类别最大为2。结果如下
T=[1
2
2];
也就是说,X(1)是一类,X(2)和X(3)归为一类。
参考资料
[1]聚类
[2]一种改进的凝聚层次聚类法
[3]四种聚类方法之比较
[4]基于凝聚的层次聚类算法的改进
[5]用MATLAB做聚类分析
[6]用matlab做聚类分析
[7]matlab聚类分析
[8]用matlab做聚类分析
[9]初识聚类算法:K均值、凝聚层次聚类和DBSCAN