Trie树(字典树)
一:概念
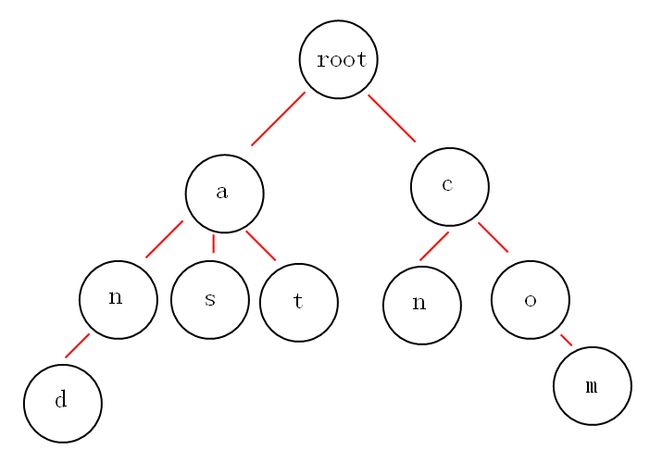
下面我们有and,as,at,cn,com这些关键词,那么如何构建trie树呢?
从上面的图中,我们或多或少的可以发现一些好玩的特性。
第一:根节点不包含字符,除根节点外的每一个子节点都包含一个字符。
第二:从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,就是该节点对应的字符串。
第三:每个单词的公共前缀作为一个字符节点保存。
二:使用范围
既然学Trie树,我们肯定要知道这玩意是用来干嘛的。
第一:词频统计。
可能有人要说了,词频统计简单啊,一个hash或者一个堆就可以打完收工,但问题来了,如果内存有限呢?还能这么
玩吗?所以这里我们就可以用trie树来压缩下空间,因为公共前缀都是用一个节点保存的。
第二: 前缀匹配
就拿上面的图来说吧,如果我想获取所有以"a"开头的字符串,从图中可以很明显的看到是:and,as,at,如果不用trie树,
你该怎么做呢?很显然朴素的做法时间复杂度为O(N2) ,那么用Trie树就不一样了,它可以做到h,h为你检索单词的长度,
可以说这是秒杀的效果。
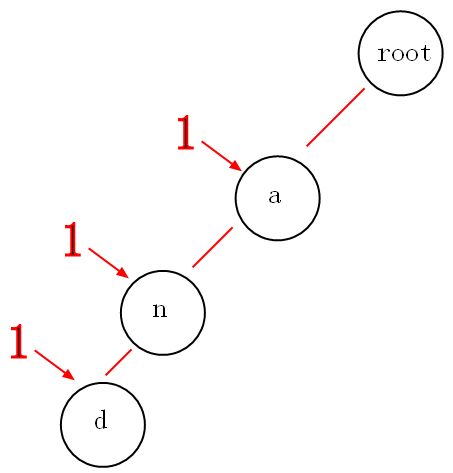
举个例子:现有一个编号为1的字符串”and“,我们要插入到trie树中,采用动态规划的思想,将编号”1“计入到每个途径的节点中,
那么以后我们要找”a“,”an“,”and"为前缀的字符串的编号将会轻而易举。
三:实际操作
到现在为止,我想大家已经对trie树有了大概的掌握,下面我们看看如何来实现。
1:定义trie树节点
为了方便,我也采用纯英文字母,我们知道字母有26个,那么我们构建的trie树就是一个26叉树,每个节点包含26个子节点。
1 #region Trie树节点 2 /// <summary> 3 /// Trie树节点 4 /// </summary> 5 public class TrieNode 6 { 7 /// <summary> 8 /// 26个字符,也就是26叉树 9 /// </summary> 10 public TrieNode[] childNodes; 11 12 /// <summary> 13 /// 词频统计 14 /// </summary> 15 public int freq; 16 17 /// <summary> 18 /// 记录该节点的字符 19 /// </summary> 20 public char nodeChar; 21 22 /// <summary> 23 /// 插入记录时的编码id 24 /// </summary> 25 public HashSet<int> hashSet = new HashSet<int>(); 26 27 /// <summary> 28 /// 初始化 29 /// </summary> 30 public TrieNode() 31 { 32 childNodes = new TrieNode[26]; 33 freq = 0; 34 } 35 } 36 #endregion
2: 添加操作
既然是26叉树,那么当前节点的后续子节点是放在当前节点的哪一叉中,也就是放在childNodes中哪一个位置,这里我们采用
int k = word[0] - 'a'来计算位置。
1 /// <summary> 2 /// 插入操作 3 /// </summary> 4 /// <param name="root"></param> 5 /// <param name="s"></param> 6 public void AddTrieNode(ref TrieNode root, string word, int id) 7 { 8 if (word.Length == 0) 9 return; 10 11 //求字符地址,方便将该字符放入到26叉树中的哪一叉中 12 int k = word[0] - 'a'; 13 14 //如果该叉树为空,则初始化 15 if (root.childNodes[k] == null) 16 { 17 root.childNodes[k] = new TrieNode(); 18 19 //记录下字符 20 root.childNodes[k].nodeChar = word[0]; 21 } 22 23 //该id途径的节点 24 root.childNodes[k].hashSet.Add(id); 25 26 var nextWord = word.Substring(1); 27 28 //说明是最后一个字符,统计该词出现的次数 29 if (nextWord.Length == 0) 30 root.childNodes[k].freq++; 31 32 AddTrieNode(ref root.childNodes[k], nextWord, id); 33 } 34 #endregion
3:删除操作
删除操作中,我们不仅要删除该节点的字符串编号,还要对词频减一操作。
/// <summary> /// 删除操作 /// </summary> /// <param name="root"></param> /// <param name="newWord"></param> /// <param name="oldWord"></param> /// <param name="id"></param> public void DeleteTrieNode(ref TrieNode root, string word, int id) { if (word.Length == 0) return; //求字符地址,方便将该字符放入到26叉树种的哪一颗树中 int k = word[0] - 'a'; //如果该叉树为空,则说明没有找到要删除的点 if (root.childNodes[k] == null) return; var nextWord = word.Substring(1); //如果是最后一个单词,则减去词频 if (word.Length == 0 && root.childNodes[k].freq > 0) root.childNodes[k].freq--; //删除途经节点 root.childNodes[k].hashSet.Remove(id); DeleteTrieNode(ref root.childNodes[k], nextWord, id); }
4:测试
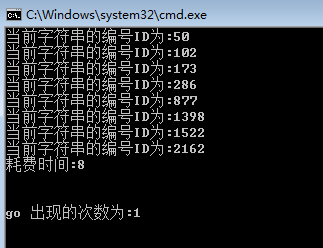
这里我从网上下载了一套的词汇表,共2279条词汇,现在我们要做的就是检索“go”开头的词汇,并统计go出现的频率。
1 public static void Main() 2 { 3 Trie trie = new Trie(); 4 5 var file = File.ReadAllLines(Environment.CurrentDirectory + "//1.txt"); 6 7 foreach (var item in file) 8 { 9 var sp = item.Split(new char[] { ' ' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); 10 11 trie.AddTrieNode(sp.LastOrDefault().ToLower(), Convert.ToInt32(sp[0])); 12 } 13 14 Stopwatch watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); 15 16 //检索go开头的字符串 17 var hashSet = trie.SearchTrie("go"); 18 19 foreach (var item in hashSet) 20 { 21 Console.WriteLine("当前字符串的编号ID为:{0}", item); 22 } 23 24 watch.Stop(); 25 26 Console.WriteLine("耗费时间:{0}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds); 27 28 Console.WriteLine("\n\ngo 出现的次数为:{0}\n\n", trie.WordCount("go")); 29 }
下面我们拿着ID到txt中去找一找,嘿嘿,是不是很有意思。
测试文件:1.txt
完整代码:
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Diagnostics; 6 using System.Threading; 7 using System.IO; 8 9 namespace ConsoleApplication2 10 { 11 public class Program 12 { 13 public static void Main() 14 { 15 Trie trie = new Trie(); 16 17 var file = File.ReadAllLines(Environment.CurrentDirectory + "//1.txt"); 18 19 foreach (var item in file) 20 { 21 var sp = item.Split(new char[] { ' ' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); 22 23 trie.AddTrieNode(sp.LastOrDefault().ToLower(), Convert.ToInt32(sp[0])); 24 } 25 26 Stopwatch watch = Stopwatch.StartNew(); 27 28 //检索go开头的字符串 29 var hashSet = trie.SearchTrie("go"); 30 31 foreach (var item in hashSet) 32 { 33 Console.WriteLine("当前字符串的编号ID为:{0}", item); 34 } 35 36 watch.Stop(); 37 38 Console.WriteLine("耗费时间:{0}", watch.ElapsedMilliseconds); 39 40 Console.WriteLine("\n\ngo 出现的次数为:{0}\n\n", trie.WordCount("go")); 41 } 42 } 43 44 public class Trie 45 { 46 public TrieNode trieNode = new TrieNode(); 47 48 #region Trie树节点 49 /// <summary> 50 /// Trie树节点 51 /// </summary> 52 public class TrieNode 53 { 54 /// <summary> 55 /// 26个字符,也就是26叉树 56 /// </summary> 57 public TrieNode[] childNodes; 58 59 /// <summary> 60 /// 词频统计 61 /// </summary> 62 public int freq; 63 64 /// <summary> 65 /// 记录该节点的字符 66 /// </summary> 67 public char nodeChar; 68 69 /// <summary> 70 /// 插入记录时的编号id 71 /// </summary> 72 public HashSet<int> hashSet = new HashSet<int>(); 73 74 /// <summary> 75 /// 初始化 76 /// </summary> 77 public TrieNode() 78 { 79 childNodes = new TrieNode[26]; 80 freq = 0; 81 } 82 } 83 #endregion 84 85 #region 插入操作 86 /// <summary> 87 /// 插入操作 88 /// </summary> 89 /// <param name="word"></param> 90 /// <param name="id"></param> 91 public void AddTrieNode(string word, int id) 92 { 93 AddTrieNode(ref trieNode, word, id); 94 } 95 96 /// <summary> 97 /// 插入操作 98 /// </summary> 99 /// <param name="root"></param> 100 /// <param name="s"></param> 101 public void AddTrieNode(ref TrieNode root, string word, int id) 102 { 103 if (word.Length == 0) 104 return; 105 106 //求字符地址,方便将该字符放入到26叉树中的哪一叉中 107 int k = word[0] - 'a'; 108 109 //如果该叉树为空,则初始化 110 if (root.childNodes[k] == null) 111 { 112 root.childNodes[k] = new TrieNode(); 113 114 //记录下字符 115 root.childNodes[k].nodeChar = word[0]; 116 } 117 118 //该id途径的节点 119 root.childNodes[k].hashSet.Add(id); 120 121 var nextWord = word.Substring(1); 122 123 //说明是最后一个字符,统计该词出现的次数 124 if (nextWord.Length == 0) 125 root.childNodes[k].freq++; 126 127 AddTrieNode(ref root.childNodes[k], nextWord, id); 128 } 129 #endregion 130 131 #region 检索操作 132 /// <summary> 133 /// 检索单词的前缀,返回改前缀的Hash集合 134 /// </summary> 135 /// <param name="s"></param> 136 /// <returns></returns> 137 public HashSet<int> SearchTrie(string s) 138 { 139 HashSet<int> hashSet = new HashSet<int>(); 140 141 return SearchTrie(ref trieNode, s, ref hashSet); 142 } 143 144 /// <summary> 145 /// 检索单词的前缀,返回改前缀的Hash集合 146 /// </summary> 147 /// <param name="root"></param> 148 /// <param name="s"></param> 149 /// <returns></returns> 150 public HashSet<int> SearchTrie(ref TrieNode root, string word, ref HashSet<int> hashSet) 151 { 152 if (word.Length == 0) 153 return hashSet; 154 155 int k = word[0] - 'a'; 156 157 var nextWord = word.Substring(1); 158 159 if (nextWord.Length == 0) 160 { 161 //采用动态规划的思想,word最后节点记录这途经的id 162 hashSet = root.childNodes[k].hashSet; 163 } 164 165 SearchTrie(ref root.childNodes[k], nextWord, ref hashSet); 166 167 return hashSet; 168 } 169 #endregion 170 171 #region 统计指定单词出现的次数 172 173 /// <summary> 174 /// 统计指定单词出现的次数 175 /// </summary> 176 /// <param name="root"></param> 177 /// <param name="word"></param> 178 /// <returns></returns> 179 public int WordCount(string word) 180 { 181 int count = 0; 182 183 WordCount(ref trieNode, word, ref count); 184 185 return count; 186 } 187 188 /// <summary> 189 /// 统计指定单词出现的次数 190 /// </summary> 191 /// <param name="root"></param> 192 /// <param name="word"></param> 193 /// <param name="hashSet"></param> 194 /// <returns></returns> 195 public void WordCount(ref TrieNode root, string word, ref int count) 196 { 197 if (word.Length == 0) 198 return; 199 200 int k = word[0] - 'a'; 201 202 var nextWord = word.Substring(1); 203 204 if (nextWord.Length == 0) 205 { 206 //采用动态规划的思想,word最后节点记录这途经的id 207 count = root.childNodes[k].freq; 208 } 209 210 WordCount(ref root.childNodes[k], nextWord, ref count); 211 } 212 213 #endregion 214 215 #region 修改操作 216 /// <summary> 217 /// 修改操作 218 /// </summary> 219 /// <param name="newWord"></param> 220 /// <param name="oldWord"></param> 221 /// <param name="id"></param> 222 public void UpdateTrieNode(string newWord, string oldWord, int id) 223 { 224 UpdateTrieNode(ref trieNode, newWord, oldWord, id); 225 } 226 227 /// <summary> 228 /// 修改操作 229 /// </summary> 230 /// <param name="root"></param> 231 /// <param name="newWord"></param> 232 /// <param name="oldWord"></param> 233 /// <param name="id"></param> 234 public void UpdateTrieNode(ref TrieNode root, string newWord, string oldWord, int id) 235 { 236 //先删除 237 DeleteTrieNode(oldWord, id); 238 239 //再添加 240 AddTrieNode(newWord, id); 241 } 242 #endregion 243 244 #region 删除操作 245 /// <summary> 246 /// 删除操作 247 /// </summary> 248 /// <param name="root"></param> 249 /// <param name="newWord"></param> 250 /// <param name="oldWord"></param> 251 /// <param name="id"></param> 252 public void DeleteTrieNode(string word, int id) 253 { 254 DeleteTrieNode(ref trieNode, word, id); 255 } 256 257 /// <summary> 258 /// 删除操作 259 /// </summary> 260 /// <param name="root"></param> 261 /// <param name="newWord"></param> 262 /// <param name="oldWord"></param> 263 /// <param name="id"></param> 264 public void DeleteTrieNode(ref TrieNode root, string word, int id) 265 { 266 if (word.Length == 0) 267 return; 268 269 //求字符地址,方便将该字符放入到26叉树种的哪一颗树中 270 int k = word[0] - 'a'; 271 272 //如果该叉树为空,则说明没有找到要删除的点 273 if (root.childNodes[k] == null) 274 return; 275 276 var nextWord = word.Substring(1); 277 278 //如果是最后一个单词,则减去词频 279 if (word.Length == 0 && root.childNodes[k].freq > 0) 280 root.childNodes[k].freq--; 281 282 //删除途经节点 283 root.childNodes[k].hashSet.Remove(id); 284 285 DeleteTrieNode(ref root.childNodes[k], nextWord, id); 286 } 287 #endregion 288 } 289 }1. 什么是trie树
1.Trie树 (特例结构树)
Trie树,又称单词查找树、字典树,是一种树形结构,是一种哈希树的变种,是一种用于快速检索的多叉树结构。典型应用是用于统计和排序大量的字符串(但不仅限于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频统计。它的优点是:最大限度地减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希表高。Trie的核心思想是空间换时间。利用字符串的公共前缀来降低查询时间的开销以达到提高效率的目的。Trie树也有它的缺点,Trie树的内存消耗非常大.当然,或许用左儿子右兄弟的方法建树的话,可能会好点.2. 三个基本特性:
1)根节点不包含字符,除根节点外每一个节点都只包含一个字符。2)从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串。3)每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符都不相同。3 .例子
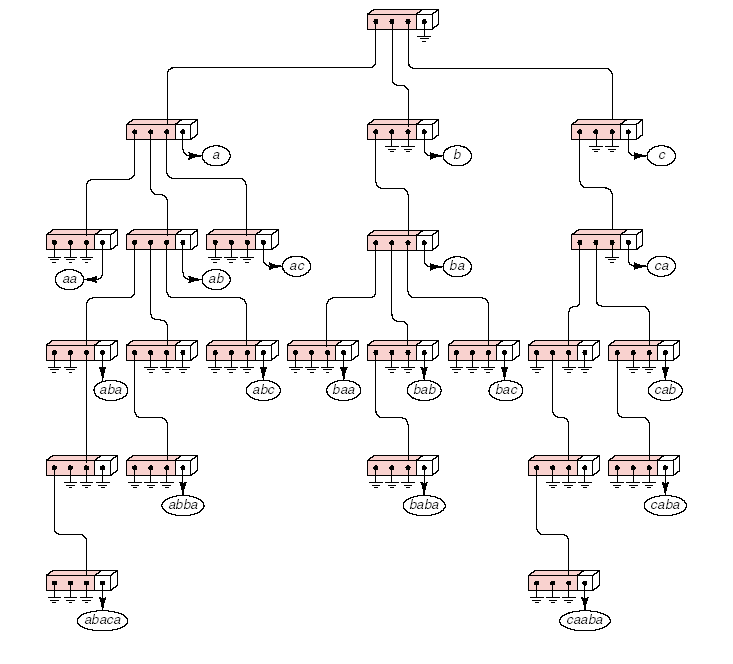
和二叉查找树不同,在trie树中,每个结点上并非存储一个元素。 trie树把要查找的关键词看作一个字符序列。并根据构成关键词字符的先后顺序构造用于检索的树结构。 在trie树上进行检索类似于查阅英语词典。一棵m度的trie树或者为空,或者由m棵m度的trie树构成。例如,电子英文词典,为了方便用户快速检索英语单词,可以建立一棵trie树。例如词典由下面的单词成:a、b、c、aa、ab、ac、ba、ca、aba、abc、baa、bab、bac、cab、abba、baba、caba、abaca、caaba
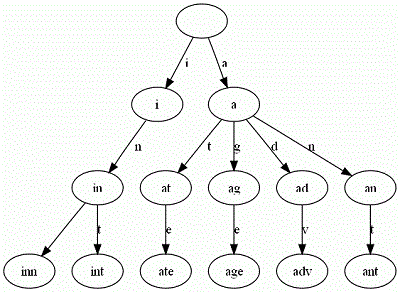
再举一个例子。给出一组单词,inn, int, at, age, adv, ant, 我们可以得到下面的Trie:
可以看出:
- 每条边对应一个字母。
- 每个节点对应一项前缀。叶节点对应最长前缀,即单词本身。
- 单词inn与单词int有共同的前缀“in”, 因此他们共享左边的一条分支,root->i->in。同理,ate, age, adv, 和ant共享前缀"a",所以他们共享从根节点到节点"a"的边。
查询操纵非常简单。比如要查找int,顺着路径i -> in -> int就找到了。
2. trie树的实现
1.插入过程
对于一个单词,从根开始,沿着单词的各个字母所对应的树中的节点分支向下走,直到单词遍历完,将最后的节点标记为红色,表示该单词已插入trie树。
2. 查找过程
其方法为:
(1) 从根结点开始一次搜索;
(2) 取得要查找关键词的第一个字母,并根据该字母选择对应的子树并转到该子树继续进行检索;
即从根开始按照单词的字母顺序向下遍历trie树,一旦发现某个节点标记不存在或者单词遍历完成而最后的节点未标记为红色,则表示该单词不存在,若最后的节点标记为红色,表示该单词存在。如下图中:trie树中存在的就是abc、d、da、dda四个单词。在实际的问题中可以将标记颜色的标志位改为数量count等其他符合题目要求的变量。
- // stdafx.h : include file for standard system include files,
- // or project specific include files that are used frequently, but
- // are changed infrequently
- //
- #pragma once
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include "stdlib.h"
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string.h>
- using namespace std;
- //宏定义
- #define TRUE 1
- #define FALSE 0
- #define NULL 0
- #define OK 1
- #define ERROR 0
- #define INFEASIBLE -1
- #define OVERFLOW -2
- const int num_chars = 26;
- class Trie {
- public:
- Trie();
- Trie(Trie& tr);
- virtual ~Trie();
- int trie_search(const char* word, char* entry ) const;
- int insert(const char* word, const char* entry);
- int remove(const char* word, char* entry);
- protected:
- struct Trie_node{
- char* data; //若不为空,表示从root到此结点构成一个单词
- Trie_node* branch[num_chars]; //分支
- Trie_node(); //构造函数
- };
- Trie_node* root; //根结点(指针)
- };
- // Test.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
- //
- #include "stdafx.h"
- Trie::Trie_node::Trie_node() {
- data = NULL;
- for (int i=0; i<num_chars; ++i)
- branch[i] = NULL;
- }
- Trie::Trie():root(NULL) {}
- Trie::~Trie(){}
- int Trie::trie_search(const char* word, char* entry ) const {
- int position = 0; //层数
- char char_code;
- Trie_node *location = root; //从根结点开始
- while( location!=NULL && *word!=0 ) {
- if (*word >= 'A' && *word <= 'Z')
- char_code = *word-'A';
- else if (*word>='a' && *word<='z')
- char_code = *word-'a';
- else return 0;// 不合法的单词
- //转入相应分支指针
- location = location->branch[char_code];
- position++;
- word++;
- }
- //找到,获取数据,成功返回
- if ( location != NULL && location->data != NULL ) {
- strcpy(entry,location->data);
- return 1;
- }
- else return 0;// 不合法的单词
- }
- int Trie::insert(const char* word, const char* entry) {
- int result = 1, position = 0;
- if ( root == NULL ) root = new Trie_node; //初始插入,根结点为空
- char char_code;
- Trie_node *location = root; //从根结点开始
- while( location!=NULL && *word!=0 ) {
- if (*word>='A' && *word<='Z') char_code = *word-'A';
- else if (*word>='a' && *word<='z') char_code = *word-'a';
- else return 0;// 不合法的单词
- //不存在此分支
- if( location->branch[char_code] == NULL )
- location->branch[char_code] = new Trie_node; //创建空分支
- //转入分支
- location = location->branch[char_code];
- position++;word++; }
- if (location->data != NULL) result = 0;//欲插入的单词已经存在
- else { //插入数据
- location->data = new char[strlen(entry)+1]; //分配内存
- strcpy(location->data, entry); //给data赋值表明单词存在
- }
- return result;
- }
- int main(){
- Trie t;
- char entry[100];
- t.insert("a", "DET");
- t.insert("abacus","NOUN");
- t.insert("abalone","NOUN");
- t.insert("abandon","VERB");
- t.insert("abandoned","ADJ");
- t.insert("abashed","ADJ");
- t.insert("abate","VERB");
- t.insert("this", "PRON");
- if (t.trie_search("this", entry))
- cout<<"'this' was found. pos: "<<entry<<endl;
- if (t.trie_search("abate", entry))
- cout<<"'abate' is found. pos: "<<entry<<endl;
- if (t.trie_search("baby", entry))
- cout<<"'baby' is found. pos: "<<entry<<endl;
- else
- cout<<"'baby' does not exist at all!"<<endl;
- }
3. 查找分析
3. trie树的应用:
1. 字符串检索,词频统计,搜索引擎的热门查询
事先将已知的一些字符串(字典)的有关信息保存到trie树里,查找另外一些未知字符串是否出现过或者出现频率。
举例:
1)有一个1G大小的一个文件,里面每一行是一个词,词的大小不超过16字节,内存限制大小是1M。返回频数最高的100个词。
2)给出N 个单词组成的熟词表,以及一篇全用小写英文书写的文章,请你按最早出现的顺序写出所有不在熟词表中的生词。
3)给出一个词典,其中的单词为不良单词。单词均为小写字母。再给出一段文本,文本的每一行也由小写字母构成。判断文本中是否含有任何不良单词。例如,若rob是不良单词,那么文本problem含有不良单词。
4)1000万字符串,其中有些是重复的,需要把重复的全部去掉,保留没有重复的字符串
5)寻找热门查询:搜索引擎会通过日志文件把用户每次检索使用的所有检索串都记录下来,每个查询串的长度为1-255字节。假设目前有一千万个记录,这些查询串的重复读比较高,虽然总数是1千万,但是如果去除重复和,不超过3百万个。一个查询串的重复度越高,说明查询它的用户越多,也就越热门。请你统计最热门的10个查询串,要求使用的内存不能超过1G。
2. 字符串最长公共前缀
Trie树利用多个字符串的公共前缀来节省存储空间,反之,当我们把大量字符串存储到一棵trie树上时,我们可以快速得到某些字符串的公共前缀。举例:
1) 给出N 个小写英文字母串,以及Q 个询问,即询问某两个串的最长公共前缀的长度是多少. 解决方案:
首先对所有的串建立其对应的字母树。此时发现,对于两个串的最长公共前缀的长度即它们所在结点的公共祖先个数,于是,问题就转化为了离线 (Offline)的最近公共祖先(Least Common Ancestor,简称LCA)问题。
而最近公共祖先问题同样是一个经典问题,可以用下面几种方法:
1. 利用并查集(Disjoint Set),可以采用采用经典的Tarjan 算法;
2. 求出字母树的欧拉序列(Euler Sequence )后,就可以转为经典的最小值查询(Range Minimum Query,简称RMQ)问题了;
3. 排序
Trie树是一棵多叉树,只要先序遍历整棵树,输出相应的字符串便是按字典序排序的结果。
举例: 给你N 个互不相同的仅由一个单词构成的英文名,让你将它们按字典序从小到大排序输出。
4 作为其他数据结构和算法的辅助结构
如后缀树,AC自动机等。