编译原理实验二 tiny文法的LL(1)分析
通过LL(1)分析方法对tiny的文法进行处理,然后输入tiny程序,进行语法分析,其中也包含了词法扫描,词法扫描使用DFA状态图的循环扫描方法。
1、文法的规范化:消除文法中的左递归和提取文法的左公因子,并且对tiny的文法进行拆解,比如一条文法有几个选择,则拆成几条,最后的文法规则整理结果如下:
0 program --> stmt-sequence 1 stmt-sequence --> statement stmt' 2 stmt' --> ;statement stmt' 3 stmt' --> $ 4 statement --> if-stmt 5 statement --> repeat-stmt 6 statement --> assign-stmt 7 statement --> read-stmt 8 statement --> write-stmt 9 statement --> While-stmt 10 statement --> Dowhile-stmt 11 statement --> for-stmt 12 if-stmt --> if exp then stmt-sequence else-part' end 13 else-part' --> else stmt-sequence 14 else-part' --> $ 15 repeat-stmt --> repeat stmt-sequence until exp 16 assign-stmt --> identifier := exp 17 read-stmt --> read identifier 18 write-stmt --> write exp 19 exp --> simple-exp cmp-exp' 20 cmp-exp' --> comparison-op simple-exp 21 cmp-exp' --> $ 22 comparison-op --> < 23 comparison-op --> = 24 simple-exp --> term term' 25 term' --> addop term 26 term' --> $ 27 addop --> + 28 addop --> - 29 term --> factor factor' 30 factor' --> mulop factor 31 factor' --> $ 32 mulop --> * 33 mulop --> / 34 mulop --> % 35 factor --> (exp) 36 factor --> number 37 factor --> identifier 38 While-stmt --> while exp do stmt-sequence endwhile 39 Dowhile-stmt --> do stmt-sequence while exp 40 for-stmt --> for identifier := simple-exp for-choose' 41 for-choose' --> to simple-exp do stmt-sequence enddo 42 for-choose' --> downto simple-exp do stmt-sequence enddo
注:每条文法前面的标号是自行添加上去以便查看和分析,不属于程序处理范围。其中第0条文法中program为开始符号,’$’表示空推导,” -->”表示推导符号。
2、求出终结符号集和非终结符号集
扫描文法,求出终结符号集TerminalSet,非终结符号集NonTerminalSet。其中推导符号左边的token,全都属于非终结符号集,第一遍扫描可以求出非终结符号集。然后对文法推导符号右边的token进行扫描,消除掉属于非终结符号的token,剩下的token就都属于终结符号集。处理结果如下:
终结符号集:; if then end else repeat until identifier := read write < = + - * / % ( ) number while do endwhile for to enddo downto
非终结符号集:program stmt-sequence stmt' statement if-stmt else-part' repeat-stmt assign-stmt read-stmt write-stmt exp cmp-exp' comparison-op simple-exp term' addop term factor' mulop factor While-stmt Dowhile-stmt for-stmt for-choose'
3、求出first集合
first集合的求解算法伪代码自行google,具体实现见下面附件的代码。结果如下(其中字符’$’表示空推导):
program: if repeat identifier read write while do for stmt-sequence: if repeat identifier read write while do for stmt': ; $ statement: if repeat identifier read write while do for if-stmt: if else-part': else $ repeat-stmt: repeat assign-stmt: identifier read-stmt: read write-stmt: write exp: ( number identifier cmp-exp': $ < = comparison-op: < = simple-exp: ( number identifier term': $ + - addop: + - term: ( number identifier factor': $ * / % mulop: * / % factor: ( number identifier While-stmt: while Dowhile-stmt: do for-stmt: for for-choose': to downto
4、求出follow集合
follow集合求解算法伪代码也自行google,结果如下(其中字符’#’表示输入的结束):
program: # stmt-sequence: # else end until endwhile while enddo stmt': # else end until endwhile while enddo statement: ; # else end until endwhile while enddo if-stmt: ; # else end until endwhile while enddo else-part': end repeat-stmt: ; # else end until endwhile while enddo assign-stmt: ; # else end until endwhile while enddo read-stmt: ; # else end until endwhile while enddo write-stmt: ; # else end until endwhile while enddo exp: then ; # ) do else end until endwhile while enddo cmp-exp': then ; # ) do else end until endwhile while enddo comparison-op: ( number identifier simple-exp: < = then ; # to downto do ) else end until endwhile while enddo term': < = then ; # to downto do ) else end until endwhile while enddo addop: ( number identifier term: + - < = then ; # to downto do ) else end until endwhile while enddo factor': + - < = then ; # to downto do ) else end until endwhile while enddo mulop: ( number identifier factor: * / % + - < = then ; # to downto do ) else end until endwhile while enddo While-stmt: ; # else end until endwhile while enddo Dowhile-stmt: ; # else end until endwhile while enddo for-stmt: ; # else end until endwhile while enddo for-choose': ; # else end until endwhile while enddo
5、构造LL(1)分析表M[A,a]算法
文法规则的序号,见步骤1中的排序
6、分析算法,构造LL(1)分析树
为了在分析过程中构造分析树,除了分析栈,还要多开一个保存分析树节点的栈。
1)但分析栈中的栈顶元素和用户输入的token,值相等或类型匹配时,就把两个栈的栈顶元素出栈。
2)但进行文法规则的替换时,把两个栈的栈顶元素出栈,根据替换的文法规则,新建分析树节点(文法推导符号右部有多少个非终结符号/终结符号,就要建立多少个节点),然后这些新建节点作为刚才分析树栈中出栈token的子节点,连接好,之后再压入分析树节点的栈中。
3)栈顶元素是空推导时,则两个栈分析出栈,不做其他操作。
具体实现见代码。。。
7、文件cs的关系
共有3个类:父类Tiny,包含了tiny语言的特殊符号、保留字以及几个判断函数;子类TinyScan继承自Tiny,实现tiny的词法分析功能;子类SyntaxParse继承自Tiny,实现tiny的文法分析功能。
1)类Tiny的相关信息
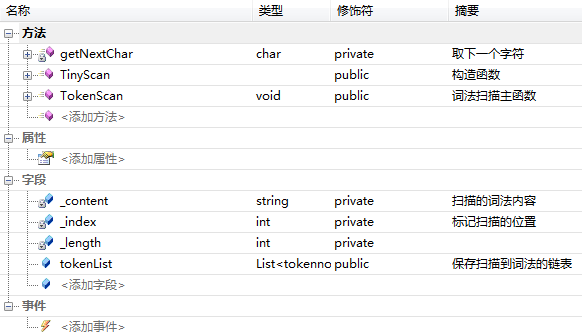
2)类TinyScan的相关信息
3)类SyntaxParse的相关信息
代码文件:http://cid-780607117452312e.office.live.com/self.aspx/.Public/syntax%20parse.rar