Treap的读书笔记2
二叉排序树是一种动态排序的数据结构,支持插入、删除、查找等操作,且平均时间复杂度为O(log(N)),但是普通二叉排序树不能保证树退化为一颗分支的情况,此时最坏情况下的时间复杂度为O(N)。此时,平衡二叉树的产生了。平衡二叉树是一种动态调整平衡的数据结构,但理想的平衡二叉树很难,于是人们使用AVL、红黑树、Treap、伸展树等来替代平衡二叉树,这些数据结构可以很好地改善最坏情况。但实现起来并不是很容易的事。
Treap是Heap+Tree,通俗来讲就是堆与树的结合,每个节点除了关键字key以及节点之间的连接关系外,还要保存一个优先级priority,注意这里的优先级不同于其他节点的随机数字,随机才能较好的期望平衡度,保证可以很好维护二叉树的性质。其中在Treap中关键字key遵循二叉查找树的性质,即:
(1)、空树是一颗二叉查找树;
(2)、若左子树不为空,则左子树中的全部关键字均小于该节点关键字;
(3)、若右子树不为空,则右子树中的全部关键字均不小于该节点关键字;
(4)、若左右子树非空,则左右子树也是一颗二叉查找树。
Treap中的优先级priority遵循Heap的性质,此处的堆已不再是棵完全二叉树,而是用指针代替数组下标实现的树结构,满足所有根节点优先级小于(或大于)左右孩子节点的优先级(在左右孩子存在的情况下,小于为小顶堆,大于为大顶堆)。
由于每个节点上的优先级是随机产生的,所以期望高度可以达到很好的程度。在算法导论的12.4节中,其证明了随机构造的二叉查找树的期望高度为O(lgn),因而treap的期望高度亦是O(lgn)。
Treap支持二叉树的所有操作,且平摊时间复杂度为O(log(N)),便于实现,性能好,克服了二叉查找树最坏情况时间复杂度为O(N)的弊端,有不存在AVL、红黑树等编码和理解难度,与伸展树有类似好处。下面简要谈谈Treap的几种基本操作。
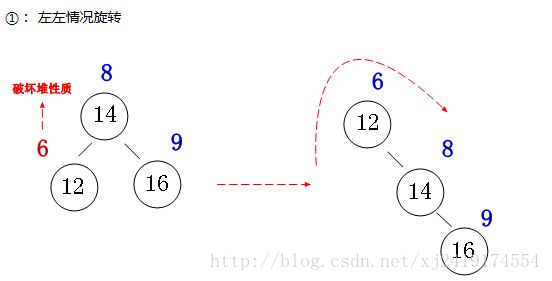
左旋:
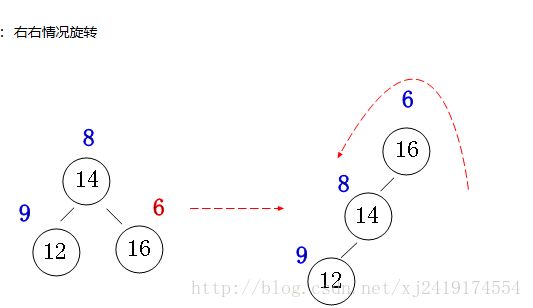
右旋:
以上截图来自http://www.cnblogs.com/huangxincheng/archive/2012/07/30/2614484.html,在此表示感谢!
查找:
查找直接用二叉树的性质,参考源代码。
插入:
先找到插入位置,在执行插入操作,然后维护堆的性质,即根据优先级调整以维护小顶堆或大顶堆的性质。关于维护队的性质,参考我前面的关于对的博客。
删除:
类比二叉查找树一样,删除结点存在三种情况:
(1)、叶子结点,跟二叉查找树一样,直接释放本节点即可。
(2)、只有一个还自己节点,跟二叉查找树一样操作。
(3)、有两个孩子节点,可以像二叉查找树一样转换为删除右子树最小节点或左子树最大节点,然后将只赋值到本应删除的节点处,此时可以一起复制优先级,然后向该分支调整,也可不赋值优先级保留原来的优先级,我的程序保留原来优先级。
更新:
先删除原节点,然后插入新节点。
由于期望高度为O(log(N)),所以以上所有操作的平潭时间复杂度为O(log(N))。
代码:
之前写了个带父亲指针的,感觉有点复杂,于是写了下面这段代码。查看带父亲指针的代码点击此处,感觉那个封装的比较好。
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
class Treap
{
private:
int num,key,pri;
Treap *child[2];
public:
int compare(int);
Treap(int);
Treap* rotate(Treap*,int);
Treap* erase(Treap*,int);
Treap* leafNode();
bool find(int);
void setNum();
Treap* insert(Treap*,int);
void rotatePrint(Treap*,int);
};
Treap::Treap(int tKey)
{
num=0;
key=tKey;
pri=rand()%1000;
child[0]=child[1]=NULL;
}
int Treap::compare(int tKey)
{
return key<tKey?1:0;
}
void Treap::setNum()
{
num=1;
if(child[0]!=NULL)
num+=child[0]->num;
if(child[1]!=NULL)
num+=child[1]->num;
}
Treap*Treap::rotate(Treap* tRoot,int dir)
{
Treap* ch=tRoot->child[dir];
tRoot->child[dir]=ch->child[dir^1];
ch->child[dir^1]=tRoot;
tRoot->setNum();
ch->setNum();
return ch;
}
Treap* Treap::insert(Treap *tRoot,int tKey)
{
if(NULL==tRoot)
return new Treap(tKey);
int dir=this->compare(tKey);
tRoot->child[dir]=tRoot->child[dir]->insert(tRoot->child[dir],tKey);
if(tRoot->pri>tRoot->child[dir]->pri)
tRoot=rotate(tRoot,dir);
else tRoot->setNum();
return tRoot;
}
Treap* Treap::leafNode()
{
if(NULL==child[0]&&NULL==child[1])
{
delete this;
return NULL;
}
else if(NULL==child[0])
{
Treap *p=this->child[1];
delete this;
return p;
}
else if(NULL==child[1])
{
Treap *p=this->child[0];
delete this;
return p;
}
}
Treap* Treap::erase(Treap* tRoot,int tKey)
{
if(NULL==tRoot)
return NULL;
if(key==tKey)
{
if(child[0]==NULL||child[1]==NULL)
return leafNode();
Treap *q=this,*p=this->child[1];
bool left=false;
while(p->child[0]!=NULL)
{
left=true;
q=p;
p=p->child[0];
}
this->key=p->key;
if(!left)
q->child[1]=p->leafNode();
else q->child[0]=p->leafNode();
return this;
}
int dir=this->compare(tKey);
tRoot->child[dir]=tRoot->child[dir]->erase(tRoot->child[dir],tKey);
return tRoot;
}
bool Treap::find(int tKey)
{
if(NULL==this)
return false;
if(key==tKey)
return true;
int dir=this->compare(tKey);
return child[dir]->find(tKey);
}
void Treap::rotatePrint(Treap* tRoot,int dep)
{
if(NULL==tRoot)
return ;
rotatePrint(tRoot->child[0],dep+1);
for(int i=0;i<dep;i++)
cout<<" ";
cout<<"("<<tRoot->key<<","<<tRoot->pri<<")"<<endl;
rotatePrint(tRoot->child[1],dep+1);
}
void menu()
{
//Treap *root=new Treap(10);
Treap *root=NULL;
srand(unsigned(clock()));
int val,choice;
while(true)
{
cout<<"***************菜单*************"<<endl;
cout<<" 1.插入"<<endl;
cout<<" 2.删除"<<endl;
cout<<" 3.查找"<<endl;
cout<<" 4.退出"<<endl;
cout<<"您的选择:[ ]\b\b\b";
cin>>choice;
cout<<"请输入数:";
cin>>val;
if(1==choice)
root=root->insert(root,val);
else if(2==choice)
root=root->erase(root,val);
else if(3==choice)
{
if(root->find(val))
cout<<"查找成功!"<<endl;
else cout<<"查找失败!"<<endl;
}
else if(4==choice)
exit(0);
cout<<"==================="<<endl;
root->rotatePrint(root,0);
}
}
int main()
{
while(true)
menu();
}