平衡树练习——被虐记~~
最近做的一份jsoi2011冬令营的卷子,瞬间被虐暴了。。。。。
其中以两道平衡树最为奇葩。
蒟蒻今天终于写完了两道平衡树——调了好长好长时间![]() ,高级数据结构能力太渣了
,高级数据结构能力太渣了![]() 。
。
--------------------------------------------华丽的分割线--------------------------------------------
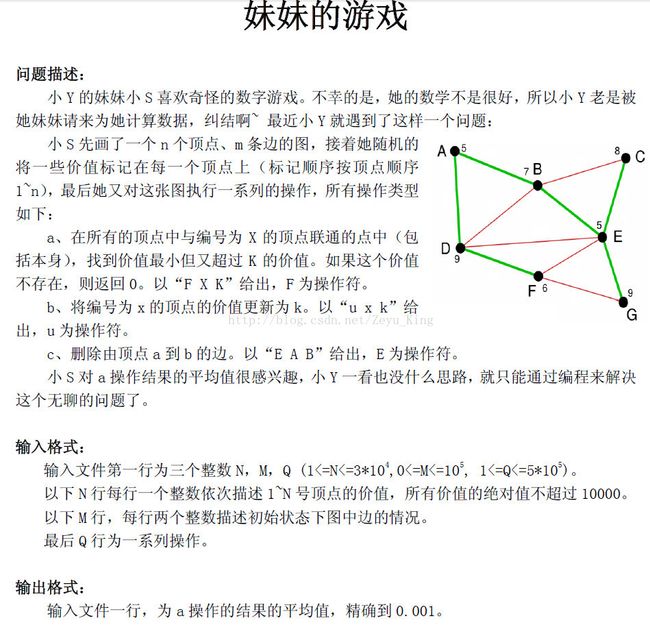
(最近搞了个强大的截图工具)题面就不概述了,直接放图吧
一眼看上去就是splay吧。
读入后从最后一个询问倒序处理,删除变成添加,用启发式合并,修改变成复原,询问直接处理吧![]()
然后蒟蒻令人捉急的代码能力就开始显现出来了,一调一下午。。。。。
主要是忘记了splay删除怎么写了![]() 。。。原来写了个好龊好龊的,现在好不容易想起来,这里补一个备忘
。。。原来写了个好龊好龊的,现在好不容易想起来,这里补一个备忘
void del(int x,int tr){
Splay(x,0,tr);
int pr=son[x][0], nx=son[x][1];
if (pr==0)
{ root[tr]=nx; fa[nx]=0; return; }
if (nx==0)
{ root[tr]=pr; fa[pr]=0; return; }
while (son[pr][1]) pr=son[pr][1];
while (son[nx][0]) nx=son[nx][0];
Splay(pr,0,tr); Splay(nx,pr,tr);
son[nx][0]=0; Splay(nx,0,tr);
}
看着这凝结着我半天的代码我情何以堪啊。。。。
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int Maxn=30005, Maxm=100005, Maxq=500005;
int son[Maxn][2],fa[Maxn],size[Maxn],root[Maxn],ft[Maxn];
int n,m,i,q,m1,m2,cnt,ans,tot,num[Maxq],data[Maxn];
bool v[Maxm];
char s[Maxq];
vector <int> e[Maxn];
struct EDGE
{
int x,y;
bool operator <(const EDGE &a)const
{ return (x<a.x) || (x==a.x && y<a.y); }
bool operator ==(const EDGE &a)const
{ return (x==a.x && y==a.y); }
} edge[Maxm], g[Maxq], tmp;
void rotate(int x,int f,int K){
if (fa[f]!=0){
if (son[fa[f]][0]==f)
son[fa[f]][0]=x;
else son[fa[f]][1]=x;
}
fa[x]=fa[f];
if (son[x][K^1]) fa[son[x][K^1]]=f;
son[f][K]=son[x][K^1];
son[x][K^1]=f; fa[f]=x;
size[f]=size[son[f][0]] +size[son[f][1]]+ 1;
}
void Splay(int x,int y,int tr){
int f,gf;
while (fa[x]!=y){
f=fa[x]; gf=fa[f];
if (gf==y){
if (son[f][0]==x) rotate(x,f,0);
if (son[f][1]==x) rotate(x,f,1);
} else
{
if (son[f][0]==x && son[gf][0]==f) rotate(f,gf,0), rotate(x,f,0);
if (son[f][1]==x && son[gf][1]==f) rotate(f,gf,1), rotate(x,f,1);
if (son[f][0]==x && son[gf][1]==f) rotate(x,f,0), rotate(x,gf,1);
if (son[f][1]==x && son[gf][0]==f) rotate(x,f,1), rotate(x,gf,0);
}
}
if (y==0) root[tr]=x;
size[x]=size[son[x][0]] +size[son[x][1]]+ 1;
}
void del(int x,int tr){
Splay(x,0,tr);
int pr=son[x][0], nx=son[x][1];
if (pr==0)
{ root[tr]=nx; fa[nx]=0; return; }
if (nx==0)
{ root[tr]=pr; fa[pr]=0; return; }
while (son[pr][1]) pr=son[pr][1];
while (son[nx][0]) nx=son[nx][0];
Splay(pr,0,tr); Splay(nx,pr,tr);
son[nx][0]=0; Splay(nx,0,tr);
}
void ins(int x,int tr){
son[x][0]= son[x][1]= fa[x]=0;
int y=root[tr];
if (y==0){
root[tr]=x;
size[x]=1;
} else
while (true){
if (data[x]>data[y]){
if (son[y][1]) y=son[y][1];
else {son[y][1]=x; fa[x]=y; break;}
}else
{
if (son[y][0]) y=son[y][0];
else {son[y][0]=x; fa[x]=y; break;}
}
}
Splay(x,0,tr);
}
int query(int x,int tr){
int ret=0;
int y=root[tr];
while (y){
if (data[y]>=x){
ret=data[y];
y=son[y][0];
} else y=son[y][1];
}
return ret;
}
void get_together(int x,int y){
ft[x]=y;
while (e[x].size()){
int tmp=e[x].back();
e[x].pop_back();
e[y].push_back(tmp);
son[tmp][0]=son[tmp][1]=0;
fa[tmp]=0;
ins(tmp,y);
}
}
int get_ft(int x){
int xx=x, xxx;
while (ft[xx]!=xx) xx=ft[xx];
while (x!=xx) xxx=x, x=ft[x], ft[xxx]=xx;
return xx;
}
int main(){
freopen("boring.in","r",stdin);
freopen("boring.out","w",stdout);
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&q);
for (i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&data[i]);
for (i=1;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d%d\n",&edge[i].x,&edge[i].y);
if (edge[i].x>edge[i].y)
swap(edge[i].x,edge[i].y);
}
sort(edge+1,edge+m+1);
for (i=1;i<=q;i++){
scanf("%c%d%d\n",&s[i],&g[i].x,&g[i].y);
if (s[i]=='U') swap(data[g[i].x],g[i].y);
tmp=g[i];
if (tmp.x>tmp.y) swap(tmp.x,tmp.y);
if (s[i]!='E') continue;
num[i]=lower_bound(edge+1,edge+m+1,tmp)-edge;
if (edge[ num[i] ]==tmp){
while (edge[ num[i] ]==tmp && v[num[i]]) num[i]++;
v[num[i]]=1;
} else num[i]=0;
}
for (i=1;i<=n;i++){
size[i]=1;
ft[i]=i; root[i]=i;
e[i].push_back(i);
}
for (i=1;i<=m;i++)
if (v[i]==0){
m1=get_ft(edge[i].x);
m2=get_ft(edge[i].y);
if (m1==m2) continue;
if (e[m1].size()<e[m2].size())
get_together(m1,m2);
else get_together(m2,m1);
}
for (i=q;i>0;i--){
if (s[i]=='F'){
m1=get_ft(g[i].x);
cnt+=query(g[i].y,m1);
tot++;
} else
if (s[i]=='U'){
m1=get_ft(g[i].x);
del(g[i].x,m1);
data[g[i].x]=g[i].y;
ins(g[i].x,m1);
} else
if (s[i]=='E'){
m1=get_ft(g[i].x);
m2=get_ft(g[i].y);
if (num[i]==0) continue;
v[num[i]]=0;
if (m1==m2) continue;
if (e[m1].size()<e[m2].size())
get_together(m1,m2);
else get_together(m2,m1);
}
}
double ans=(double)cnt/tot;
printf("%.3lf\n",ans);
return 0;
}
--------------------------------------------华丽的分割线--------------------------------------------
暴力链表会吧,空间O(10^9)。。。。10分
朴素暴力会吧,时间O(n^2)。。。。30分
用Splay优化朴素暴力,离散化啥的,呵呵呵呵呵。。。。。。
P很好做啊,Splay维护就好了,关键是L咋办,怎么离散化,蛋疼啊。。。。
注意到问么其实对数列只进行了几次插入,也就是说很多子序列都是以公差为一递增的等差数列!
好有用的样子。这样我们只要保证每个连续的字序列至少开头在Splay树上,找到开头加一下就得到答案了!
分析一下插队的特点(a,b)我们只要把a,a+1,b都放到树里就行了![]()
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define update(x) if (tip[x]!=0) push(x)
const int Maxn=200005;
int fa[Maxn],son[Maxn][2],rk[Maxn],tip[Maxn],a[Maxn],b[Maxn],c[Maxn];
int n,m,N,x,i,ta,tb,root,q[Maxn];
char s[Maxn];
void push(int x){
int lc=son[x][0], rc=son[x][1];
if (lc){
rk[lc]+=tip[x];
tip[lc]+=tip[x];
}
if (rc){
rk[rc]+=tip[x];
tip[rc]+=tip[x];
}
tip[x]=0;
}
void rotate(int x,int f,int K){
if (fa[f]){
if (son[fa[f]][0]==f) son[fa[f]][0]=x;
else son[fa[f]][1]=x;
}
fa[x]=fa[f];
son[f][K]=son[x][K^1];
if (son[x][K^1]) fa[son[x][K^1]]=f;
son[x][K^1]=f; fa[f]=x;
}
void Splay(int x,int y){
int f, gf;
while (fa[x]!=y){
f=fa[x]; gf=fa[f];
update(gf); update(f); update(x);
if (gf==y){
if (son[f][0]==x) rotate(x,f,0);
if (son[f][1]==x) rotate(x,f,1);
} else
{
if (son[f][0]==x && son[gf][0]==f) rotate(f,gf,0), rotate(x,f,0);
if (son[f][1]==x && son[gf][1]==f) rotate(f,gf,1), rotate(x,f,1);
if (son[f][0]==x && son[gf][1]==f) rotate(x,f,0), rotate(x,gf,1);
if (son[f][1]==x && son[gf][0]==f) rotate(x,f,1), rotate(x,gf,0);
}
}
update(x);
if (y==0) root=x;
}
int build(int l,int r){
if (l>r) return 0;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
rk[mid]=c[mid];
if (l==r) return l;
son[mid][0]=build(l,mid-1);
son[mid][1]=build(mid+1,r);
fa[son[mid][0]]= fa[son[mid][1]]= mid;
return mid;
}
void del(int x,int K){
Splay(x,0);
if (son[x][0]) rk[son[x][0]]+=K, tip[son[x][0]]+=K;
int pr=son[x][0], nx=son[x][1];
if (pr==0)
{ root=son[x][1]; fa[root]=0; return; }
if (nx==0)
{ root=son[x][0]; fa[root]=0; return; }
while (son[pr][1]){ update(pr); pr=son[pr][1]; }
while (son[nx][0]){ update(nx); nx=son[nx][0]; }
Splay(pr,0); Splay(nx,pr);
son[nx][0]=0;
}
void ins(int x,int y,int K){
Splay(y,0); rk[x]=rk[y]-1;
son[x][0]= son[x][1]= 0;
while (y){
update(y);
if (rk[y]>rk[x]){
if (son[y][0]==0)
{fa[ son[y][0]=x ]=y; break;}
else y=son[y][0];
} else
{
if (son[y][1]==0)
{fa[ son[y][1]=x ]=y; break;}
else y=son[y][1];
}
}
Splay(x,0);
if (son[x][0]) rk[son[x][0]]+=K, tip[son[x][0]]+=K;
}
void work1(int x){
x=lower_bound(c,c+N+1,x)-c;
Splay(x,0);
printf("%d\n",rk[x]);
}
void work2(int x){
int y=root, z;
while (y){
update(y);
if (rk[y]==x) {printf("%d\n",c[y]);return;}
if (rk[y]>x) y=son[y][0];
else z=y, y=son[y][1];
}
printf("%d\n", c[z]+(x-rk[z]) );
}
int main(){
freopen("queue.in","r",stdin);
freopen("queue.out","w",stdout);
scanf("%d",&n);
c[N=1]=1; c[N=2]=1000000000;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&a[i],&b[i]);
c[++N]=a[i]; c[++N]=b[i];
c[++N]=a[i]+1;
}
scanf("%d\n",&m);
for (i=1;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%c %d\n",&s[i],&q[i]);
if (s[i]=='P') c[++N]=q[i];
}
sort(c+1,c+N+1);
N=unique(c+1,c+N+1)-c-1;
root=build(1,N);
for (i=1;i<=n;i++){
a[i]=lower_bound(c+1,c+N+1,a[i])-c;
b[i]=lower_bound(c+1,c+N+1,b[i])-c;
del(a[i],1), ins(a[i],b[i],-1);
}
for (i=1;i<=m;i++){
if (s[i]=='P') work1(q[i]);
else work2(q[i]);
}
return 0;
}
--------------------------------------------华丽的分割线--------------------------------------------
有了这次教训,看来数据结构还是要加强,这几天写写树剖和LCT吧![]()
bless all~~~~