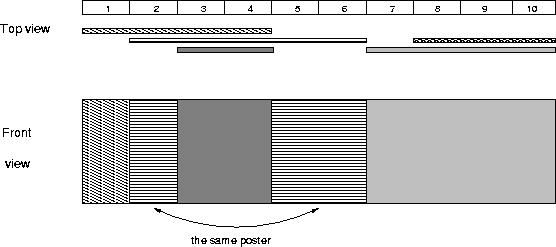
Mayor's posters(线段树区间更新+离散化)
Link:http://poj.org/problem?id=2528
用到的线段树功能有:update:成段替换 query:简单hash
AC code:
/*
不离散化势必MLE,此题离散化即是区间压缩,就是把
一些无用的区间进行压缩,而不改变区间的覆盖关系,
从而达到节省空间的目的。
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#define LL long long
#define MAXN 40005
using namespace std;
int linecover[MAXN];
LL ans;
struct node{
int l,r,c;
}tree[MAXN*3];
struct linenode{
int id;
int s;
int f;
}p[MAXN*3];
struct lisan{
int id;
int st;
int ed;
}pp[MAXN*3];
bool cmp(linenode x,linenode y)
{
return x.s<y.s;
}
void build(int rt,int s,int e)
{
tree[rt].l=s;
tree[rt].r=e;
tree[rt].c=0;
if(s==e)
{
return;
}
int mid=(s+e)/2;
build(rt*2,s,mid);
build(rt*2+1,mid+1,e);
}
void update(int rt,int l,int r,int cnt)
{
if(tree[rt].l==l&&tree[rt].r==r)
{
tree[rt].c=cnt;
return;
}
int mid=(tree[rt].l+tree[rt].r)/2;
if(tree[rt].c!=0)//pushdown操作
{
tree[rt*2].c=tree[rt*2+1].c=tree[rt].c;
tree[rt].c=0;
}
if(r<=mid)
{
update(rt*2,l,r,cnt);
}
else if(l>mid)
{
update(rt*2+1,l,r,cnt);
}
else
{
update(rt*2,l,mid,cnt);
update(rt*2+1,mid+1,r,cnt);
}
}
void query(int rt,int l,int r)
{
if(tree[rt].c!=0)
{
if(!linecover[tree[rt].c])
{
ans++;
linecover[tree[rt].c]=1;
}
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)/2;
query(rt*2,l,mid);
query(rt*2+1,mid+1,r);
}
int main()
{
int t,n,i,st,ed;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&st,&ed);
p[i*2-1].s=st;
p[i*2-1].f=0;
p[i*2-1].id=i;
p[i*2].s=ed;
p[i*2].id=i;
p[i*2].f=1;
}
sort(p+1,p+2*n+1,cmp);
int tmp=p[1].s;
int cnt=1;
/*不知为何,我把下面两行注释掉的代码写在外面poj就会RE,全部写在循环里面才AC*/
//pp[p[1].id].id=p[1].id;
//pp[p[1].id].st=cnt;//排序后第一个点肯定是某一条线段的起点
for(i=1;i<=2*n;i++)//离散化
{
if(tmp!=p[i].s)
{
cnt++;
tmp=p[i].s;
}
pp[p[i].id].id=p[i].id;
if(p[i].f==0)
{
pp[p[i].id].st=cnt;
}
else if(p[i].f==1)
{
pp[p[i].id].ed=cnt;
}
}
memset(linecover,0,sizeof(linecover));
build(1,1,cnt);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
update(1,pp[i].st,pp[i].ed,pp[i].id);
}
ans=0;
query(1,1,cnt);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}