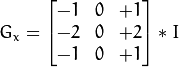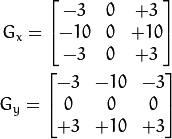Sobel滤波,Laplace滤波介绍与opencv实现
四、高通滤波器
前面一章介绍了使用内核矩阵实现低通滤波器,这个滤波器能够删除或者减弱高频分量。这本节中,我们将介绍相反转换的增加高频分量的方法,也就是高通滤波器。主要用于边缘的检测。
4.1 Sobel函数
opencv中提供了函数cv::Sobel,利用矩阵卷积方法 近似 实现方向导数的计算。
函数头文件:#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
函数定义:
CV_EXPORTS_W void Sobel( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth,
int dx, int dy, int ksize=3,
double scale=1, double delta=0,
int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT ); 函数使用:
cv::Sobel(image,sobelX,CV_8U,1,0,3,0.4,128);
cv::Sobel(image,sobelY,CV_8U,0,1,3,0.4,128);函数参数介绍:
int ddepth : 图像深度,或者说图像处理后值的大小范围
dx,dy :决定是对横向和纵向的Sobel处理
ksize :内核矩阵的大小,默认为3
scale :函数处理后值乘以的系数 即 值*scale
delta :函数处理后值的补偿, 即 值*scale + delta
函数说明:
函数实现对图像进行求方向导数,当ksize等于3时,方向导数可以近似用内核Gx,Gy和图像I卷积,如下:
当然还有另外一个比Sobel函数的近似效果更好的 Scharr函数,其内核矩阵如下:
4.2 Laplace函数
在opencv中也提供cv:Laplace函数 ,对图像求二阶导数。因为图像是二维的,所以不用分开求横向和纵向的导数,然后相加。laplace的函数计算如下:,当梯度最大时,二阶导数为0,也能很好的表现出函数边界和轮廓。
函数定义:
//! applies Laplacian operator to the image
CV_EXPORTS_W void Laplacian( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth,
int ksize=1, double scale=1, double delta=0,
int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT );
五、程序实例
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include "laplacianZC.h"
int main()
{
// Read input image
cv::Mat image= cv::imread("boldt.jpg",0);
if (!image.data)
return 0;
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Original Image");
cv::imshow("Original Image",image);
cv::imwrite("Original Image.jpg",image);
// Compute Sobel X derivative
cv::Mat sobelX;
cv::Sobel(image,sobelX,CV_8U,1,0,3,0.4,128);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Sobel X Image");
cv::imshow("Sobel X Image",sobelX);
cv::imwrite("Sobel X Image.jpg",sobelX);
// Compute Sobel Y derivative
cv::Mat sobelY;
cv::Sobel(image,sobelY,CV_8U,0,1,3,0.4,128);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Sobel Y Image");
cv::imshow("Sobel Y Image",sobelY);
cv::imwrite("Sobel Y Image.jpg",sobelY);
// Compute norm of Sobel
cv::Sobel(image,sobelX,CV_16S,1,0);
cv::Sobel(image,sobelY,CV_16S,0,1);
cv::Mat sobel;
//compute the L1 norm
sobel= abs(sobelX)+abs(sobelY);
double sobmin, sobmax;
cv::minMaxLoc(sobel,&sobmin,&sobmax);
std::cout << "sobel value range: " << sobmin << " " << sobmax << std::endl;
// Print window pixel values
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<12; j++)
std::cout << std::setw(5) << static_cast<int>(sobel.at<short>(i+135,j+362)) << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
// Conversion to 8-bit image
// sobelImage = -alpha*sobel + 255
cv::Mat sobelImage;
sobel.convertTo(sobelImage,CV_8U,-255./sobmax,255);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Sobel Image");
cv::imshow("Sobel Image",sobelImage);
cv::imwrite("Sobel Image.jpg",sobelImage);
// Apply threshold to Sobel norm (low threshold value)
cv::Mat sobelThresholded;
cv::threshold(sobelImage, sobelThresholded, 225, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Binary Sobel Image (low)");
cv::imshow("Binary Sobel Image (low)",sobelThresholded);
cv::imwrite("Binary Sobel Image (low).jpg",sobelThresholded);
// Apply threshold to Sobel norm (high threshold value)
cv::threshold(sobelImage, sobelThresholded, 190, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Binary Sobel Image (high)");
cv::imshow("Binary Sobel Image (high)",sobelThresholded);
cv::imwrite("Binary Sobel Image (high).jpg",sobelThresholded);
// Compute Laplacian 3x3
cv::Mat laplace;
cv::Laplacian(image,laplace,CV_8U,1,1,128);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Laplacian Image");
cv::imshow("Laplacian Image",laplace);
cv::imwrite("Laplacian Image 3x3 .jpg",laplace);
// Print window pixel values
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<12; j++)
std::cout << std::setw(5) << static_cast<int>(laplace.at<uchar>(i+135,j+362))-128 << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
// Compute Laplacian 7x7
cv::Laplacian(image,laplace,CV_8U,7,0.01,128);
// Display the image
cv::namedWindow("Laplacian Image");
cv::imshow("Laplacian Image",laplace);
cv::imwrite("Laplacian Image 7x7 .jpg",laplace);
// Print window pixel values
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<12; j++)
std::cout << std::setw(5) << static_cast<int>(laplace.at<uchar>(i+135,j+362))-128 << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// Extract small window
cv::Mat window(image,cv::Rect(362,135,12,12));
cv::namedWindow("Image window");
cv::imshow("Image window",window);
cv::imwrite("window.bmp",window);
// Compute Laplacian using LaplacianZC class
LaplacianZC laplacian;
laplacian.setAperture(7);
cv::Mat flap= laplacian.computeLaplacian(image);
double lapmin, lapmax;
cv::minMaxLoc(flap,&lapmin,&lapmax);
std::cout << "Laplacian value range=[" << lapmin << "," << lapmax << "]\n";
laplace= laplacian.getLaplacianImage();
cv::namedWindow("Laplacian Image (7x7)");
cv::imshow("Laplacian Image (7x7)",laplace);
cv::imwrite("Laplacian Image (7x7).jpg",laplace);
// Print Laplacian values
std::cout << std::endl;
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<12; j++)
std::cout << std::setw(5) << static_cast<int>(flap.at<float>(i+135,j+362)/100) << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// Compute and display the zero-crossing points
cv::Mat zeros;
zeros= laplacian.getZeroCrossings(lapmax);
cv::namedWindow("Zero-crossings");
cv::imshow("Zero-crossings",zeros);
cv::imwrite("Zero-crossings.jpg",zeros);
// Compute and display the zero-crossing points (Sobel version)
zeros= laplacian.getZeroCrossings();
zeros= laplacian.getZeroCrossingsWithSobel(50);
cv::namedWindow("Zero-crossings (2)");
cv::imshow("Zero-crossings (2)",zeros);
cv::imwrite("Zero-crossings (2).jpg",zeros);
// Print window pixel values
for (int i=0; i<12; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<12; j++)
std::cout << std::setw(2) << static_cast<int>(zeros.at<uchar>(i+135,j+362)) << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// Display the image with window
cv::rectangle(image,cv::Point(362,135),cv::Point(374,147),cv::Scalar(255,255,255));
cv::namedWindow("Original Image with window");
cv::imshow("Original Image with window",image);
cv::imwrite("Original Image with window.jpg",image);
cv::waitKey();
return 0;
}
原图形:
程序和图形结果下载:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/skeeee/5763305